
Vojvodina, officially the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, is an autonomous province that occupies the northernmost part of Serbia, located in Central Europe. It lies within the Pannonian Basin, bordered to the south by the national capital Belgrade and the Sava and Danube Rivers. The administrative centre, Novi Sad, is the second-largest city in Serbia.

Bačka or Bácska is a geographical and historical area within the Pannonian Plain bordered by the river Danube to the west and south, and by the river Tisza to the east. It is divided between Serbia and Hungary. Most of the area is located within the Vojvodina region in Serbia and Novi Sad, the capital of Vojvodina, lies on the border between Bačka and Syrmia. The smaller northern part of the geographical area is located within Bács-Kiskun County in Hungary.

Vrbas is a town and municipality located in the South Bačka District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. As of 2022, the town has a population of 20,892, while the municipality has 36,601 inhabitants.

Beočin is a town and municipality located in the South Bačka District of the autonomous province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The population of the town is 7,839, whilst Beočin's municipality population is 15,726. There is also a Beočin Monastery from the 16th century in the municipality.

Tovariševo is a village in Serbia, in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 3,102 people.
Vojvodina is an autonomous province located in northern Serbia. It consists of the Pannonian Plain in the south, and the Danube and Sava rivers in the north.

The Serbs of Vojvodina are the largest ethnic group in this northern province of Serbia. For centuries, Vojvodina was ruled by several European powers, but Vojvodina Serbs never assimilated into cultures of those countries. Thus, they have consistently been a recognized indigenous ethnic minority with its own culture, language and religion. According to the 2022 census, there were 1,190,785 Serbs in Vojvodina or 68.43% of the population of the province.

Kisač is a suburban settlement of the city of Novi Sad, Serbia. The settlement has a Slovak ethnic majority.

Bački Jarak is a town located in the Temerin municipality, in the South Bačka District of Serbia. It is situated in the Autonomous Province of Vojvodina. The town has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 5,687 people.

Crvenka is a small town located in the municipality of Kula in the West Bačka District, Autonomous Province of Vojvodina, Serbia. The town has a Serbian ethnic majority, and it had a population of 9,001 in 2011.

Mošorin is a village located in the Titel municipality, South Bačka District, Vojvodina, Serbia. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 2,569 people.

Hungarians in Serbia are a recognized national minority in Serbia. According to the 2022 census, the population of ethnic Hungarians in Serbia is 184,442, constituting 2.8% of the total population, which makes them the second-largest ethnic group in the country behind Serbs and the largest minority group. The vast majority of them live in the northern autonomous province of Vojvodina, where they number 182,321 and make up 10.5% of the province's population. Almost 99% of all Hungarians in Serbia live in the province of Vojvodina. Most Hungarians in Serbia are Roman Catholics, while smaller numbers of them are Protestant. Their cultural center is located in Subotica.

The Banat was a political entity established in 1941 after the occupation and partition of Yugoslavia by the Axis Powers in the historical Banat region. It was formally under the control of the German puppet Government of National Salvation in Belgrade, which theoretically had limited jurisdiction over all of the Territory of the Military Commander in Serbia, but all power within the Banat was in the hands of the local minority of ethnic Germans (Volksdeutsche). The regional civilian commissioner and head of the ethnic German minority was Josef Lapp. Following the ousting of Axis forces in 1944, this German-ruled region was dissolved and most of its territory was included into Vojvodina, one of the two autonomous provinces of Serbia within the new SFR Yugoslavia.
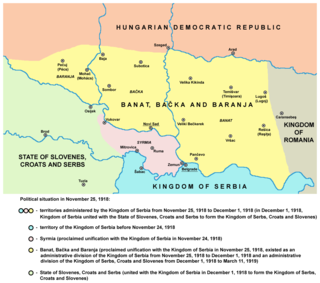
Banat, Bačka and Baranya was a province of the Kingdom of Serbia and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes between November 1918 and 1922. It included the geographical regions of Banat, Bačka, and Baranya and its administrative center was Novi Sad. They were later separated from the country to become SAP Vojvodina in 1945 with the creation of Federal Yugoslavia; smaller parts of Baranya were incorporated into Croatia or ceded to Kingdom of Hungary, while a portion of Banat was ceded to Kingdom of Romania.
The communist purges in Serbia in 1944–1945 are atrocities that were committed by members of the Yugoslav Partisan Movement and the post-war communist authorities after they gained control over Serbia, against people perceived as war criminals, quislings and ideological opponents. Most of these purges were committed between October 1944 and May 1945. During this time, at least 55,973 people died of various causes, including death by execution or by illness in retention camps. The victims – the vast majority of them deliberately summarily executed, without a trial – were of different ethnic backgrounds, but were mostly Germans, Serbs and Hungarians. Some contend that the killings were not planned, but were unorganised vendettas of individuals during the post-war chaos, or that those considered victims of execution instead died in battle against the Partisans.

