Related Research Articles

Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects vertebrates and Anopheles mosquitoes. Human malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, fatigue, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. Symptoms usually begin 10 to 15 days after being bitten by an infected Anopheles mosquito. If not properly treated, people may have recurrences of the disease months later. In those who have recently survived an infection, reinfection usually causes milder symptoms. This partial resistance disappears over months to years if the person has no continuing exposure to malaria. The mosquito vector is itself harmed by Plasmodium infections, causing reduced lifespan.
Antimalarial medications or simply antimalarials are a type of antiparasitic chemical agent, often naturally derived, that can be used to treat or to prevent malaria, in the latter case, most often aiming at two susceptible target groups, young children and pregnant women. As of 2018, modern treatments, including for severe malaria, continued to depend on therapies deriving historically from quinine and artesunate, both parenteral (injectable) drugs, expanding from there into the many classes of available modern drugs. Incidence and distribution of the disease is expected to remain high, globally, for many years to come; moreover, known antimalarial drugs have repeatedly been observed to elicit resistance in the malaria parasite—including for combination therapies featuring artemisinin, a drug of last resort, where resistance has now been observed in Southeast Asia. As such, the needs for new antimalarial agents and new strategies of treatment remain important priorities in tropical medicine. As well, despite very positive outcomes from many modern treatments, serious side effects can impact some individuals taking standard doses.

Artemisia is a large, diverse genus of plants belonging to the daisy family, Asteraceae, with almost 500 species. Common names for various species in the genus include mugwort, wormwood, and sagebrush.

Artemisia vulgaris, commonly known as mugwort,common mugwort, or wormwood, is a species of flowering plant in the daisy family Asteraceae. It is one of several species in the genus Artemisia commonly known as mugwort, although Artemisia vulgaris is the species most often called mugwort. Mugworts have been used medicinally and as culinary herbs.

Plasmodium falciparum is a unicellular protozoan parasite of humans, and the deadliest species of Plasmodium that causes malaria in humans. The parasite is transmitted through the bite of a female Anopheles mosquito and causes the disease's most dangerous form, falciparum malaria. P. falciparum is therefore regarded as the deadliest parasite in humans. It is also associated with the development of blood cancer and is classified as a Group 2A (probable) carcinogen.

Pharmacognosy is the study of crude drugs obtained from medicinal plants, animals, fungi, and other natural sources. The American Society of Pharmacognosy defines pharmacognosy as "the study of the physical, chemical, biochemical, and biological properties of drugs, drug substances, or potential drugs or drug substances of natural origin as well as the search for new drugs from natural sources".

Artemisia annua, also known as sweet wormwood, sweet annie, sweet sagewort, annual mugwort or annual wormwood, is a common type of wormwood native to temperate Asia, but naturalized in many countries including scattered parts of North America.
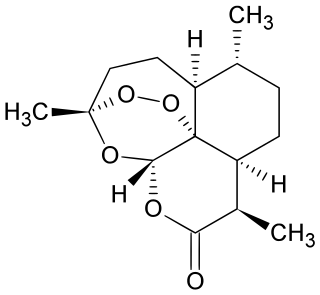
Artemisinin and its semisynthetic derivatives are a group of drugs used in the treatment of malaria due to Plasmodium falciparum. It was discovered in 1972 by Tu Youyou, who shared the 2015 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for her discovery. Artemisinin-based combination therapies (ACTs) are now standard treatment worldwide for P. falciparum malaria as well as malaria due to other species of Plasmodium. Artemisinin is extracted from the plant Artemisia annua an herb employed in Chinese traditional medicine. A precursor compound can be produced using a genetically engineered yeast, which is much more efficient than using the plant.

