
The Manhattan Project was a research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. It was led by the United States with the support of the United Kingdom and Canada. From 1942 to 1946, the project was under the direction of Major General Leslie Groves of the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers. Nuclear physicist Robert Oppenheimer was the director of the Los Alamos Laboratory that designed the actual bombs. The Army component of the project was designated the Manhattan District as its first headquarters were in Manhattan; the placename gradually superseded the official codename, Development of Substitute Materials, for the entire project. Along the way, the project absorbed its earlier British counterpart, Tube Alloys. The Manhattan Project began modestly in 1939, but grew to employ more than 130,000 people and cost nearly US$2 billion. Over 90 percent of the cost was for building factories and to produce fissile material, with less than 10 percent for development and production of the weapons. Research and production took place at more than thirty sites across the United States, the United Kingdom, and Canada.

A nuclear weapon is an explosive device that derives its destructive force from nuclear reactions, either fission or a combination of fission and fusion reactions, producing a nuclear explosion. Both bomb types release large quantities of energy from relatively small amounts of matter.

The Hanford Site is a decommissioned nuclear production complex operated by the United States federal government on the Columbia River in Benton County in the U.S. state of Washington. The site has been known by many names, including Site W and the Hanford Nuclear Reservation. Established in 1943 as part of the Manhattan Project, the site was home to the Hanford Engineer Works and B Reactor, the first full-scale plutonium production reactor in the world. Plutonium manufactured at the site was used in the first atomic bomb, which was tested in the Trinity nuclear test, and in the Fat Man bomb that was used in the bombing of Nagasaki.

The American frontier, also known as the Old West or the Wild West, encompasses the geography, history, folklore, and culture associated with the forward wave of American expansion in mainland North America that began with European colonial settlements in the early 17th century and ended with the admission of the last few western territories as states in 1912. This era of massive migration and settlement was particularly encouraged by President Thomas Jefferson following the Louisiana Purchase, giving rise to the expansionist attitude known as "Manifest Destiny" and the historians' "Frontier Thesis". The legends, historical events and folklore of the American frontier have embedded themselves into United States culture so much so that the Old West, and the Western genre of media specifically, has become one of the defining periods of American national identity.
The Göttingen Manifesto was a declaration of 18 leading nuclear scientists of West Germany against arming the West German army with tactical nuclear weapons in the 1950s, the early part of the Cold War, as the West German government under chancellor Adenauer had suggested.
This is an English language bibliography of scholarly books and articles on the Cold War. Because of the extent of the Cold War, the conflict is well documented.

Atomic tourism or nuclear tourism is a recent form of tourism in which visitors learn about the Atomic Age by traveling to significant sites in atomic history such as museums with atomic weapons, missile silos, vehicles that carried atomic weapons or sites where atomic weapons were detonated.
The War of 1812 bibliography is a selective, annotated bibliography using APA style citations of the many books related to the War of 1812. There are thousands of books and articles written about this topic. Only the most useful are presented.
The Atomic Heritage Foundation (AHF) is a nonprofit organization originally based in Washington, DC, dedicated to the preservation and interpretation of the Manhattan Project and the Atomic Age and its legacy. Founded by Cynthia Kelly in 2002, the Foundation's stated goal is, "to provide the public not only a better understanding of the past but also a basis for addressing scientific, technical, political, social and ethical issues of the 21st century." AHF works with Congress, the Department of Energy, the National Park Service, state and local governments, nonprofit organizations and the former Manhattan Project communities to preserve and interpret historic sites and develop useful and accessible educational materials for veterans, teachers, and the general public. In June 2019, the Atomic Heritage Foundation and the National Museum of Nuclear Science & History signed an agreement that granted stewardship of the Atomic Heritage Foundation website and all of the AHF's physical collections to the museum. The Atomic Heritage Foundation website is now run by the National Museum of Nuclear Science & History. Additionally, the museum now houses the Atomic Heritage Foundation's physical collections which will eventually be integrated into the Nuclear Museum's own collection.
Francis J. Gavin is an American historian currently serving as the Giovanni Agnelli Distinguished Professor and Director of the Henry A. Kissinger Center for Global Affairs at Johns Hopkins University School of Advanced International Studies in Washington, D.C. He is also the chairman of the Board of Editors for the Texas National Security Review.

