Related Research Articles

Kamarupi Prakrit is the postulated Middle Indo-Aryan (MIA) Prakrit language used in ancient Kamarupa. This language is the historical ancestor of the Kamatapuri lects and the modern Assamese language; and can be dated prior to 1250 CE, when the proto-Kamta language, the parent of the Kamatapuri lects, began to develop. Though not substantially proven, the existence of the language that predated the Kamatapuri lects and modern Assamese is widely believed to be descended from it.

Kamarupa, an early state during the Classical period on the Indian subcontinent, was the first historical kingdom of Assam.

Naraka, also known as Narakasura, is an asura king in Hindu mythology. In Assamese tradition, he is regarded as the legendary progenitor of all three dynasties of Pragjyotisha-Kamarupa, and the founding ruler of the legendary Bhauma dynasty of Pragjyotisha. Though the myths about Naraka are first mentioned in the Mahabharata, later texts embellish them. According to later post-Vedic texts such as the Brahma Purana and Vishnu Purana, he was the son of Bhudevi, fathered either by the Varaha incarnation of Vishnu or Hiranyaksha. He is claimed as one who established Pragjyotisha. He was killed by Krishna and Satyabhama. His son Bhagadatta—of Mahabharata fame—succeeded him.

The history of Assam is the history of a confluence of people from the east, west, south and the north; the confluence of the Austroasiatic, Tibeto-Burman (Sino-Tibetan), Tai and Indo-Aryan cultures. Although invaded over the centuries, it was never a vassal or a colony to an external power until the third Burmese invasion in 1821, and, subsequently, the British ingress into Assam in 1824 during the First Anglo-Burmese War.

The Varman dynasty (350–650) was the first historical dynasty of the Kamarupa kingdom. It was established by Pushyavarman, a contemporary of Samudragupta. The earlier Varmans were subordinates of the Gupta Empire, but as the power of the Guptas waned, Mahendravarman (470–494) performed two horse sacrifices and the status of Kamarupa as an independent state remained unimpaired. As per the Apsad Inscription of Adityasen, Susthivarman was defeated by Mahasengupta on the bank of Lauhitya. The first of the three Kamarupa dynasties, the Varmans were followed by the Mlechchha and then the Pala dynasties.

The Mlechchha dynasty ruled Kamarupa from their capital at Harruppesvar in present-day Tezpur, Assam, after the fall of the Varman dynasty. According to historical records, there were twenty one rulers in this dynasty, but the line is obscure and names of some intervening rulers are not known. Like all other Kamarupa dynasties a semi-mythical lineage from Narakasura was constructed to accord legitimacy to their rule. The Mlechchha dynasty in Kamarupa was followed by the Pala kings. The dynasty is unrelated to the previous Varman dynasty.

Pragjyotisha is a mythological kingdom that is mentioned in a multitude of Hindu epics. It came to be associated with the historical Kamarupa after Bhaskaravarman of the Varman dynasty by drawing his lineage from Naraka/Bhagadatta of the legendary Pragjyotisha to bring his peripheral kingdom closer to mainland traditions at a time when he was emerging as a powerful king with interests in North India. The identification with the mythical Naraka/Bhagadatta lineage continued to be used by the Mlechchhas and Palas for roughly similar purposes.
Though the precise Etymology of Assam, a state in India is unclear—there is general agreement that it is related to the Ahom people. Whatever the source of the English name, Assam is itself an anglicization.
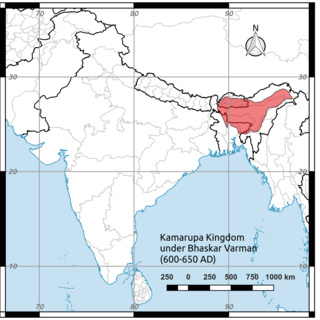
Bhaskaravarman (600–650) was king of medieval Kamarupa and the last of the Varman dynasty. After being captured by the Gauda king during the reign of his father, he was able to re-establish the rule of the Varmans. He made political alliances with Harshavardhana of Thaneswar, against the alliance of the Gauda and East Malwa. He was visited by Xuanzang and Wang Xuance, the envoys of the Tang dynasty who have left accounts of the king and the kingdom.

The earliest Indo-Aryan migration to Assam is estimated to have occurred between the 2nd century BCE and 1st century CE—not earlier than 500 BCE. The earliest epigraphic record suggests that the Indo-Aryan migration began latest by the middle of the 4th century CE. They came from the Gangetic Plains into a region already inhabited by people who spoke Austroasiatic and Tibeto-Burman languages.

