Related Research Articles

The Book of Joshua is the sixth book in the Hebrew Bible and the Old Testament, and is the first book of the Deuteronomistic history, the story of Israel from the conquest of Canaan to the Babylonian exile. It tells of the campaigns of the Israelites in central, southern and northern Canaan, the destruction of their enemies, and the division of the land among the Twelve Tribes, framed by two set-piece speeches, the first by God commanding the conquest of the land, and, at the end, the second by Joshua warning of the need for faithful observance of the Law (torah) revealed to Moses.

The history of ancient Israel and Judah spans from the early appearance of the Israelites in Canaan's hill country during the late second millennium BCE, to the establishment and subsequent downfall of the two Israelite kingdoms in the mid-first millennium BCE. This history unfolds within the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. The earliest documented mention of "Israel" as a people appears on the Merneptah Stele, an ancient Egyptian inscription dating back to around 1208 BCE. Archaeological evidence suggests that ancient Israelite culture evolved from the pre-existing Canaanite civilization. During the Iron Age II period, two Israelite kingdoms emerged, covering much of Canaan: the Kingdom of Israel in the north and the Kingdom of Judah in the south.

The Kingdom of Judah was an Israelite kingdom of the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Centered in the highlands to the west of the Dead Sea, the kingdom's capital was Jerusalem. It was ruled by the Davidic line for four centuries. Jews are named after Judah, and primarily descend from people who lived in the region.

The Kingdom of Israel, also called the Northern Kingdom or the Kingdom of Samaria, was an Israelite kingdom that existed in the Southern Levant during the Iron Age. Its beginnings date back to the first half of the 10th century BCE. It controlled the areas of Samaria, Galilee and parts of Transjordan; the former two regions underwent a period in which a large number of new settlements were established shortly after the kingdom came into existence. It had four capital cities in succession: Shiloh, Shechem, Tirzah, and the city of Samaria. In the 9th century BCE, it was ruled by the Omride dynasty, whose political centre was the city of Samaria.

Samaria, the Hellenized form of the Hebrew name Shomron, is used as a historical and biblical name for the central region of the Land of Israel. It is bordered by Judea to the south and Galilee to the north. The region is known to the Palestinians in Arabic under two names, Samirah, and Mount Nablus.

The Israelites were a Hebrew-speaking ethnoreligious group consisting of tribes that inhabited much of Canaan during the Iron Age.

The Babylonian captivity or Babylonian exile was the period in Jewish history during which a large number of Judeans from the ancient Kingdom of Judah were forcibly relocated to Babylonia by the Neo-Babylonian Empire. The deportations occurred in multiple waves: After the siege of Jerusalem in 597 BCE, around 7,000 individuals were deported to Mesopotamia. Further deportations followed the destruction of Jerusalem and Solomon's Temple in 587 BCE.

Lachish was an ancient Israelite city in the Shephelah region of Canaan on the south bank of the Lakhish River mentioned several times in the Hebrew Bible. The current tell by that name, known as Tel Lachish or Tell el-Duweir, has been identified with Lachish. Today, it is an Israeli national park operated and maintained by the Israel Nature and Parks Authority. It lies near the present-day moshav of Lakhish, which was named in honor of the ancient city.

Israel Finkelstein is an Israeli archaeologist, professor emeritus at Tel Aviv University and the head of the School of Archaeology and Maritime Cultures at the University of Haifa. Finkelstein is active in the archaeology of the Levant and is an applicant of archaeological data in reconstructing biblical history. Finkelstein is the current excavator of Megiddo, a key site for the study of the Bronze and Iron Ages in the Levant.

Tel Hazor, also Chatsôr, translated in LXX as Hasōr, named in Arabic Tell Waqqas / Tell Qedah el-Gul, is an archaeological tell at the site of ancient Hazor, located in Israel, Upper Galilee, north of the Sea of Galilee, in the northern Korazim Plateau. From the Middle Bronze Age to the Iron Age, Hazor was the largest fortified city in the region and one of the most important in the Fertile Crescent. It maintained commercial ties with Babylon and Syria, and imported large quantities of tin for the bronze industry. In the Book of Joshua, Hazor is described as "the head of all those kingdoms". Though scholars largely do not consider the Book of Joshua to be historically accurate, archaeological excavations have emphasized the city's importance.

