Cartography is the study and practice of making maps. Combining science, aesthetics, and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality can be modeled in ways that communicate spatial information effectively.
A geographic information system (GIS) is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present spatial or geographic data. GIS applications are tools that allow users to create interactive queries, analyze spatial information, edit data in maps, and present the results of all these operations. GIS sometimes refers to geographic information science (GIScience), the science underlying geographic concepts, applications, and systems.

A mind map is a diagram used to visually organize information. A mind map is hierarchical and shows relationships among pieces of the whole. It is often created around a single concept, drawn as an image in the center of a blank page, to which associated representations of ideas such as images, words and parts of words are added. Major ideas are connected directly to the central concept, and other ideas branch out from those major ideas.

A map is a symbolic depiction emphasizing relationships between elements of some space, such as objects, regions, or themes.

The Tube map is a schematic transport map of the lines, stations and services of the London Underground, known colloquially as "the Tube", hence the map's name. The first schematic Tube map was designed by Harry Beck in 1931. Since then, it has been expanded to include more of London's public transport systems, including the Docklands Light Railway, London Overground, TfL Rail, Tramlink and the Emirates Air Line cable car.

A geographic coordinate system is a coordinate system that enables every location on Earth to be specified by a set of numbers, letters or symbols. The coordinates are often chosen such that one of the numbers represents a vertical position and two or three of the numbers represent a horizontal position; alternatively, a geographic position may be expressed in a combined three-dimensional Cartesian vector. A common choice of coordinates is latitude, longitude and elevation. To specify a location on a plane requires a map projection.

A map projection is a systematic transformation of the latitudes and longitudes of locations from the surface of a sphere or an ellipsoid into locations on a plane. Maps cannot be created without map projections. All map projections necessarily distort the surface in some fashion. Depending on the purpose of the map, some distortions are acceptable and others are not; therefore, different map projections exist in order to preserve some properties of the sphere-like body at the expense of other properties. There is no limit to the number of possible map projections.

In modern mapping, a topographic map is a type of map characterized by large-scale detail and quantitative representation of relief, usually using contour lines, but historically using a variety of methods. Traditional definitions require a topographic map to show both natural and man-made features. A topographic survey is typically published as a map series, made up of two or more map sheets that combine to form the whole map. A contour line is a line connecting places of equal elevation.

Topography is the study of the shape and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area could refer to the surface shapes and features themselves, or a description.
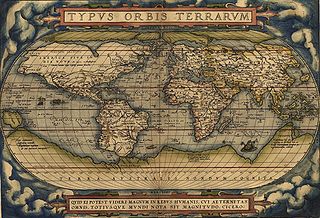
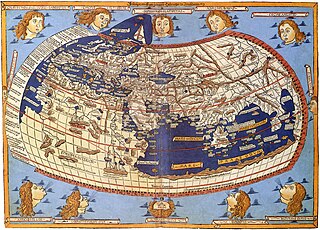
A world map is a map of most or all of the surface of the Earth. World maps form a distinctive category of maps due to the problem of projection. Maps by necessity distort the presentation of the earth's surface. These distortions reach extremes in a world map. The many ways of projecting the earth reflect diverse technical and aesthetic goals for world maps.
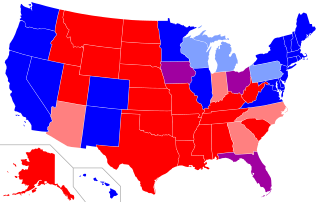
Since the 2000 United States presidential election, red states and blue states have referred to states of the United States whose voters predominantly choose either the Republican Party (red) or Democratic Party (blue) presidential candidates. Since then, the use of the term has been expanded to differentiate between states being perceived as liberal and those perceived as conservative. Examining patterns within states reveals that the reversal of the two parties' geographic bases has happened at the state level, but it is more complicated locally, with urban/rural divides associated with many of the largest changes.
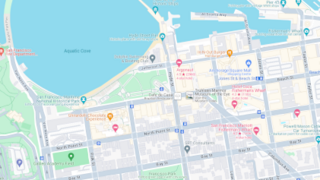
Google Maps is a web mapping service developed by Google. It offers satellite imagery, aerial photography, street maps, 360° panoramic views of streets, real-time traffic conditions, and route planning for traveling by foot, car, bicycle and air, or public transportation.
MapReduce is a programming model and an associated implementation for processing and generating big data sets with a parallel, distributed algorithm on a cluster.

OpenStreetMap (OSM) is a collaborative project to create a free editable map of the world. Rather than the map itself, the data generated by the project is considered its primary output. The creation and growth of OSM has been motivated by restrictions on use or availability of map information across much of the world, and the advent of inexpensive portable satellite navigation devices. OSM is considered a prominent example of volunteered geographic information.

Bing Maps is a web mapping service provided as a part of Microsoft's Bing suite of search engines and powered by the Bing Maps for Enterprise framework.

The Provinces of India, earlier Presidencies of British India and still earlier, Presidency towns, were the administrative divisions of British governance in India. Collectively, they were called British India. In one form or another, they existed between 1612 and 1947, conventionally divided into three historical periods:

Ordnance Survey (OS) is the national mapping agency of the United Kingdom which covers the island of Great Britain. Since 1 April 2015 part of Ordnance Survey has operated as Ordnance Survey Ltd, a government-owned company, 100% in public ownership. The Ordnance Survey Board remains accountable to the Secretary of State for Business, Energy and Industrial Strategy. It is also a member of the Public Data Group.

The United States Geological Survey is a scientific agency of the United States government. The scientists of the USGS study the landscape of the United States, its natural resources, and the natural hazards that threaten it. The organization has four major science disciplines, concerning biology, geography, geology, and hydrology. The USGS is a fact-finding research organization with no regulatory responsibility.

















