The Atlanta Gay Center was a community center that served the gay community in Atlanta, Georgia (United States). It was founded in 1976. [1] It has since closed and been replaced by the Atlanta Gay and Lesbian Community Center.
The center published a bi-weekly newspaper, and operated the Gay Helpline for the Atlanta area. The center was the meeting place for several support groups including those for teens, interracial couples, older couples, and P-FLAG. [2]
During the early 1980s, in the early days of HIV/AIDS awareness, the Atlanta Gay Center offered free testing and support groups.

The LGBTQ community is a loosely defined grouping of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender individuals united by a common culture and social movements. These communities generally celebrate pride, diversity, individuality, and sexuality. LGBTQ activists and sociologists see LGBT community-building as a counterweight to heterosexism, homophobia, biphobia, transphobia, sexualism, and conformist pressures that exist in the larger society. The term pride or sometimes gay pride expresses the LGBT community's identity and collective strength; pride parades provide both a prime example of the use and a demonstration of the general meaning of the term. The LGBT community is diverse in political affiliation. Not all people who are lesbian, gay, bisexual, or transgender consider themselves part of the LGBT community.
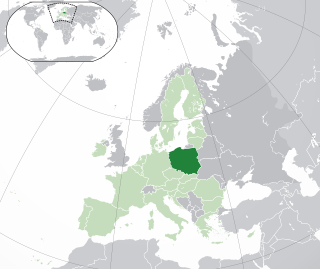
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Poland face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. According to ILGA-Europe's 2024 report, the status of LGBTQ rights in Poland is the worst among the European Union countries.
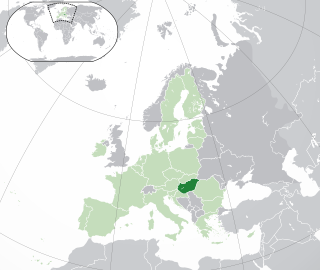
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people in Hungary face legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Homosexuality is legal in Hungary for both men and women. Discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation and sex is banned in the country. However, households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for all of the same legal rights available to heterosexual married couples. Registered partnership for same-sex couples was legalised in 2009, but same-sex marriage remains banned. The Hungarian government has passed legislation that restricts the civil rights of LGBT Hungarians – such as ending legal recognition of transgender Hungarians and banning LGBT content and displays for minors. This trend continues under the Fidesz government of Viktor Orbán. In June 2021, Hungary passed an anti-LGBT law on banning "homosexual and transexual propaganda" effective since 1 July. The law has been condemned by seventeen member states of the European Union. In July 2020, the European Commission started legal action against Hungary and Poland for violations of fundamental rights of LGBTQI people, stating: "Europe will never allow parts of our society to be stigmatized."

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Bulgaria face significant challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female same-sex relationships are legal in Bulgaria, but same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex couples. Discrimination on the basis of sexual orientation has been banned since 2004, with discrimination based on "gender change" being outlawed since 2015. In July 2019, a Bulgarian court recognized a same-sex marriage performed in France in a landmark ruling. For 2020, Bulgaria was ranked 37 of 49 European countries for LGBT rights protection by ILGA-Europe. Like most countries in Central and Eastern Europe, post-Communist Bulgaria holds socially conservative attitudes when it comes to such matters as homosexuality and transgender people.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people in Ukraine face legal and social challenges not experienced by non-LGBT individuals; historically, the prevailing social and political attitudes have been intolerant of LGBT people, and strong evidence suggests this attitude remains in parts of the wider society. Since the fall of the Soviet Union and Ukraine's independence in 1991, the Ukrainian LGBT community has gradually become more visible and more organized politically, organizing several LGBT events in Kyiv, Odesa, Kharkiv, and Kryvyi Rih.

The rights of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Singapore have evolved over the decades. Same-sex sexual activity is legal for both males and females; for men it was officially legalised in 2022 after being de facto decriminalised since 2007, and for women it was always legal. Prior to 2022, same-sex sexual activity between males was de jure illegal under the British colonial-era Section 377A of the Penal Code. The law had been de facto unenforced for decades. In February 2022, the Court of Appeal in the Supreme Court reaffirmed that 377A cannot be used to prosecute men for having sex with other men, and that it is "unenforceable in its entirety". Transgender rights in the country are also progressive in the region, which included Singapore being the first country in Asia to legalise sex reassignment surgery in 1973.
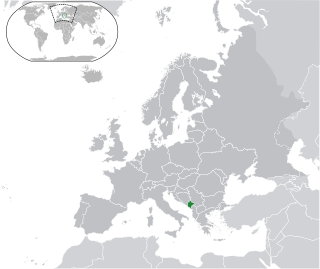
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in Montenegro face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBT residents. Both male and female same-sex sexual activity are legal in Montenegro, but households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender (LGBT) individuals in the Republic of the Philippines have faced many difficulties in their homeland, such as prejudice, violence, abuse, assault, harassment and other forms of anti-LGBT rhetoric. Many LGBT Filipinos are met with mixed attitudes and reactions by their families, friends and others in their communities, as well as professionals, educators, their national public officials, politicians, attorneys and others working for the government and the rest of the general population.