Artemisia II of Caria was a naval strategist, commander and the sister and the successor of Mausolus, ruler of Caria. Mausolus was a satrap of the Achaemenid Empire, yet enjoyed the status of king or dynast of the Hecatomnid dynasty. After the death of her brother/husband, Artemisia reigned for two years, from 353 to 351 BCE. Her ascension to the throne prompted a revolt in some of the island and coastal cities under her command due to their objection to a female ruler. Her administration was conducted on the same principles as that of her husband; in particular, she supported the oligarchical party on the island of Rhodes.

Artemether is a medication used for the treatment of malaria. The injectable form is specifically used for severe malaria rather than quinine. In adults, it may not be as effective as artesunate. It is given by injection in a muscle. It is also available by mouth in combination with lumefantrine, known as artemether/lumefantrine.

Artesunate (AS) is a medication used to treat malaria. The intravenous form is preferred to quinine for severe malaria. Often it is used as part of combination therapy, such as artesunate plus mefloquine. It is not used for the prevention of malaria. Artesunate can be given by injection into a vein, injection into a muscle, by mouth, and by rectum.
Sesquiterpene lactones (SLs) are a class of sesquiterpenoids that contain a lactone ring. They are most often found in plants of the family Asteraceae. Other plant families with SLs are Umbelliferae and Magnoliaceae (magnolias). A collection of colorless, lipophilic solids, SLs are a rich source of drugs. They can be allergenic and toxic in grazing livestock causing severe neurological problems in horses. Some are also found in corals of the order Alcyonacea.

Jay D. Keasling is a professor of chemical engineering and bioengineering at the University of California, Berkeley. He is also associate laboratory director for biosciences at the Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory and chief executive officer of the Joint BioEnergy Institute. He is considered one of the foremost authorities in synthetic biology, especially in the field of metabolic engineering.

The history of malaria extends from its prehistoric origin as a zoonotic disease in the primates of Africa through to the 21st century. A widespread and potentially lethal human infectious disease, at its peak malaria infested every continent except Antarctica. Its prevention and treatment have been targeted in science and medicine for hundreds of years. Since the discovery of the Plasmodium parasites which cause it, research attention has focused on their biology as well as that of the mosquitoes which transmit the parasites.
Project 523 is a code name for a 1967 secret military project of the People's Republic of China to find antimalarial medications. Named after the date the project launched, 23 May, it addressed malaria, an important threat in the Vietnam War. At the behest of Ho Chi Minh, Prime Minister of North Vietnam, Zhou Enlai, the Premier of the People's Republic of China, convinced Mao Zedong, Chairman of the Chinese Communist Party, to start the mass project "to keep [the] allies' troops combat-ready", as the meeting minutes put it. More than 500 Chinese scientists were recruited. The project was divided into three streams. The one for investigating traditional Chinese medicine discovered and led to the development of a class of new antimalarial drugs called artemisinins. Launched during and lasting throughout the Cultural Revolution, Project 523 was officially terminated in 1981.

China–Comoros relations refers to the current and historical relationship between China and the Comoros. China has an embassy in Moroni and the Comoros has an embassy in Beijing. Relations were established by Comorian President Ali Soilih on 13 November 1975 and have been described as "friendly and cooperative". On 2 September of 2024, they decided to upgrade their relationship to "Strategic Partnership".
Pregnancy-associated malaria (PAM) or placental malaria is a presentation of malaria in pregnancy which is life-threatening to both pregnant women and unborn fetuses. PAM occurs when a pregnant woman contracts malaria, generally as a result of Plasmodium falciparum infection, and because she is pregnant, is at greater risk of associated complications such as placental malaria. Placental malaria interferes with the transmission of vital substances through the fetal placenta, which can result in stillbirths, miscarriages, and dangerously low birth weights.

