
The Columbia River is the largest river in the Pacific Northwest region of North America. The river forms in the Rocky Mountains of British Columbia, Canada. It flows northwest and then south into the U.S. state of Washington, then turns west to form most of the border between Washington and the state of Oregon before emptying into the Pacific Ocean. The river is 1,243 mi (2,000 km) long, and its largest tributary is the Snake River. Its drainage basin is roughly the size of France and extends into seven states of the United States and one Canadian province. The fourth-largest river in the United States by flow, the Columbia has the greatest flow of any river into the eastern Pacific.

The National Wildlife Refuge System (NWRS) is a system of protected areas of the United States managed by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS), an agency within the Department of the Interior. The National Wildlife Refuge System is the system of public lands and waters set aside to conserve America's fish, wildlife, and plants. Since President Theodore Roosevelt designated Florida's Pelican Island National Wildlife Refuge as the first wildlife refuge in 1903, the system has grown to over 568 national wildlife refuges and 38 wetland management districts encompassing about 859,000,000 acres (3,476,200 km2).
The National Audubon Society is an American non-profit environmental organization dedicated to conservation of birds and their habitats. Located in the United States and incorporated in 1905, Audubon is one of the oldest of such organizations in the world. There are completely independent Audubon Societies in the United States, which were founded several years earlier such as the Massachusetts Audubon Society, Indiana Audubon Society, and Connecticut Audubon Society. The societies are named for 19th century naturalist John James Audubon.
Steelhead, or occasionally steelhead trout, is the anadromous form of the coastal rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss irideus) or Columbia River redband trout. Steelhead are native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific basin in Northeast Asia and North America. Like other sea-run (anadromous) trout and salmon, steelhead spawn in freshwater, smolts migrate to the ocean to forage for several years and adults return to their natal streams to spawn. Steelhead are iteroparous, although their survival rate is approximately only 10–20%.

The National Wildlife Federation (NWF) is the largest private, nonprofit conservation education and advocacy organization in the United States, with over six million members and supporters, and 51 state and territorial affiliated organizations.

Malheur National Wildlife Refuge is a National Wildlife Refuge located roughly 30 miles (48 km) south of the city of Burns in Oregon's Harney Basin. Administered by the United States Fish and Wildlife Service, the refuge area is roughly T-shaped with the southernmost base at Frenchglen, the northeast section at Malheur Lake and the northwest section at Harney Lake.
The Fish and Wildlife Coordination Act (FWCA) of the United States was enacted March 10, 1934, to protect fish and wildlife when federal actions result in the control or modification of a natural stream or body of water. The Act provides the basic authority for the involvement of the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (Service) in evaluating impacts to fish and wildlife from proposed water resource development projects.

Johnson Creek is a 25-mile (40 km) tributary of the Willamette River in the Portland metropolitan area of the U.S. state of Oregon. Part of the drainage basin of the Columbia River, its catchment consists of 54 square miles (140 km2) of mostly urban land occupied by about 180,000 people as of 2012. Passing through the cities of Gresham, Portland, and Milwaukie, the creek flows generally west from the foothills of the Cascade Range through sediments deposited by glacial floods on a substrate of basalt. Though polluted, it is free-flowing along its main stem and provides habitat for salmon and other migrating fish.

Tryon Creek is a 4.85-mile (7.81 km) tributary of the Willamette River in the U.S. state of Oregon. Part of the drainage basin of the Columbia River, its watershed covers about 6.5 square miles (16.8 km2) in Multnomah and Clackamas counties. The stream flows southeast from the Tualatin Mountains through the Multnomah Village neighborhood of Portland and the Tryon Creek State Natural Area to the Willamette in the city of Lake Oswego. Parks and open spaces cover about 21 percent of the watershed, while single-family homes dominate most of the remainder. The largest of the parks is the state natural area, which straddles the border between the two cities and counties.

Fanno Creek is a 15-mile (24 km) tributary of the Tualatin River in the U.S. state of Oregon. Part of the drainage basin of the Columbia River, its watershed covers about 32 square miles (83 km2) in Multnomah, Washington, and Clackamas counties, including about 7 square miles (18 km2) within the Portland city limits.

