
Artichoke production in Italy has a long history. Italy is the world's largest producer of artichokes. [1] With Spain and France, the three countries produce more than 80% of the world's artichokes. [2]

Artichoke production in Italy has a long history. Italy is the world's largest producer of artichokes. [1] With Spain and France, the three countries produce more than 80% of the world's artichokes. [2]
There are two theories as to its origin: artichokes may have come from the Levant, derived from the cardoon or thistle through a cross-fertilization process, while others attribute it to the work of Italian horticulturists. [3] The first record of artichoke cultivation in Italy was during the fifteenth century in Naples, where it was considered a new food species. [4]
In 1466, Filippo Strozzi brought the first artichoke to Florence. By 1473, it had arrived in Venice. In 1915, 64,000 tons were produced. [5] Italy produces dozens of varieties. [6]
Agriculture encompasses crop and livestock production, aquaculture, and forestry for food and non-food products. Agriculture was a key factor in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people to live in cities. While humans started gathering grains at least 105,000 years ago, nascent farmers only began planting them around 11,500 years ago. Sheep, goats, pigs, and cattle were domesticated around 10,000 years ago. Plants were independently cultivated in at least 11 regions of the world. In the 20th century, industrial agriculture based on large-scale monocultures came to dominate agricultural output.

A cereal is a grass cultivated for its edible grain. Cereals are the world's largest crops, and are therefore staple foods. They include rice, wheat, rye, oats, barley, millet, and maize. Edible grains from other plant families, such as buckwheat and quinoa, are pseudocereals. Most cereals are annuals, producing one crop from each planting, though rice is sometimes grown as a perennial. Winter varieties are hardy enough to be planted in the autumn, becoming dormant in the winter, and harvested in spring or early summer; spring varieties are planted in spring and harvested in late summer. The term cereal is derived from the name of the Roman goddess of grain crops and fertility, Ceres.

The potato is a starchy root vegetable native to the Americas that is consumed as a staple food in many parts of the world. Potatoes are tubers of the plant Solanum tuberosum, a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.

A society is a group of individuals involved in persistent social interaction or a large social group sharing the same spatial or social territory, typically subject to the same political authority and dominant cultural expectations. Societies are characterized by patterns of relationships between individuals who share a distinctive culture and institutions; a given society may be described as the sum total of such relationships among its constituent members.

A banana is an elongated, edible fruit – botanically a berry – produced by several kinds of large herbaceous flowering plants in the genus Musa. In some countries, cooking bananas are called plantains, distinguishing them from dessert bananas. The fruit is variable in size, color and firmness, but is usually elongated and curved, with soft flesh rich in starch covered with a peel, which may have a variety of colors when ripe. It grows upward in clusters near the top of the plant. Almost all modern edible seedless (parthenocarp) cultivated bananas come from two wild species – Musa acuminata and Musa balbisiana, or hybrids of them.

The cantaloupe is a type of true melon with sweet, aromatic, and usually orange flesh. Originally, cantaloupe refers to the true cantaloupe or European cantaloupe with non- to slightly netted and often ribbed rind. Today, it also refers to the muskmelon with strongly netted rind, which is called cantaloupe in North America, rockmelon in Australia and New Zealand, and spanspek in Southern Africa. Cantaloupes range in mass from 0.5 to 5 kilograms.

Slow Food is an organization that promotes local food and traditional cooking. It was founded by Carlo Petrini in Italy in 1986 and has since spread worldwide. Promoted as an alternative to fast food, it strives to preserve traditional and regional cuisine and encourages farming of plants, seeds, and livestock characteristic of the local ecosystem. It promotes local small businesses and sustainable foods. It also focuses on food quality, rather than quantity. It was the first established part of the broader slow movement. It speaks out against overproduction and food waste. It sees globalization as a process in which small and local farmers and food producers should be simultaneously protected from and included in the global food system.

Horticulture is the art and science of growing plants. This definition is seen in its etymology, which is derived from the Latin words hortus, which means "garden" and cultura which means "to cultivate". There are various divisions of horticulture because plants are grown for a variety of purposes. These divisions include, but are not limited to: gardening, plant production/propagation, arboriculture, landscaping, floriculture and turf maintenance. For each of these, there are various professions, aspects, tools used and associated challenges; Each requiring highly specialized skills and knowledge of the horticulturist.

The Jerusalem artichoke, also called sunroot, sunchoke, wild sunflower, topinambur, or earth apple, is a species of sunflower native to central North America. It is cultivated widely across the temperate zone for its tuber, which is used as a root vegetable.

The cardoon, also called the artichoke thistle, is a thistle in the family Asteraceae. It is a naturally occurring species that also has many cultivated forms, including the globe artichoke. It is native to the Mediterranean region, where it was domesticated in ancient times and still occurs as a wild plant.
Project Artichoke was a project developed and enacted by the United States Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) for the purpose of researching methods of interrogation. Project Artichoke was succeeded by Project MKUltra, which began in 1953.

The artichoke, also known by the names French artichoke, globe artichoke, and green artichoke in the United States, is a variety of a species of thistle cultivated as food.

Agriculture began independently in different parts of the globe, and included a diverse range of taxa. At least eleven separate regions of the Old and New World were involved as independent centers of origin. The development of agriculture about 12,000 years ago changed the way humans lived. They switched from nomadic hunter-gatherer lifestyles to permanent settlements and farming.
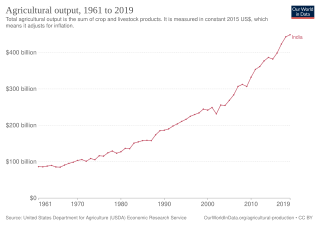
The history of agriculture in India dates back to the Neolithic period. India ranks second worldwide in farm outputs. As per the Indian economic survey 2020 -21, agriculture employed more than 50% of the Indian workforce and contributed 20.2% to the country's GDP.

The tomato, Solanum lycopersicum, is a plant whose fruit is an edible berry that is eaten as a vegetable. The tomato is a member of the nightshade family that includes tobacco, potato, and chili peppers. It originated from and was domesticated in western South America. It was introduced to the Old World by the Spanish in the Columbian exchange in the 16th century.

An apple is a round, edible fruit produced by an apple tree. Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus Malus. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, Malus sieversii, is still found. Apples have been grown for thousands of years in Eurasia and were introduced to North America by European colonists. Apples have religious and mythological significance in many cultures, including Norse, Greek, and European Christian tradition.

The lemon is a species of small evergreen tree in the Citrus genus of the flowering plant family Rutaceae, native to Asia, including Northeast India where it was first grown. It is a hybrid of the citron and the bitter orange.

China is the world's leading producer and consumer of eggplants. The leading producers, after China, are India, Turkey, Japan, Egypt and Italy; a Mediterranean climate favours its production. China has produced eggplants since the 5th century BC for various reasons, not just for food. The eggplant is originally from India and reached coastal regions of mainland China first and then Taiwan; the long slender variety is the preferred one for cooking. Dark eggplant skins were historically used by aristocratic women to make black dye, which they often used to "stain their teeth to a black lustre". In Japan, this is called ohaguro.

Agriculture is a significant sector in Wisconsin's economy, producing nearly $104 billion in revenue annually. The significance of the state's agricultural production is exemplified by the depiction of a Holstein cow, an ear of corn, and a wheel of cheese on Wisconsin's state quarter design. In 2017 there were 64,800 farms in the state, operating across 14.3 million acres of land.