Related Research Articles

The atomic number or proton number of a chemical element is the number of protons found in the nucleus of every atom of that element. The atomic number uniquely identifies a chemical element. It is identical to the charge number of the nucleus. In an uncharged atom, the atomic number is also equal to the number of electrons.

Atomic theory is the scientific theory that matter is composed of particles called atoms. Atomic theory traces its origins to an ancient philosophical tradition known as atomism. According to this idea, if one were to take a lump of matter and cut it into ever smaller pieces, one would eventually reach a point where the pieces could not be further cut into anything smaller. Ancient Greek philosophers called these hypothetical ultimate particles of matter atomos, a word which meant "uncut".

Ernest Rutherford, 1st Baron Rutherford of Nelson, was a New Zealand-born British physicist who came to be known as the father of nuclear physics. Encyclopædia Britannica considers him to be the greatest experimentalist since Michael Faraday (1791–1867). He also spent a substantial amount of his career abroad, in both Canada and the United Kingdom.

Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
A proton is a subatomic particle, symbol
p
or
p+
, with a positive electric charge of +1e elementary charge and a mass slightly less than that of a neutron. Protons and neutrons, each with masses of approximately one atomic mass unit, are jointly referred to as "nucleons".

In physics, radiation is the emission or transmission of energy in the form of waves or particles through space or through a material medium. This includes:

Rutherford scattering is the elastic scattering of charged particles by the Coulomb interaction. It is a physical phenomenon explained by Ernest Rutherford in 1911 that led to the development of the planetary Rutherford model of the atom and eventually the Bohr model. Rutherford scattering was first referred to as Coulomb scattering because it relies only upon the static electric (Coulomb) potential, and the minimum distance between particles is set entirely by this potential. The classical Rutherford scattering process of alpha particles against gold nuclei is an example of "elastic scattering" because neither the alpha particles nor the gold nuclei are internally excited. The Rutherford formula further neglects the recoil kinetic energy of the massive target nucleus.

A beta particle, also called beta ray or beta radiation, is a high-energy, high-speed electron or positron emitted by the radioactive decay of an atomic nucleus during the process of beta decay. There are two forms of beta decay, β− decay and β+ decay, which produce electrons and positrons respectively.

An inelastic collision, in contrast to an elastic collision, is a collision in which kinetic energy is not conserved due to the action of internal friction.

Johannes Wilhelm "Hans" Geiger was a German physicist. He is best known as the co-inventor of the detector component of the Geiger counter and for the Geiger–Marsden experiment which discovered the atomic nucleus. He was the brother of meteorologist and climatologist Rudolf Geiger.
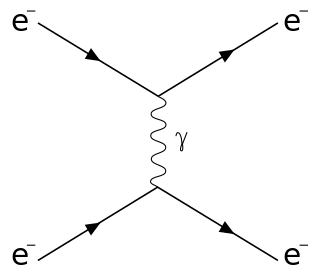
Scattering is a term used in physics to describe a wide range of physical processes where moving particles or radiation of some form, such as light or sound, are forced to deviate from a straight trajectory by localized non-uniformities in the medium through which they pass. In conventional use, this also includes deviation of reflected radiation from the angle predicted by the law of reflection. Reflections of radiation that undergo scattering are often called diffuse reflections and unscattered reflections are called specular (mirror-like) reflections. Originally, the term was confined to light scattering. As more "ray"-like phenomena were discovered, the idea of scattering was extended to them, so that William Herschel could refer to the scattering of "heat rays" in 1800. John Tyndall, a pioneer in light scattering research, noted the connection between light scattering and acoustic scattering in the 1870s. Near the end of the 19th century, the scattering of cathode rays and X-rays was observed and discussed. With the discovery of subatomic particles and the development of quantum theory in the 20th century, the sense of the term became broader as it was recognized that the same mathematical frameworks used in light scattering could be applied to many other phenomena.

Sir James Chadwick, was a British physicist who was awarded the 1935 Nobel Prize in Physics for his discovery of the neutron in 1932. In 1941, he wrote the final draft of the MAUD Report, which inspired the U.S. government to begin serious atomic bomb research efforts. He was the head of the British team that worked on the Manhattan Project during World War II. He was knighted in Britain in 1945 for his achievements in physics.
The Geiger–Marsden experiments were a landmark series of experiments by which scientists learned that every atom has a nucleus where all of its positive charge and most of its mass is concentrated. They deduced this after measuring how an alpha particle beam is scattered when it strikes a thin metal foil. The experiments were performed between 1908 and 1913 by Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden under the direction of Ernest Rutherford at the Physical Laboratories of the University of Manchester.