Dobrinci is a village in Serbia. It is situated in the Ruma municipality, in the Srem District, Vojvodina province. The village has a Serb ethnic majority and its population numbering 1,716 people.
The Germans of Serbia are an ethnic minority of Serbia which numbers 4,064 people according to last population census from 2011. The Germans of Serbia usually refer to themselves as Swabian, and they are grouped into the Danube Swabians or Banat Swabians in the Vojvodina region, where the majority of the population resides. Germans settled parts of Serbia in the late 17th century during Habsburg administration. The German population of Vojvodina was more numerous in the past. More than 250,000 left during the withdrawal of Nazi forces. As a consequence of the World War II events in Yugoslavia, the Yugoslav Communist government took a reprisals on ethnic citizens of German origin in Yugoslavia : they had their citizenship revoked and their belongings and houses were nationalized and taken from them. Between 1944 and 1946, a prison camp system was established for Yugoslav citizens of German origin, usually in settlements where they lived. After prison camps were abolished, ethnic Germans of Yugoslavia regained their rights and citizenship and most of them emigrated to Germany or Austria in the following years because of economic reasons.

The Novi Sad raid also known as the Raid in southern Bačka, the Novi Sad massacre, the Újvidék massacre, was a massacre carried out by the Királyi Honvédség, the armed forces of Hungary, during World War II, after the Hungarian occupation and annexation of former Yugoslav territories. It resulted in the deaths of 3,000–4,000 civilians in the southern Bačka (Bácska) region.

During World War II, the Kingdom of Hungary engaged in the military occupation, then annexation, of the Bačka, Baranja, Međimurje and Prekmurje regions of the Kingdom of Yugoslavia. These territories had all been under Hungarian rule prior to 1920, and had been transferred to Yugoslavia as part of the post-World War I Treaty of Trianon. They now form part of several states: Yugoslav Bačka is now part of Vojvodina, an autonomous province of Serbia, Yugoslav Baranja and Međimurje are part of modern-day Croatia, and Yugoslav Prekmurje is part of modern-day Slovenia. The occupation began on 11 April 1941 when 80,000 Hungarian troops crossed the Yugoslav border in support of the German-led Axis invasion of Yugoslavia that had commenced five days earlier. There was some resistance to the Hungarian forces from Serb Chetnik irregulars, but the defences of the Royal Yugoslav Army had collapsed by this time. The Hungarian forces were indirectly aided by the local Volksdeutsche, the German minority, which had formed a militia and disarmed around 90,000 Yugoslav troops. Despite only sporadic resistance, Hungarian troops killed many civilians during these initial operations, including some Volksdeutsche. The government of the newly formed Axis puppet state, the Independent State of Croatia, subsequently consented to the Hungarian annexation of the Međimurje area, which dismayed the Croat population of the region.

The Socialist Autonomous Province of Vojvodina was one of two autonomous provinces within the Socialist Republic of Serbia, in the former Socialist Federal Republic of Yugoslavia. The province is the direct predecessor to the modern-day Serbian Autonomous Province of Vojvodina.
