The United States detonated two atomic bombs over the Japanese cities of Hiroshima and Nagasaki on 6 and 9 August 1945, respectively. The two bombings killed between 129,000 and 226,000 people, most of whom were civilians, and remain the only use of nuclear weapons in armed conflict so far.
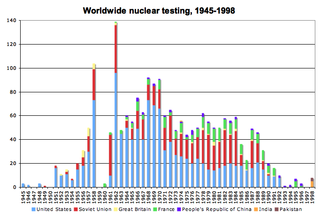
The application of nuclear technology, both as a source of energy and as an instrument of war, has been controversial.

The following works deal with the cultural, political, economic, military, biographical and geologic history of pre-territorial Montana, Montana Territory and the State of Montana.

Nuclear ethics is a cross-disciplinary field of academic and policy-relevant study in which the problems associated with nuclear warfare, nuclear deterrence, nuclear arms control, nuclear disarmament, or nuclear energy are examined through one or more ethical or moral theories or frameworks. In contemporary security studies, the problems of nuclear warfare, deterrence, proliferation, and so forth are often understood strictly in political, strategic, or military terms. In the study of international organizations and law, however, these problems are also understood in legal terms. Nuclear ethics assumes that the very real possibilities of human extinction, mass human destruction, or mass environmental damage which could result from nuclear warfare are deep ethical or moral problems. Specifically, it assumes that the outcomes of human extinction, mass human destruction, or environmental damage count as moral evils. Another area of inquiry concerns future generations and the burden that nuclear waste and pollution imposes on them. Some scholars have concluded that it is therefore morally wrong to act in ways that produce these outcomes, which means it is morally wrong to engage in nuclear warfare.

Plume is a collection of poetry, written by Kathleen Flenniken. Published in 2012 by the University of Washington Press, the poetry presents a brief history of Richland, Washington and the Hanford Nuclear Reservation. The author examines the actions of the US Department of Energy regarding the establishment and operation of Hanford, a nuclear production facility and how their actions affected the health of individuals and families living and working in or near the Reservation. While the US government assured the employees and families who lived in the area that they were safe from exposure to radioactive materials, declassified documents revealed that early protective measures were inadequate, while people were dying of radiation-induced illness. The book was a finalist for both the William Carlos Williams Award from the Poetry Society of America and the Pacific Northwest Booksellers Association Award, while it was the recipient of the Washington State Book Award in 2013.

Wahluke Slope is a geographic feature in Grant, Benton and Adams Counties of Eastern Washington. It is a broad, south-facing slope with a grade of about 8%, situated between the Saddle Mountains and the Columbia River's Hanford Reach. It has been described as "basically a 13-mile-wide gravel bar" created by the Glacial Lake Missoula floods at the end of the last ice age about 15,000 years ago. Much of the Slope, part of the Hanford Nuclear Reservation, was added to the Saddle Mountain National Wildlife Refuge in 1999. Much of the remainder is used for viniculture.
Kenneth George Young FAcSS FRHistS was a British political scientist and historian who was Professor of Public Policy at King's College London in its Department of War Studies. Earlier he was instrumental in the creation of the Department of Political Economy at KCL in 2010, and was its founding head of department.

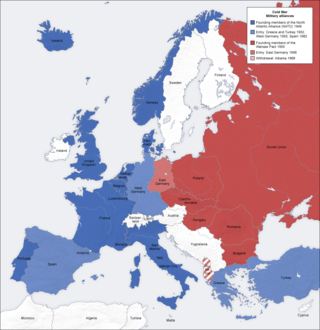
The main issues of the United States foreign policy during the 1945–1953 presidency of Harry S. Truman were working with Allies, especially Britain, the Soviet Union and China. The goals were to achieve victory over Germany and Japan; deal with the chaos in Europe and Asia in the aftermath of World War II; handle the beginning of the Cold War with the USSR; and launch new international organizations such as the United Nations and the World Bank. Truman's presidency was a turning point in foreign affairs, as the United States engaged in an liberal internationalist foreign policy and renounced isolationism by engaging in a long global conflict with the Soviet Union and its allies, forming NATO, and fighting China in the Korean War to a deadlock.
Michael Dan Gordin is an American science historian and Slavist.
African-American scientists and technicians on the Manhattan Project held a small number of positions among the several hundred scientists and technicians involved. Nonetheless, African-American men and women made important contributions to the Manhattan Project during World War II. At the time, their work was shrouded in secrecy, intentionally compartmentalized and decontextualized so that almost no one knew the purpose or intended use of what they were doing.












