
Nayarit, officially the Free and Sovereign State of Nayarit, is one of the 31 states that, along with Mexico City, comprise the Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 20 municipalities and its capital city is Tepic.

The Sierra Madre Occidental is a major mountain range system of the North American Cordillera, that runs northwest–southeast through northwestern and western Mexico, and along the Gulf of California. The Sierra Madre is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western 'sounds' of North America, Central America, South America and West Antarctica.

The Sierra Madre Oriental is a mountain range in northeastern Mexico. The Sierra Madre Oriental is part of the American Cordillera, a chain of mountain ranges (cordillera) that consists of an almost continuous sequence of mountain ranges that form the western "backbone" of North America, Central America, South America, and Antarctica.
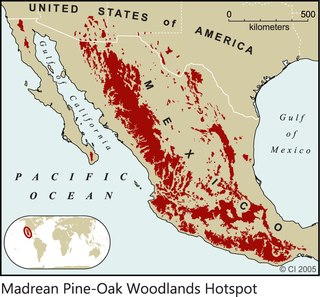
The Madrean pine–oak woodlands are subtropical woodlands found in the mountains of Mexico and the southwestern United States. They are a biogeographic region of the tropical and subtropical coniferous forests and Temperate broadleaf and mixed forests biomes, located in North America.

The Madrean Sky Islands are enclaves of Madrean pine–oak woodlands, found at higher elevations in a complex of small mountain ranges in southern and southeastern Arizona, southwestern New Mexico, and northwestern Mexico. The sky islands are surrounded at lower elevations by the Sonoran and Chihuahuan deserts. The northern west–east perimeter of the sky island region merges into the higher elevation eastern Mogollon Rim and the White Mountains of eastern Arizona.

The Sierra Madre Occidental pine–oak forests are a Tropical and subtropical coniferous forests ecoregion of the Sierra Madre Occidental range from the southwest USA region to the western part of Mexico. They are home to a large number of endemic plants and important habitat for wildlife.
El Nayar is a municipality in the Mexican state of Nayarit. The population was 30,551 in 2005 in a total area of 5,100 km². The municipal seat of Jesús María had a population of 1,520 in 2005. El Nayar is the home of the Huichol, Cora, and the Tepehuán Indians have adapted El Nayar.
La Yesca is a municipality and the municipal seat of the same in the Mexican state of Nayarit. The population of the municipality was 12,025 (2005). The population of the town and municipal seat was 356 inhabitants in 2005. The population density was 7 inhabitants per square kilometer, one of the lowest in the state.

The Sierra Madre de Oaxaca pine–oak forests is a tropical and subtropical coniferous forests ecoregion in Southern Mexico.

The Central Mexican Plateau, also known as the Mexican Altiplano, is a large arid-to-semiarid plateau that occupies much of northern and central Mexico. Averaging 1,825 m (5,988 ft) above sea level, it extends from the United States border in the north to the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt in the south, and is bounded by the Sierra Madre Occidental and Sierra Madre Oriental to the west and east, respectively.

The Sierra Madre Oriental pine–oak forests are a tropical and subtropical coniferous forests ecoregion of northeastern and Central Mexico, extending into the state of Texas in the United States.

The Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt pine–oak forests is a subtropical coniferous forest ecoregion of the Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt of central Mexico.
The Huaynamota River is a river in western Mexico. It is a tributary of the Río Grande de Santiago in the southern Sierra Madre Occidental.

The Central Mexican matorral is an ecoregion of the deserts and xeric shrublands biome of central Mexico. It is the southernmost ecoregion of the Nearctic realm.

The Sierra de Tamaulipas is an isolated, semi-tropical mountain range in the Mexican state of Tamaulipas. Its highest point is 1,260 m (4,130 ft). There are no cities or towns in the Sierra and the small population is largely agricultural. The higher elevations of the Sierra have forests of oak and pine, contrasting with the semi-arid brush that dominates at lower altitudes. Several archaeological sites establish that the Sierra de Tamaulipas was the northern outpost of the agricultural Mesoamerican peoples of eastern Mexico.

La Michilía Biosphere Reserve is a protected area in northwestern Mexico. It is located in the Sierra Madre Occidental range in southern Durango state.

The Sierra de San Juan Biosphere Reserve is a protected area in Nayarit state of western Mexico. It was established in 2003, and has an area of 198.01 km2. It lies just southwest of the city of Tepic. It protects a portion of the Sierra de San Juan, a mountain range which lies between Tepic and the Pacific Ocean.

The Cuenca Alimentadora del Distrito Nacional de Riego 043 Estado de Nayarit is a protected natural area in west-central Mexico. It extends across portions of southern Sierra Madre Occidental and the westernmost Trans-Mexican Volcanic Belt. It has an area of 23290.27 km2, covering portions of southern Durango, northern Jalisco, eastern Nayarit, southern Zacatecas, and western Aguascalientes states.

The Sierra Fría is a mountain range in central Mexico. It forms the northwestern border of Aguascalientes state and extends into adjacent Zacatecas, west of the city of Aguascalientes.

The Cuenca Alimentadora del Distrito Nacional de Riego 01 Pabellón is a protected area in central Mexico. It covers a portion of the Sierra Fría in Aguascalientes and Zacatecas states.