Supratisthitavarman ruled Kamarupa from the Varman dynasty for the period 595–600. He was son of King Susthitavarman and Queen Shyamadevi.

Brahma Pala was the founder of the Pala Dynasty (990–1138) of the Kamarupa kingdom. He married Kula Devi, by whom he had a successor to his throne named Ratna Pala.

The Kamarupa inscriptions are a number of 5th-century to early 13th-century rock, copper plate and clay seal inscriptions associated with the rulers and their subordinates of the Kamarupa region. The common language of these inscriptions is Sanskrit. The earliest of these inscriptions, the Umachal and Nagajari-Khanikargaon rock inscriptions, belong to the 5th century and written in a script which was nearly identical to the eastern variety of the Gupta script. There is a steady evolution in the script over the centuries, and last of the scripts, for example the Kanai-boroxiboa inscription using a proto-Assamese script. The script in this period is called the Kamarupi script, which continues development as the Medieval Assamese script from the 13th to the 19th century and emerges as the modern Assamese script.
Guwakuchi or Guakuchi is a village near Nalbari town in India.

Kamrupi dialects are a group of regional dialects of Assamese, spoken in the Kamrup region. It formerly enjoyed prestige status. It is one of two western dialect groups of the Assamese language, the other being Goalpariya. Kamrupi is heterogeneous with three subdialects— Barpetia dialect, Nalbariya dialect and Palasbaria dialect.

Kamrup is the modern region situated between two rivers, the Manas and the Barnadi in Western Assam, with the same territorial extent as the Colonial and post-Colonial "Undivided Kamrup district". It was the capital region of two of the three dynasties of Kamarupa and Guwahati, the current political center of Assam, is situated here. It is characterized by its cultural artifacts.

The Umachal rock inscription is one of the earliest epigraphic sources discovered in Assam. Dated to the 5th century, the rock description was discovered in the north-eastern slopes of the Nilachal Hills, near Guwahati city. The artifact is dated primarily on the basis of the identification of the named Surendravarman with Mahendravarman of the Varman dynasty. The script is in the Nagari variety of the Gupta script and the language is Sanskrit prose. Though the Nilachal Hills is known for the Kamakhya Temple, a shakta/tantra site, this temple was for Balabhadra, a god of the Vaishnavite pantheon.

The Nagajari-Khanikargaon rock inscription is a 5th-century land grant discovered in the Nagajari area of the Golaghat district. The artifact is fragmentary, with inscriptions in Sanskrit written in the eastern variety of the Brahmi script. In style, language, and script, the inscription is very similar to the Umachal and Barganga rock inscriptions. Additionally, since it betrays no influence of a local Prakrit, this inscription is often placed earlier than the Umachal rock inscription. It also indicates that Indo-Aryan culture had spread to the Golaghat region by the 5th century. It is also speculated that it might belong to a different dynasty unrelated to the Varmans of Kamarupa.

Davaka was a kingdom of ancient Indian subcontinent, located in current central region of Assam state. The references to it comes from the 4th century Allahabad pillar inscription of Samudragupta, where it is mentioned as one of five frontier kingdoms of the Gupta Empire.
The Dubi copperplate inscription are the inscriptions of a grant issued by Bhaskaravarman of Kamarupa. This is the earliest of all copper plate grants issued by Kamarupa kings discovered so far. This was an issue after an earlier charter, issued by Bhutivarman, was destroyed. There are five copper plates in this collection, with seventy-six verses in Sanskrit, written in the eastern variety of North Indian alphabet prevalent in the sixth and seventh centuries. All six plates in this grant were first discovered around 1950 during digging near a Siva temple in Dubi village about three miles from the Pathsala railway station, Kamrup district, Assam; but the sixth plate was irrecoverably destroyed soon after discovery. These plates are currently in the Assam State Museum. This plate was issued before the Nidhanpur copperplate inscription, during the earlier part of Bhaskkaravarman's reign.
References
- ↑ Sharma 1978, pp. xxxid.
- ↑ Baij Nath Puri (1968). Studies in early history and administration in Assam. Gauhati University. p. 48.
- ↑ Sharma 1978, p. xxx.
- ↑ Sarkar, Ichhimuddin (1992). Aspects of historical geography of Prāgjyotiṣa-Kāmarūpa (ancient Assam). Naya Prokash. p. 295.
- ↑ Sharma 1978, p. xxxi.
- ↑ Pathak, Guptajit; Pathak, Niranjan Ch (2008). Assam's history and its graphics. Mittal Publications. p. 56.
Bibliography
- Sharma, Mukunda Madhava (1978). Inscriptions of Ancient Assam. Gauhati University, Assam.