The absolute threshold of hearing (ATH), also known as the absolute hearing threshold or auditory threshold, is the minimum sound level of a pure tone that an average human ear with normal hearing can hear with no other sound present. The absolute threshold relates to the sound that can just be heard by the organism. The absolute threshold is not a discrete point and is therefore classed as the point at which a sound elicits a response a specified percentage of the time.

A hearing test provides an evaluation of the sensitivity of a person's sense of hearing and is most often performed by an audiologist using an audiometer. An audiometer is used to determine a person's hearing sensitivity at different frequencies. There are other hearing tests as well, e.g., Weber test and Rinne test.

An equal-loudness contour is a measure of sound pressure level, over the frequency spectrum, for which a listener perceives a constant loudness when presented with pure steady tones. The unit of measurement for loudness levels is the phon and is arrived at by reference to equal-loudness contours. By definition, two sine waves of differing frequencies are said to have equal-loudness level measured in phons if they are perceived as equally loud by the average young person without significant hearing impairment.

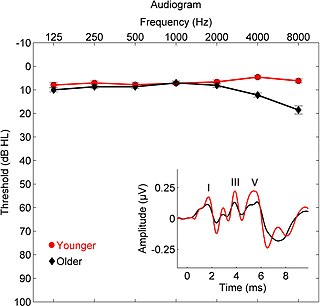
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing loss in which the root cause lies in the inner ear, sensory organ, or the vestibulocochlear nerve. SNHL accounts for about 90% of reported hearing loss. SNHL is usually permanent and can be mild, moderate, severe, profound, or total. Various other descriptors can be used depending on the shape of the audiogram, such as high frequency, low frequency, U-shaped, notched, peaked, or flat.
An otoacoustic emission (OAE) is a sound that is generated from within the inner ear. Having been predicted by Austrian astrophysicist Thomas Gold in 1948, its existence was first demonstrated experimentally by British physicist David Kemp in 1978, and otoacoustic emissions have since been shown to arise through a number of different cellular and mechanical causes within the inner ear. Studies have shown that OAEs disappear after the inner ear has been damaged, so OAEs are often used in the laboratory and the clinic as a measure of inner ear health.

Audiometry is a branch of audiology and the science of measuring hearing acuity for variations in sound intensity and pitch and for tonal purity, involving thresholds and differing frequencies. Typically, audiometric tests determine a subject's hearing levels with the help of an audiometer, but may also measure ability to discriminate between different sound intensities, recognize pitch, or distinguish speech from background noise. Acoustic reflex and otoacoustic emissions may also be measured. Results of audiometric tests are used to diagnose hearing loss or diseases of the ear, and often make use of an audiogram.
Presbycusis, or age-related hearing loss, is the cumulative effect of aging on hearing. It is a progressive and irreversible bilateral symmetrical age-related sensorineural hearing loss resulting from degeneration of the cochlea or associated structures of the inner ear or auditory nerves. The hearing loss is most marked at higher frequencies. Hearing loss that accumulates with age but is caused by factors other than normal aging is not presbycusis, although differentiating the individual effects of distinct causes of hearing loss can be difficult.

An audiogram is a graph that shows the audible threshold for standardized frequencies as measured by an audiometer. The Y axis represents intensity measured in decibels (dB) and the X axis represents frequency measured in hertz (Hz). The threshold of hearing is plotted relative to a standardised curve that represents 'normal' hearing, in dB(HL). They are not the same as equal-loudness contours, which are a set of curves representing equal loudness at different levels, as well as at the threshold of hearing, in absolute terms measured in dB(SPL).
An Audiometrist or Audiometric Officer, is a health-care professional technician who has received special training in the use of Pure tone audiometry equipment. An audiometrist conducts hearing tests, or "audiometric screening", with an Audiometer to establish hearing levels. The results are represented by an audiogram, and are usually interpreted by an audiologist, or a registered Medical Officer, unless the audiometrist is also an audiologist, with the aim of diagnosing hearing loss.

Hearing range describes the frequency range that can be heard by humans or other animals, though it can also refer to the range of levels. The human range is commonly given as 20 to 20,000 Hz, although there is considerable variation between individuals, especially at high frequencies, and a gradual loss of sensitivity to higher frequencies with age is considered normal. Sensitivity also varies with frequency, as shown by equal-loudness contours. Routine investigation for hearing loss usually involves an audiogram which shows threshold levels relative to a normal.
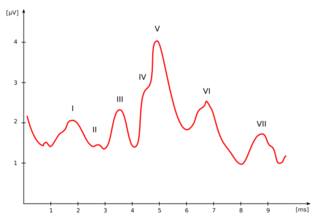
The auditory brainstem response (ABR), also called brainstem evoked response audiometry (BERA) or brainstem auditory evoked potentials (BAEPs) or brainstem auditory evoked responses (BAERs) is an auditory evoked potential extracted from ongoing electrical activity in the brain and recorded via electrodes placed on the scalp. The recording is a series of six to seven vertex positive waves of which I through V are evaluated. These waves, labeled with Roman numerals in Jewett/Williston convention, occur in the first 10 milliseconds after onset of an auditory stimulus. The ABR is termed an exogenous response because it is dependent upon external factors.

