Related Research Articles

The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consist of an almost continuous sequence that form the western "sounds" of North America, Central America, South America, and West Antarctica.

The Hoover Wilderness is a wilderness area in the Inyo and Humboldt-Toiyabe National Forests. It lies to the east of the crest of the central Sierra Nevada in California, to the north and east of Yosemite National Park - a long strip stretching nearly to Sonora Pass on the north and Tioga Pass on the south.

The Great Divide Basin or Great Divide Closed Basin is an area of land in the Red Desert of Wyoming where none of the water falling as rain to the ground drains into any ocean, directly or indirectly. It is thus an endorheic basin, one of several in North America that adjoin the Continental Divide. To the south and west of the basin is the Green River watershed, draining to the Gulf of California/Pacific Ocean; to the north and east is the North Platte watershed, draining to the Gulf of Mexico. The basin is very roughly rectangular in shape; the northwest corner is at Oregon Buttes near South Pass, about 40 miles (64 km) southwest of Lander, and the southeast corner is in the Sierra Madre Range near Bridger Pass, about 20 miles (32 km) southwest of Rawlins.

The Pánuco River, also known as the Río de Canoas, is a river in Mexico fed by several tributaries including the Moctezuma River and emptying into the Gulf of Mexico. The river is approximately 510 kilometres (320 mi) long and passes through or borders the states of Mexico, Hidalgo, Querétaro, San Luis Potosí, Tamaulipas, and Veracruz. According to the Atlas of Mexico, it is the fourth-largest river in Mexico by volume of runoff, and forms the sixth-largest river basin in Mexico by area.
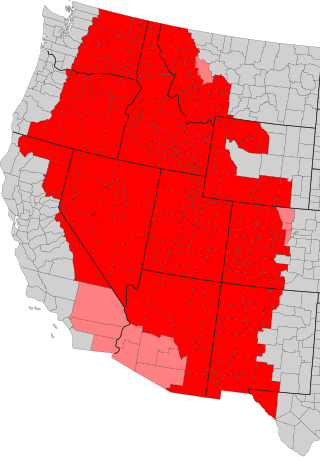
The Intermountain West, or Intermountain Region, is a geographic and geological region of the Western United States. It is located between the Rocky Mountain Front on the east and the Cascade Range and Sierra Nevada on the west.
El Nayar is a municipality in the Mexican state of Nayarit. The population was 30,551 in 2005 in a total area of 5,100 km². The municipal seat of Jesús María had a population of 1,520 in 2005. El Nayar is the home of the Huichol, Cora, and the Tepehuán Indians.
La Yesca is a municipality and the municipal seat of the same in the Mexican state of Nayarit. The population of the municipality was 12,025 (2005). The population of the town and municipal seat was 356 inhabitants in 2005. The population density was 7 inhabitants per square kilometer, one of the lowest in the state.

The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca is a mountain range in southern Mexico. It is primarily in the state of Oaxaca, and extends north into the states of Puebla and Veracruz.

The Bolsón de Mapimí is an endorheic, or internal drainage, basin in which no rivers or streams drain to the sea, but rather toward the center of the basin, often terminating in swamps and ephemeral lakes. It is located in the center-north of the Mexican Plateau. The basin is shared by the states of Durango, Coahuila, Chihuahua, and Zacatecas. It takes its name from Mapimí, a town in Durango.

The Xalbal River is a river of Guatemala. Its sources are in the Sierra de los Cuchumatanes mountain range in the department of El Quiché, where the river is called Río Xaclbal or Río Chajul. The Xaclbal river flows northwards down the tropical lowlands of Ixcan where it is called Río Xalbal, and crosses the border with Mexico, where it joins the Lacantún River, a tributary of the Usumacinta river. The Guatemalan part of Xaclbal river basin covers an area of 1,366 square kilometres (527 sq mi).
The Amapa River is a river in the Mexican states of Oaxaca and Veracruz.
The Atenguillo River is a river of Jalisco, Mexico. It is a northward-flowing tributary of the Ameca River

The Bolaños River is a river in Mexico flowing through the Sierra Madre Occidental, and a tributary of Río Grande de Santiago. It has a length of 360 km (220 mi) and a watershed of about 10,000 km2 (3,900 sq mi).
The Pantepec River is a river of Mexico that belongs to the Tuxpan River basin, on the Gulf of Mexico slope. The Pantepec River is considered the upper course of the Tuxpan River.
The Huaynamota River is a river in western Mexico. It is a tributary of the Río Grande de Santiago in the southern Sierra Madre Occidental.
The mountain chub is a species of freshwater fish in the family Cyprinidae, endemic to the Huaynamota, Juchipila and Bolaños rivers in west-central Mexico.
Brilliant is an unincorporated community in Colfax County, in the U.S. state of New Mexico.

Atherton Island is a small island in the Sacramento–San Joaquin River Delta. It is in unincorporated San Joaquin County, California, part of Stockton. Its coordinates are 37°57′22″N121°21′01″W, and the United States Geological Survey measured its elevation as 13 ft (4.0 m) in 1999. It appears on a 2015 USGS map of the area.
The Sierra los Huicholes is a mountain range in western Mexico. It is located in the states of Nayarit, Jalisco, and Zacatecas. The Sierra los Huicholes is part of the Sierra Madre Occidental, and is located in the southern portion of the range.
References
- ↑ Alvarado-Hernández, Leticia & Ibáñez-Castillo, Laura & Ruiz Garcia, Agustin & González-Leiva, Fernando & Peña, Vázquez Mario (2020). "Hourly Streamflow Forecasting for the Huaynamota River, Nayarit, Mexico, Using the Discrete Kalman Filter. Agrociencia. 54. 295–312.
- Atlas of Mexico, 1975 (http://www.lib.utexas.edu/maps/atlas_mexico/river_basins.jpg)%5B%5D.
- The Prentice Hall American World Atlas, 1984.
- Rand McNally, The New International Atlas, 1993.