Balch Creek is a 3.5-mile (5.6 km) tributary of the Willamette River in the U.S. state of Oregon. Beginning at the crest of the Tualatin Mountains, the creek flows generally east down a canyon along Northwest Cornell Road in unincorporated Multnomah County and through the Macleay Park section of Forest Park, a large municipal park in Portland. At the lower end of the park, the stream enters a pipe and remains underground until reaching the river. Danford Balch, after whom the creek is named, settled a land claim along the creek in the mid-19th century. After murdering his son-in-law, he became the first person legally hanged in Oregon.

The Columbia Slough is a narrow waterway, about 19 miles (31 km) long, in the floodplain of the Columbia River in the U.S. state of Oregon. From its source in the Portland suburb of Fairview, the Columbia Slough meanders west through Gresham and Portland to the Willamette River, about 1 mile (1.6 km) from the Willamette's confluence with the Columbia. It is a remnant of the historic wetlands between the mouths of the Sandy River to the east and the Willamette River to the west. Levees surround much of the main slough as well as many side sloughs, detached sloughs, and nearby lakes. Drainage district employees control water flows with pumps and floodgates. Tidal fluctuations cause reverse flow on the lower slough.

The Bird Alliance of Oregon (formerly Portland Audubon) is a non-profit environmental organization dedicated to bird and habitat protection across Oregon in the United States.

Rivers Without Borders is a nonprofit organization fiscally sponsored by the Tides Center in the United States. Rivers Without Borders works as a project of Tides Canada Initiatives in Canada. Tides Canada's mission is to provide uncommon solutions for the common good by leading and supporting actions that foster a healthy environment and just Canadian society.

The Summer Lake Wildlife Area is a 29.6-square-mile (77 km2) wildlife refuge located on the northwestern edge of the Great Basin drainage in south-central Oregon. It is administered by the Oregon Department of Fish and Wildlife. The refuge is an important stop for waterfowl traveling along the Pacific Flyway during their spring and fall migrations. The Summer Lake Wildlife Area also provides habitat for shorebirds and other bird species as well as wide variety of mammals and several fish species. The Ana River supplies the water for the refuge wetlands.

The United States Fish and Wildlife Service Office of Law Enforcement contributes to Service efforts to manage ecosystems, save endangered species, conserve migratory birds, preserve wildlife habitat, restore fisheries, combat invasive species, and promote international wildlife conservation. It is an office of the United States Fish and Wildlife Service (FWS).

Speyeria zerene hippolyta, the Oregon silverspot, is a threatened butterfly that is found in the U.S. states of California and Oregon. It is a subspecies of Speyeria zerene.

Oak Creek is a tributary, about 3.5 miles (5.6 km) long, of Marys River in Benton County in the U.S. state of Oregon. The stream descends from forested hills north of Corvallis through the northwest part of the city and across the campus of Oregon State University.
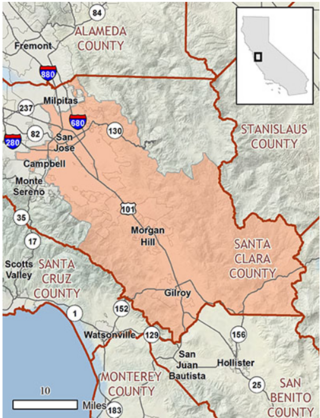
The Santa Clara Valley Habitat Conservation Plan (SCVHCP), also known as the Santa Clara Valley Habitat Plan, is an initiative issued in 2012 by the County of Santa Clara, the City of San José, the City of Morgan Hill, the City of Gilroy, the Santa Clara Valley Water District (SCVWD), and the Santa Clara Valley Transportation Authority (VTA). These governmental agencies are collectively called the "Local Partners" in regards to the Santa Clara Valley Habitat Conservation Plan. The plan's goal is to protect and encourage the growth of endangered species in Santa Clara County. It is a 50-year plan, costing an estimated $660 million as of 2012.















