
In Māori mythology the primal couple Rangi and Papa appear in a creation myth explaining the origin of the world. In some South Island dialects, Rangi is called Raki or Rakinui.
Atea is a deity in several Polynesian cultures, including the Marquesas and Tuamotu Islands, and New Zealand.
In mythology of Mangaia and the southern Cook Islands, Vatea is the father of gods and men. His mother is Varima-te-takere, who lives deep in Avaiki, the underworld. She plucks off a piece from her right side and it becomes Vatea or Avatea.

In Cook Islands mythology, Avatea was a lunar deity and the father of gods and men in Mangaian myth of origin. His eyes were thought to be the Sun and the Moon; he was also known as the god of light.

A marae, malaʻe, meʻae or malae is a communal or sacred place that serves religious and social purposes in Polynesian societies. In all these languages, the term also means cleared, free of weeds, trees. Marae generally consist of an area of cleared land roughly rectangular, bordered with stones or wooden posts perhaps with paepae (terraces) which were traditionally used for ceremonial purposes; and in some cases, a central stone ahu or a'u. In the Rapa Nui culture of Easter Island, the term ahu has become a synonym for the whole marae complex.

Atea is a municipality in the province of Zaragoza, Aragon, Spain. It is part of the comarca of Campo de Daroca.
In Māori tradition, Tainui was one of the great ocean-going canoes in which Polynesians migrated to New Zealand approximately 800 years ago. The Tainui waka was named for an infant who did not survive childbirth. At the burial site of this child, at a place in Hawaiki known then as Maungaroa, a great tree grew; this was the tree that was used to build the ocean canoe.

In Māori mythology, Tiki is the first man created by either Tūmatauenga or Tāne. He found the first woman, Marikoriko, in a pond; she seduced him and he became the father of Hine-kau-ataata. By extension, a tiki is a large or small wooden or stone carving in humanoid form, although this is a somewhat archaic usage in the Māori language. Carvings similar to tikis and coming to represent deified ancestors are found in most Polynesian cultures. They often serve to mark the boundaries of sacred or significant sites.

Scythia was a region of Central Eurasia in classical antiquity, occupied by the Eastern Iranian Scythians, encompassing Central Asia, parts of Eastern Europe east of the Vistula River with the eastern edges of the region vaguely defined by the Greeks. The Ancient Greeks gave the name Scythia to all the lands north-east of Europe and the northern coast of the Black Sea. During the Iron Age the region saw the flourishing of Scythian cultures.
Ateas was described in Greek and Roman sources as the most powerful king of Scythia, who lost his life and empire in the conflict with Philip II of Macedon in 339 BC. His name also occurs as Atheas, Ateia, Ataias, and Ateus.

Makatea, or Mangaia-te-vai-tamae, is a raised coral atoll in the northwestern part of the Tuamotus, which is a part of the French overseas collectivity of French Polynesia. It is located 79 kilometres (49 mi) southwest from Rangiroa to the west of the Palliser group, which also is in French Polynesia. Makatea is surrounded by spectacular cliffs, rising to a plateau 80 metres (260 ft) above sea level. This island is 7.5 kilometres (4.7 mi) long, with a maximum width of 7 kilometres (4.3 mi) in the south. It is 24 square kilometres (9.3 sq mi) in area. Makatea is one of the only four islands of the Tuamotu Archipelago that do not take the form of a typical atoll.
Ngāti Hei is a Māori iwi of New Zealand.

Marae Taputapuatea is a large marae complex at Opoa in Taputapuatea, on the south eastern coast of Raiatea. The site features a number of marae and other stone structures and was once considered the central temple and religious center of Eastern Polynesia. In 2017 the Taputapuatea area was inscribed on the UNESCO World Heritage Sites list with Taputapuatea marae being described as the heart of the site.
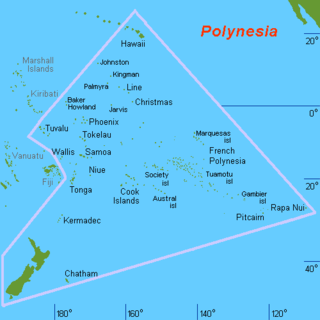
Polynesia is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are termed Polynesians, sharing many similar traits including language family, culture, and beliefs. Historically, they had a strong tradition of sailing and using stars to navigate at night. The largest country in Polynesia is New Zealand.
Atea is a deity in Polynesian mythologies.
King Ari'imate Teurura'i was a member and founder of a Polynesian royal family which reigned on the Tahitian island of Huahine and Mai'ao during the 19th century. In Tahitian, his name translate as "sovereign-demised" and "the-sky-forest" respectively.

Mangarevan narrative comprises the legends, historical tales, and sayings of the ancient Mangarevan people. It is considered a variant of a more general Polynesian narrative, developing its own unique character for several centuries before the 1830s. The religion was officially suppressed in the 19th century, and ultimately abandoned by the natives in favor of Roman Catholicism. The Mangarevan term for god was Etua.
In Niuean mythology, Fakahoko is one of the gods of the island. He is cited as one of the five original gods (tupua) of the island who fled from the lost country of Fonuagalo.
In Niuean mythology, Lagi-atea is one of the gods of the island. He is cited as one of the five original gods (tupua) of the island who fled from the mythical lost country of Fonuagalo.
Niuean mythology relates to some of the myths prevalent on the island of Niue, an Oceanic island country in free association with New Zealand. Although Niuean mythology reports a colonization before 500 AD, the island was settled by Polynesians from Samoa around 900 AD. The five principal gods of Niue are known as the tupua, and include Fao, Huanaki, Fakahoko, Laga-iki, and Lagi-atea, who by various accounts, arrived from Fonuagalo, Tulia, Toga-liulu, or perhaps other islands. In Avatele myths, the gods are said to have come from within the earth instead of Fonuagalo. There are also many other gods in Niuean mythology from fish gods to flying rats.