Pure-tone audiometry is the main hearing test used to identify hearing threshold levels of an individual, enabling determination of the degree, type and configuration of a hearing loss and thus providing a basis for diagnosis and management. Pure-tone audiometry is a subjective, behavioural measurement of a hearing threshold, as it relies on patient responses to pure tone stimuli. Therefore, pure-tone audiometry is only used on adults and children old enough to cooperate with the test procedure. As with most clinical tests, standardized calibration of the test environment, the equipment and the stimuli is needed before testing proceeds. Pure-tone audiometry only measures audibility thresholds, rather than other aspects of hearing such as sound localization and speech recognition. However, there are benefits to using pure-tone audiometry over other forms of hearing test, such as click auditory brainstem response (ABR). Pure-tone audiometry provides ear specific thresholds, and uses frequency specific pure tones to give place specific responses, so that the configuration of a hearing loss can be identified. As pure-tone audiometry uses both air and bone conduction audiometry, the type of loss can also be identified via the air-bone gap. Although pure-tone audiometry has many clinical benefits, it is not perfect at identifying all losses, such as ‘dead regions’ of the cochlea and neuropathies such as auditory processing disorder (APD). This raises the question of whether or not audiograms accurately predict someone's perceived degree of disability.
Minimum audibility curve is a standardized graph of the threshold of hearing frequency for an average human, and is used as the reference level when measuring hearing loss with an audiometer as shown on an audiogram.

Hearing, or auditory perception, is the ability to perceive sounds through an organ, such as an ear, by detecting vibrations as periodic changes in the pressure of a surrounding medium. The academic field concerned with hearing is auditory science.
Visual reinforcement audiometry (VRA) is a key behavioural test for evaluating hearing in young children. First introduced by Liden and Kankkunen in 1969, VRA is a good indicator of how responsive a child is to sound and speech and whether the child is developing awareness to sound as expected. Performed by an audiologist, VRA is the preferred behavioral technique for children that are 6 – 24 months of age. Using classic operant conditioning, a stimulus is presented, which is followed by a 90 degree head turn from midline by the child, resulting in the child being reinforced with an animation. The child is typically seated in a high chair or on a parent's lap while facing forward. A loud speaker or two are situated at 45 or 90 degrees from the child. As the auditory stimulus is presented, the child will naturally search for the sound source, resulting in a head turn and reinforcement is followed shortly after through an animated toy or video next to the speaker where the auditory stimulus was presented. Using VRA, an audiologist can obtain minimal hearing thresholds ranging in frequencies from 250 Hz - 8000 Hz using speakers, headphones, inserts earphones or through a bone conduction transducer and plot them on an audiogram. The results from the audiogram, paired with other objective measures such as a Tympanogram, Otoacoustic emissions testing and/or Auditory Brainstem Response testing can provide further insight into the child's auditory hearing status as well as future treatment plans if deemed necessary. VRA works well until about 18–24 months of age. Above 18–24 months of age, children need more interesting tasks to hold their attention, which is when audiologists introduce Conditioned Play Audiometry.
Conditioned play audiometry (CPA) is a type of audiometry done in children from ages 2 to 5 years old, in developmental age. It is the test that directly follows visual reinforcement audiometry when the child becomes able to focus on a task. It is a type of behavioral hearing test, of which there are many.

Brian C.J. Moore FMedSci, FRS is an Emeritus Professor of Auditory Perception in the University of Cambridge and an Emeritus Fellow of Wolfson College, Cambridge. His research focuses on psychoacoustics, audiology, and the development and assessment of hearing aids.
In sound technology, personal sound refers to a range of software solutions that customize an audio device's sound output to match the listener's unique hearing sensitivities. The technologies aim to optimize the sound quality in the audio device to ensure they best fit the hearing perception of each unique listener.

Identification of a hearing loss is usually conducted by a general practitioner medical doctor, otolaryngologist, certified and licensed audiologist, school or industrial audiometrist, or other audiometric technician. Diagnosis of the cause of a hearing loss is carried out by a specialist physician or otorhinolaryngologist.
Computational audiology is a branch of audiology that employs techniques from mathematics and computer science to improve clinical treatments and scientific understanding of the auditory system. Computational audiology is closely related to computational medicine, which uses quantitative models to develop improved methods for general disease diagnosis and treatment.