According to the Deuteronomistic history in the Hebrew Bible, a United Monarchy or United Kingdom of Israel existed under the reigns of Saul, Ish-bosheth, David, and Solomon, encompassing the territories of both the later kingdoms of Judah and Israel.

Tel Arad or Tell 'Arad is an archaeological tell, or mound, located west of the Dead Sea, about 10 kilometres west of the modern Israeli city of Arad in an area surrounded by mountain ridges which is known as the Arad Plain. The site is about 10.1 ha.

Kedesh was an ancient Canaanite and later Israelite settlement in Upper Galilee, mentioned several times in the Hebrew Bible. Its remains are located in Tel Kedesh, 3 km northeast of the modern Kibbutz Malkiya in Israel on the Israeli-Lebanese border.

The Fall of Jericho, as described in the biblical Book of Joshua, was the first military engagement fought by the Israelites in the course of the conquest of Canaan. According to Joshua 6:1–27, the walls of Jericho fell after the Israelites marched around the city walls once a day for six days, seven times on the seventh day, with the priests blowing their horns daily and the people shouting on the last day. Excavations at Tell es-Sultan, the biblical Jericho, have failed to find any traces of a city at the relevant time, which has led to a consensus among scholars that the story has its origins in the nationalist propaganda of much later kings of Judah and their claims to the territory of the Kingdom of Israel.

David Ussishkin is an Israeli archaeologist and professor emeritus of archaeology.
The history of the Jews and Judaism in the Land of Israel begins in the 2nd millennium BCE, when Israelites emerged as an outgrowth of southern Canaanites. During biblical times, a postulated United Kingdom of Israel existed but then split into two Israelite kingdoms occupying the highland zone: the Kingdom of Israel (Samaria) in the north, and the Kingdom of Judah in the south. The Kingdom of Israel was conquered by the Neo-Assyrian Empire, and the Kingdom of Judah by the Neo-Babylonian Empire. Initially exiled to Babylon, upon the defeat of the Neo-Babylonian Empire by the Achaemenid Empire under Cyrus the Great, many of the Jewish exiles returned to Jerusalem, building the Second Temple.
Biblical minimalism, also known as the Copenhagen School because two of its most prominent figures taught at Copenhagen University, is a movement or trend in biblical scholarship that began in the 1990s with two main claims:
- that the Bible cannot be considered reliable evidence for what had happened in ancient Israel; and
- that "Israel" itself is a problematic subject for historical study.
Niels Peter Lemche is a biblical scholar at the University of Copenhagen, whose interests include early Israel and its relationship with history, the Old Testament, and archaeology.

Avraham Biran was an Israeli archaeologist, best known for heading excavations at Tel Dan in northern Israel. He headed the Institute of Archaeology at Hebrew Union College in Jerusalem for many years.
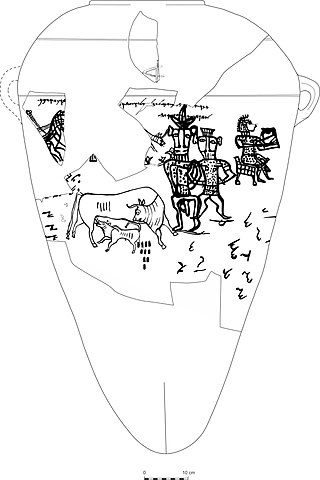
Yahwism, as it is called by modern scholars, was the religion of ancient Israel and Judah. An ancient Semitic religion of the Iron Age, Yahwism was essentially polytheistic and had a pantheon, with various gods and goddesses being worshipped by the Israelites. At the head of this pantheon was Yahweh, held in an especially high regard as the two Israelite kingdoms' national god. Some scholars hold that the goddess Asherah was worshipped as Yahweh's consort, though other scholars disagree. Following this duo were second-tier gods and goddesses, such as Baal, Shamash, Yarikh, Mot, and Astarte, each of whom had their own priests and prophets and numbered royalty among their devotees.
References
- ↑
- Blakely, Jeffrey A.; Horton, Fred L. (2001). "On Site Identifications Old and New: The Example of Tell el-Hesi". Near Eastern Archaeology . 64 (1/2): 32-33. doi:10.2307/3210818. JSTOR 3210818.
- ↑ "Proof of King David? Not yet. But riveting site shores up roots of Israelite era". Times of Israel. 14 May 2018. Retrieved 24 October 2019.