Tu Youyou is a Nobel Prize-winning Chinese malariologist and pharmaceutical chemist. She discovered artemisinin and dihydroartemisinin, used to treat malaria, a breakthrough in twentieth-century tropical medicine, saving millions of lives in South China, Southeast Asia, Africa, and South America.
Zhou Yiqing is a professor of medicine at the Institute of Microbiology and Epidemiology of the People's Liberation Army Academy of Military Medical Sciences. He was one of the scientists who participated in the Project 523 of the Chinese Government under Chairman Mao Zedong. The project resulted in the discovery of artemisinins, a class of antimalarial drugs, from the medicinal plant Artemisia annua.
Dirk Pohlmann is a German journalist, author, screenwriter, director and producer of about 25 historical documentaries for German public media Arte, ARD and ZDF.
References
- ↑ "biotechnologie.de". biotechnologie.de. Retrieved 2021-11-15.
- ↑ "Impact". Artemiflow. Retrieved 2021-11-15.
- ↑ Cody McDevitt (February 15, 2019). "Anti-malarial medicine company may set up shop in Somerset; CEO a Somerset grad". Daily American.
- ↑ "Pionier der Glykowissenschaften: Peter Seeberger erhält Stifterverbandspreis 2017". www.mpg.de (in German). Retrieved 2021-11-15.
- ↑ "Potsdamer Forscher revolutionieren Malaria-Wirkstoff". Der Tagesspiegel Online (in German). Retrieved 2021-11-15.
- ↑ Hope for millions. Thanks to a German invention, an anti-malarial drug can be produced easily and cheaply. By Reiner Luyken, January 19, 2012 DIE ZEIT No. 4/201217
- ↑ Frank Odenthal (2021-11-13). "Backwash of innovation".
- 1 2 Journalist, Volker Budinger, Diplom-Biologe, freier (2021-01-21). "Artemisinin-Herstellung wie in der Pflanze – nur schneller". DAZ.online. Retrieved 2021-11-15.
{{cite web}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link) - ↑ Odenthal, Frank. "Backwash of innovation". FairPlanet. Retrieved 2021-11-15.
- ↑ "UK to Grow Malaria-fighting Plants". UKNow. 2018-03-29. Retrieved 2024-02-15.
- ↑ "Wissenschaftspreis: Forschung zwischen Grundlagen und Anwendung - Preisträger 2017". Stifterverband (in German). 2019-06-23. Retrieved 2021-11-15.
- ↑ "UK to Grow Malaria-fighting Plants | University of Kentucky Research". www.research.uky.edu. Retrieved 2021-11-15.
- ↑ "Mit grüner Chemie gegen Malaria". Innovations Report (in German). 2018-02-21. Retrieved 2021-11-15.
- ↑ "UK, ArtemiLife Partner to Test for Anti-Cancer Activity of Artemisia Annua Extracts". UKNow. 2020-06-03. Retrieved 2024-02-15.
- ↑ Nie, C., Trimpert, J., Moon, S. et al.In vitro efficacy of Artemisia extracts against SARS-CoV-2. Virol J 18, 182 (2021). doi : 10.1186/s12985-021-01651-8
- ↑ Laborjournal. "Gutes aus Grünzeug". Laborjournal (in German). Retrieved 2021-11-15.
- ↑ Zhou, Yuyong; Gilmore, Kerry; Ramirez, Santseharay; Settels, Eva; Gammeltoft, Karen A.; Pham, Long V.; Fahnøe, Ulrik; Feng, Shan; Offersgaard, Anna; Trimpert, Jakob; Bukh, Jens (2021-07-16). "In vitro efficacy of artemisinin-based treatments against SARS-CoV-2". Scientific Reports. 11 (1): 14571. doi:10.1038/s41598-021-93361-y. ISSN 2045-2322. PMC 8285423 . PMID 34272426.
- ↑ Bartens, Werner; Dörries, Bernd (26 June 2020). "Corona: Beifuß als Heilmittel gegen Covid-19?". Süddeutsche.de (in German). Retrieved 2021-11-15.
- ↑ "Pflanzenextrakte aus Beifuß sollen vor Covid-19 schützen – das steckt dahinter". FOCUS Online (in German). Retrieved 2021-11-15.