
An uncrewed aerial vehicle (UAV), commonly known as a drone, is an aircraft without any human pilot, crew, or passengers on board. UAVs were originally developed through the twentieth century for military missions too "dull, dirty or dangerous" for humans, and by the twenty-first, they had become essential assets to most militaries. As control technologies improved and costs fell, their use expanded to many non-military applications. These include aerial photography, area coverage, precision agriculture, forest fire monitoring, river monitoring, environmental monitoring, policing and surveillance, infrastructure inspections, smuggling, product deliveries, entertainment, and drone racing.

Aerial photography is the taking of photographs from an aircraft or other airborne platforms. When taking motion pictures, it is also known as aerial videography.

AAI Corporation is an aerospace and defense development and manufacturing firm, located in Hunt Valley, Maryland, US. Formerly a wholly owned subsidiary of United Industrial Corporation, AAI was acquired by Textron in 2007. It currently operates as a unit of Textron Systems and employs more than 2,000.

AeroVironment, Inc. is an American defense contractor headquartered in Arlington, Virginia, that designs and manufactures unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Paul B. MacCready Jr., a designer of human-powered aircraft, founded the company in 1971. The company is best known for its lightweight human-powered and solar-powered vehicles. The company is the US military's top supplier of small drones —notably the Raven, Switchblade, Wasp and Puma models.

The Boeing Insitu ScanEagle is a small, long-endurance, low-altitude unmanned surveillance and reconnaissance aerial vehicle built by Insitu, a subsidiary of Boeing, and is used for reconnaissance. The ScanEagle was designed by Insitu based on the Insitu SeaScan, a commercial UAV that was intended for fish-spotting. The ScanEagle continues to receive improvements through upgrades and changes.
Access 5 was a national project run by NASA in collaboration with industry, the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA), and the United States Department of Defense (DoD), in order to introduce high altitude, long endurance (HALE) remotely operated aircraft (ROA) for routine flights in the National Airspace System (NAS). It was the first project in the United States to formally attempt to integrated unmanned aircraft into the national airspace system (NAS). The primary objective was to open up airspace for commercial unmanned aviation. Access 5 commenced in May 2004 and was slated to run for five years. The project received initial funding in the amount of $101M from NASA and guarantees of support from the ROA industry. It was managed out of Dryden Flight Research Center. The program was managed by Jeff Bauer out of NASA Dryden and R. Scott Dann, a General Atomics program manager who filled the role of industry director. R. Scott Dann was also the founder and first president of the UAV National Industry Team (UNITE). A good portion of the leadership on the Access 5 program were involved in the NASA ERAST program, another pioneering program in UAS development.
The Next Generation Air Transportation System (NextGen) is an ongoing United States Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) project to modernize the National Airspace System (NAS). The FAA began work on NextGen improvements in 2007 and plans to finish the final implementation segment by 2030. The goals of the modernization include using new technologies and procedures to increase the safety, efficiency, capacity, access, flexibility, predictability, and resilience of the NAS while reducing the environmental impact of aviation.

The UAV Challenge - Outback Rescue, also known as the UAV Outback Challenge or UAV Challenge, is an annual competition for the development of unmanned aerial vehicles. The competition was first held in 2007 and features an open challenge for adults, and a high-school challenge. The event is aimed at promoting the civilian use of unmanned aerial vehicles and the development of low-cost systems that could be used for search and rescue missions. The event is one of the largest robotics challenges in the world and one of the highest stakes UAV challenges, with the 2018 Medical Express version of the event offering $75,000 to the winner.
Autonomous Systems Technology Related Airborne Evaluation & Assessment (ASTRAEA) is a project to develop unmanned aerial vehicles (UAV) to fly in civil airspace. Both UK government agencies and companies such as AOS Group, BAE Systems, Qinetiq, Rolls-Royce plc, Cassidian, Cobham plc, EADS and Thales UK are involved. The project began in 2006.
The Northrop Grumman RQ-180 is an American stealth unmanned aerial vehicle (UAV) surveillance aircraft intended for contested airspace. As of 2019, there had been no images or statements released, but growing evidence points to the existence of the RQ-180 and its use in regular front-line service. The use of the nickname "White Bat" in a 2021 video released by the US Air Force Profession of Arms Center of Excellence (PACE) suggests that the military may be preparing to release information on the RQ-180.
Unmanned aircraft system simulation focuses on training pilots to control an unmanned aircraft or its payload from a control station. Flight simulation involves a device that artificially re-creates aircraft flight and the environment in which it flies for pilot training, design, or other purposes. It includes replicating the equations that govern how aircraft fly, how they react to applications of flight controls, the effects of other aircraft systems, and how the aircraft reacts to external factors such as air density, turbulence, wind shear, cloud, precipitation, etc.
The US Federal Aviation Administration has adopted the name small unmanned aircraft system (sUAS) to describe aircraft systems without a flight crew on board weighing less than 55 pounds. More common names include UAV, drone, remotely piloted vehicle (RPV), remotely piloted aircraft (RPA), and remotely operated aircraft (ROA). These unmanned aircraft flown in the USA's National Airspace System must operate under the rules of a Community Based Organization for recreational purposes or 14 CFR Part 107 for commercial operations. All UAVs weighing more than 250 grams flown for any purpose must be registered with the FAA.

Regulation of unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) involves setting safety requirements, outlining regulations for the safe flying of drones, and enforcing action against errant users.

The Commercial UAS Modernization Act is a bill introduced in the 114th Congress by U.S. Senators Cory Booker (D-NJ) and John Hoeven (R-ND) that would create temporary guidelines for the use of unmanned aircraft systems and regulations for the commercial drone industry. Most commercial use of drones in the U.S. is currently banned by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA).

Pix4D is a Swiss software company that specializes in photogrammetry. It was founded in 2011 as a spinoff from the École Polytechnique Fédérale de Lausanne (EPFL) Computer Vision Lab in Switzerland. It develops a suite of software products that use photogrammetry and computer vision algorithms to transform DSLR, fisheye, RGB, thermal and multispectral images into 3D maps and 3D modeling. The company has 7 international offices, with its headquarters in Lausanne, Switzerland.
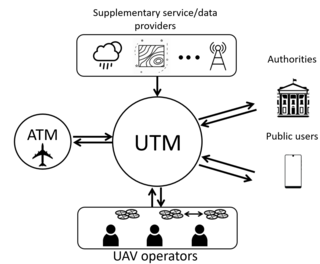
Unmanned aircraft system traffic management (UTM) is an air traffic management ecosystem under development for autonomously controlled operations of unmanned aerial systems (UAS) by the FAA, NASA, other federal partner agencies, and industry. They are collaboratively exploring concepts of operation, data exchange requirements, and a supporting framework to enable multiple UAS operations beyond visual line-of-sight at altitudes under 400 ft above ground level in airspace where FAA air traffic services are not provided.

Applied Aeronautics is a commercial drone manufacturer. Founded in 2014, Applied Aeronautics is headquartered in Austin, Texas. Applied Aeronautics is a manufacturer of affordable drones and drone related accessories for commercial and government customers. Their flagship product is the Albatross, an electric, long-range, fixed wing UAV.
A weather drone, or weather-sensing uncrewed aerial vehicle (UAV), – is a remotely piloted aircraft weighing less than 25 kg and carrying sensors that collect thermodynamic and kinematic data from the mid and lower atmosphere.