LGBT pride is the promotion of the self-affirmation, dignity, equality, and increased visibility of lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBTQ) people as a social group. Pride, as opposed to shame and social stigma, is the predominant outlook that bolsters most LGBT rights movements. Pride has lent its name to LGBT-themed organizations, institutes, foundations, book titles, periodicals, a cable TV channel, and the Pride Library.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) rights in Kosovo have improved in recent years, most notably with the adoption of the new Constitution, banning discrimination based on sexual orientation. Kosovo remains one of the few Muslim-majority countries that hold regular pride parades.

LGBTQ+ rights in the Cayman Islands are regarded as some of the most progressive in the Caribbean. While the British territory still has a long way to go, it continues to relax its stance on this subject. Both male and female types of same-sex sexual activity are legal in the Cayman Islands. Same-sex unions became legal in 2020.

Atlanta Pride, also colloquially called the Atlanta Gay Pride Festival, is a week-long annual lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender (LGBTQ) pride festival held in Atlanta, Georgia. Established in 1971, it is one of the oldest and largest pride festivals in the United States. According to the Atlanta Pride Committee, as of 2017, attendance had continually grown to around 300,000. Originally held in June, Atlanta Pride has been held in October every year since 2008, typically on a weekend closest to National Coming Out Day.
Cambodia does not recognize same-sex marriage or civil unions, but does recognize a registry program known as the "declaration of family relationship" offering limited legal rights to same-sex couples. As of June 2021, the registry has been introduced to 68 communes. Same-sex marriage has received support from King Norodom Sihamoni and his late father, King Norodom Sihanouk.
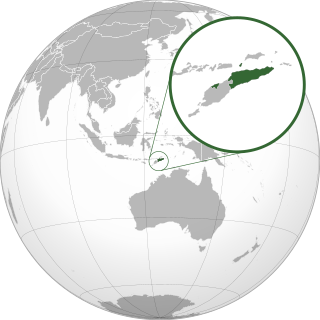
Lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender (LGBT) people in East Timor face legal challenges not experienced by non-LGBTQ residents. Both male and female same-sex sexual activity are legal in East Timor, but same-sex couples and households headed by same-sex couples are not eligible for the same legal protections available to opposite-sex married couples.

The black gay pride movement is a global campaign tailored for black people who are also members of the LGBTQ community. Starting in the 1990s, black gay pride movements began as a way to provide black LGBT people an alternative to the largely white mainstream LGBT movement. According to some, white gay prides are seen to enforce, both consciously and unconsciously, a long history of ignoring the people of color who share in their experiences. The history of racial segregation seen in other organizations such as nursing associations, journalism associations, and fraternities is carried on into the black gay prides seen today. The exclusion of people of color in gay pride events is perceived by some to play into existing undertones of white superiority and racist political movements.

Lesbian, gay, bisexual, transgender, and queer (LGBTQ) people in the U.S. state of Georgia enjoy most of the same rights as non-LGBTQ people. LGBTQ rights in the state have been a recent occurrence, with most improvements occurring from the 2010s onward. Same-sex sexual activity has been legal since 1998, although the state legislature has not repealed its sodomy law. Same-sex marriage has been legal in the state since 2015, in accordance with Obergefell v. Hodges. In addition, the state's largest city Atlanta, has a vibrant LGBTQ community and holds the biggest Pride parade in the Southeast. The state's hate crime laws, effective since June 26, 2020, explicitly include sexual orientation.
The state of Georgia mostly improved in its treatment of lesbian, gay, bisexual and transgender residents in the years after 1970, when LGBT residents began to openly establish events, organizations and outlets for fellow LGBT residents and increase in political empowerment.
Atlanta Black Pride started in 1996 and is one of two officially recognized festivals for the African-American LGBT community. It is held in Atlanta each year at the end of August and beginning of September. Atlanta Black Pride is the largest black gay pride celebration in the world with an estimated 100,000 people annually in attendance. Atlanta Black Pride heavily contributes to the annual $65 million economic impact on Atlanta's economy during the city's eventful Labor Day weekend most recently organized by Traxx Girls Inc & Atlanta Black Pride Weekend LLC due to the administration dissolve of In The Life Atlanta.
Throughout Dallas–Fort Worth, there is a large lesbian, gay, bisexual, and transgender community. Since 2005, DFW has constituted one of the largest LGBT communities in Texas.

Rainbow capitalism is the involvement of capitalism, corporate capitalism, and consumerism in appropriating and profiting from the LGBT movement. It developed in the 20th and 21st centuries as the LGBT community became more accepted in society and developed sufficient purchasing power, known as pink money. Early rainbow capitalism was limited to gay bars and gay bathhouses, though it expanded to most industries by the early-21st century.