Daniel Rutherford was a Scottish physician, chemist and botanist who is known for the isolation of nitrogen in 1772.
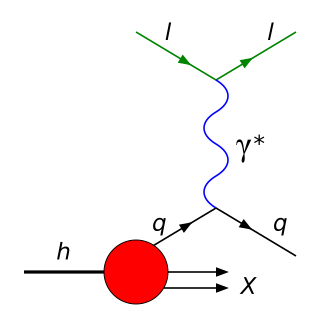
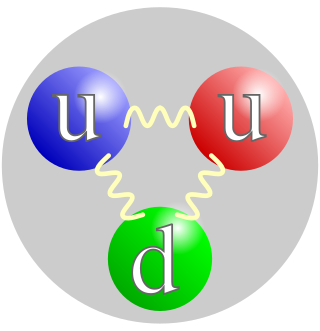
Deep inelastic scattering is the name given to a process used to probe the insides of hadrons, using electrons, muons and neutrinos. It provided the first convincing evidence of the reality of quarks, which up until that point had been considered by many to be a purely mathematical phenomenon. It is a relatively new process, first attempted in the 1960s and 1970s. It is an extension of Rutherford scattering to much higher energies of the scattering particle and thus to much finer resolution of the components of the nuclei.
This is a timeline of subatomic particle discoveries, including all particles thus far discovered which appear to be elementary given the best available evidence. It also includes the discovery of composite particles and antiparticles that were of particular historical importance.

The Rutherford model was devised by the New Zealand-born physicist Ernest Rutherford to describe an atom. Rutherford directed the Geiger–Marsden experiment in 1909, which suggested, upon Rutherford's 1911 analysis, that J. J. Thomson's plum pudding model of the atom was incorrect. Rutherford's new model for the atom, based on the experimental results, contained new features of a relatively high central charge concentrated into a very small volume in comparison to the rest of the atom and with this central volume also containing the bulk of the atomic mass of the atom. This region would be known as the "nucleus" of the atom.
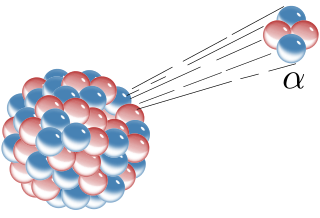
Alpha particles, also called alpha rays or alpha radiation, consist of two protons and two neutrons bound together into a particle identical to a helium-4 nucleus. They are generally produced in the process of alpha decay, but may also be produced in other ways. Alpha particles are named after the first letter in the Greek alphabet, α. The symbol for the alpha particle is α or α2+. Because they are identical to helium nuclei, they are also sometimes written as He2+
or 4
2He2+
indicating a helium ion with a +2 charge. Once the ion gains electrons from its environment, the alpha particle becomes a normal helium atom 4
2He.

Clan Rutherford or Rutherfurd/Rutherfurd is a Lowland Scottish clan of the Scottish Borders. The clan is officially recognized by the Lord Lyon King of Arms, however as it does not currently have a clan chief that is recognized by the Lord Lyon King of Arms it is therefore considered to be an armigerous clan.

The discovery of the neutron and its properties was central to the extraordinary developments in atomic physics in the first half of the 20th century. Early in the century, Ernest Rutherford developed a crude model of the atom, based on the gold foil experiment of Hans Geiger and Ernest Marsden. In this model, atoms had their mass and positive electric charge concentrated in a very small nucleus. By 1920 chemical isotopes had been discovered, the atomic masses had been determined to be (approximately) integer multiples of the mass of the hydrogen atom, and the atomic number had been identified as the charge on the nucleus. Throughout the 1920s, the nucleus was viewed as composed of combinations of protons and electrons, the two elementary particles known at the time, but that model presented several experimental and theoretical contradictions.
References
- ↑ Cassidy, David C.; Holton, Gerald James; Rutherford, Floyd James (2002). Understanding physics. Birkhäuser. p. 766. ISBN 0-387-98756-8.