Related Research Articles

An adjustable spanner or adjustable wrench is any of various styles of spanner (wrench) with a movable jaw, allowing it to be used with different sizes of fastener head rather than just one fastener size, as with a conventional fixed spanner.
Henry Maudslay was an English machine tool innovator, tool and die maker, and inventor. He is considered a founding father of machine tool technology. His inventions were an important foundation for the Industrial Revolution.

Atlas Copco is a Swedish multinational industrial company that was founded in 1873. It manufactures industrial tools and equipment.
Haworth Inc. is a privately held, family-owned office furniture manufacturer headquartered in Holland, Michigan, United States. Founded in 1948 by G. W. Haworth, the company designs and manufactures furniture solutions including seating, tables, movable walls, panels, storage, and wood casegoods. Haworth's furniture pieces, combined with interior design and technology solutions, are intended to create a focus on “organic workspaces that help people perform their best.” Haworth employs 7,500 workers and has 650 dealerships in more than 120 countries. 2021 global sales reached $1.96 billion, a 6.2-percent increase from 2020.
Craftsman is a line of tools, lawn and garden equipment, and work wear. Originally a house brand established by Sears, the brand is now owned by Stanley Black & Decker.

Woodturning is the craft of using a wood lathe with hand-held tools to cut a shape that is symmetrical around the axis of rotation. Like the potter's wheel, the wood lathe is a simple mechanism that can generate a variety of forms. The operator is known as a turner, and the skills needed to use the tools were traditionally known as turnery. In pre-industrial England, these skills were sufficiently difficult to be known as 'the misterie' of the turners guild. The skills to use the tools by hand, without a fixed point of contact with the wood, distinguish woodturning and the wood lathe from the machinist's lathe, or metal-working lathe.
Delta Power Equipment Corp. designs, manufactures and distributes power woodworking tools under the Delta Machinery brand.
A combination machine is a woodworking machine that combines the functions of two or more separate machines into a single unit. For example, a combination machine might consist of a tablesaw with a side-mounted jointer. Another common example of this type of machine is the jointer-thicknesser which combines the function of a jointer with that of a planer.

The Milwaukee Electric Tool Corporation is an American company that develops, manufactures, and markets power tools. It is a brand and subsidiary of Techtronic Industries, a Hong Kong-based company, along with AEG, Ryobi, Hoover, Dirt Devil, and Vax. It produces corded and cordless power tools, hand tools, pliers, hand saws, cutters, screwdrivers, trims, knives, and tool combo kits. It is since 2016 the biggest supplier of cordless power tools in North America, coming close with Bosch in second place, and Stanley Black & Decker at third place.

James Hartness was an American inventor, mechanical engineer, entrepreneur, amateur astronomer, and politician who served as the 58th governor of Vermont from 1921 to 1923.
South Bend Lathe is a brand of machine tools. Today's South Bend Lathe corporation is the successor to the original South Bend Lathe Works, an American machine tool builder that for many decades was one of the most important builders of metalworking lathes in the U.S. and in the world.
Kennametal is an American supplier of tooling and industrial materials founded in 1938 by Philip M. McKenna in the Latrobe, Pennsylvania area.

A surform tool features perforated sheet metal and resembles a food grater. A surform tool consists of a steel strip with holes punched out and the rim of each hole sharpened to form a cutting edge. The strip is mounted in a carriage or handle. Surform tools were called "cheese graters" decades before they entered the market as kitchen utensils used to grate cheese. Surform planes have been described as a cross between a rasp and a plane.
Ingersoll Rand Inc., is a multinational company that provides flow creation and industrial products. The company was formed in February 2020 through the merger of the Industrial segment of Ingersoll-Rand Plc and Gardner Denver. Its products are sold under more than 40 brands across all major global markets.

Bahco is a Swedish brand within the hand tool industry, which is now part of SNA Europe, part of Snap-on. Its roots go back to the industrial revolution in Sweden in the late eighteen hundreds, starting with innovations such as the pipe wrench and the modern adjustable wrench. Since then, the product range has expanded with a total assortment of products that today includes over 7000 hand tools.
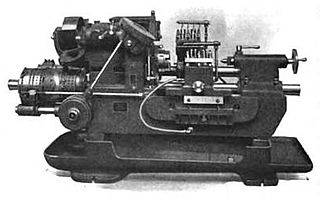
In metalworking and woodworking, an automatic lathe is a lathe with an automatically controlled cutting process. Automatic lathes were first developed in the 1870s and were mechanically controlled. From the advent of NC and CNC in the 1950s, the term automatic lathe has generally been used for only mechanically controlled lathes, although some manufacturers market Swiss-type CNC lathes as 'automatic'.
A Lego clone is a line or brand of children's construction blocks which is mechanically compatible with Lego brand blocks, but is produced by another manufacturer. The blocks were originally patented by The Lego Group in 1961 as "toy building bricks", and the company has since remained dominant in this market. Some competitors have moved to take advantage of Lego brand recognition by advertising their own products as compatible with Lego, with statements such as "compatible with leading building bricks".
George Cohen, Sons and Company was a scrap metal merchant with offices in Commercial Road, London. The company was founded by George Henry Cohen (d.1890) as Messrs. George Cohen & Co. in 1834 and changed its name to George Cohen, Sons and Co. in 1883 on the appointment of Michael Cohen, son of the founder. After the First World War the company won a number of large contracts to dispose of surplus munitions including "400,000 tons of high explosives and other shells". The company also engaged in demolition work, with projects including the towers of Crystal Palace, which had survived the great fire, the Dome of Discovery and Skylon at the Festival of Britain, and London's tram system. In 1940 the company moved its head offices to Hammersmith.

RLF Brands is a US manufacturer of Shopsmith combination machines for woodworking. The brand has its origins in the ShopSmith 10ER launched in the late 1940s, an immediate success with do-it-yourself homeowners. Later the brand changed hands twice before becoming dormant in 1966. Shopsmith, Inc. was founded in 1972 to resume manufacture of ShopSmith parts and products. In 2009 Shopsmith, Inc. went into bankruptcy, and reorganized as RLF Brands. RLF continues to use the Shopsmith brand name.
References
- Justices of the Michigan Supreme Court; various (1920). Michigan Reports: Cases Decided in the Supreme Court of Michigan. Phelphs & Stevens, printers.
{{cite book}}: CS1 maint: multiple names: authors list (link)