The T-62 is a Soviet main battle tank that was first introduced 1961. As a further development of the T-55 series, the T-62 retained many similar design elements of its predecessor including low profile and thick turret armor. In contrast with previous tanks, which were armed with rifled tank guns, the T-62 was the first tank armed with a smoothbore tank gun that could fire APFSDS rounds at higher velocities. While the T-62 became the standard tank in the Soviet arsenal, it did not fully replace the T-55 in export markets due to its higher manufacturing costs and maintenance requirements compared to its predecessor. Although the T-62 was replaced in Russia and the successor states of the Soviet Union, it is still used in some countries and its design features became standardized in subsequent Soviet and Russian mass-produced tanks.

The BMP-3 is a Soviet and Russian infantry fighting vehicle, successor to the BMP-1 and BMP-2. The abbreviation BMP stands for Boevaya Mashina Pehoty.

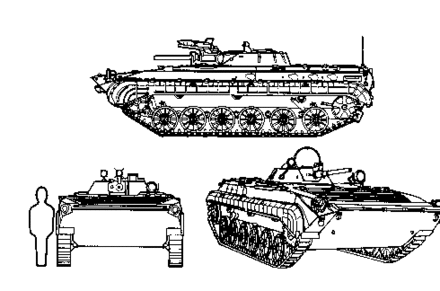
The BMP-2 is a second-generation, amphibious infantry fighting vehicle introduced in the 1980s in the Soviet Union, following on from the BMP-1 of the 1960s.

The MT-LB is a Soviet multi-purpose fully amphibious auxiliary armored tracked vehicle, which was first introduced in the 1950s. It is also produced in Poland, where its YaMZ engine replaced by Polish one.

The BMD-1 is a Soviet airborne amphibious tracked infantry fighting vehicle, which was introduced in 1969 and first seen by the West in 1970. BMD stands for Boyevaya Mashina Desanta. It can be dropped by parachute and although it resembles the BMP-1 it is in fact much smaller. The BMD-1 was used as an IFV by the Soviet Army's airborne divisions. An improved variant of the BMD-1 was developed, the BMD-2. The BMD-1 also provided a basis for the BTR-D airborne multi-purpose tracked APC.

The BMD-2 is a Soviet airborne infantry fighting vehicle, introduced in 1985. It is a variant of BMD-1 with a new turret and some changes done to the hull. BMD stands for Boyevaya Mashina Desanta. It was developed as a replacement of BMD-1 but it failed to replace it completely because of a downfall of Soviet economy in 1980s. NATO gave it the designation BMD M1981/1.

The Warrior tracked vehicle family is a series of British armoured vehicles, originally developed to replace the older FV430 series of armoured vehicles. The Warrior started life as the MCV-80, "Mechanised Combat Vehicle for the 1980s". One of the requirements of the new vehicle was a top speed able to keep up with the projected new MBT, the MBT-80 - later cancelled and replaced by what became the Challenger 1 - which the then-current FV432 could not. The project was begun in the 1970s. GKN Defence won the production contract in 1980. GKN Defence was purchased by BAE Systems, via Alvis plc.

The BTR-D is a Soviet airborne multi-purpose tracked armoured personnel carrier which was introduced in 1974 and first seen by the West in 1979 during the Soviet–Afghan War. BTR-D stands for Bronetransportyor Desanta. It is based on the BMD-1 airborne IFV. NATO gave it the designation BMD M1979.

The BMD-3 is an infantry fighting vehicle (IFV) originating from the former Soviet Union. This armored fighting vehicle is one of the lightest in its class and is intended to be a fire support platform for use by airborne and air assault units. The primary armament is a 30 mm 2A42 autocannon capable of firing different types of ammunition which include high-explosive and armor-piecing. The BMD-3 possesses multiple secondary weapons such as the 9M113 Konkurs missile and the AGS-17 grenade launcher to defeat a wide range of targets from enemy infantry to other armored fighting vehicles.

The BTR-T is a Russian heavy infantry combat vehicle, designed by the Design Bureau of Transport Machine-Building (Omsktransmash) state-run production association.

The BVP M-80, is a tracked Yugoslavian-made infantry fighting vehicle, produced from the 1980s until the country's collapse in the 1990s.

The MLI-84 is a tracked Romanian infantry fighting vehicle currently in service with the Romanian Land Forces. It was derived from the chassis of the Soviet BMP-1 but possessing a lengthened hull, a 12.7×108mm DShK 1938/46 heavy machine gun mounted on the roof of the troop compartment and MLI-84M having Oerlikon KBA autocannon and new ATGMs.
BWP-2000 is a prototype Polish IFV developed from early 1990s to 1999 but eventually canceled.

List of models and variants of the T-80 main battle tank.
The Soviet BMP-1 is a tracked, amphibious infantry fighting vehicle (IFV) with a long service history.

The BMP series of infantry fighting vehicles were among the first production line Infantry Fighting Vehicles. Included in the series are the mainline BMPs, the airborne variant BMDs, and licensed modified and reverse engineered versions. BMP stands for Boyevaya Mashina Pekhoty, meaning "infantry fighting vehicle"). They were initially developed in the 1960s in the Soviet Union.
The 2A42 Cobra is an overhead-mount modular one-man gun turret designed by the ZTS Dubnica nad Váhom design bureau. It is specially designed to fit many different types of tracked and wheeled IFVs and APCs such as the BMP-1, BMD-1, BTR-70, BTR-80 and the OT-64 SKOT.

The T-15 Armata, with industrial designation "Object 149", is a Russian heavy infantry fighting vehicle first seen in public in 2015 during rehearsals for the Moscow Victory Day Parade. The T-15 is expected to replace the BMP-2 and MT-LB based platforms of the Russian Ground Forces.

The ZBD-03 or Type 03 is a Chinese airborne infantry fighting vehicle. It features a light-weight chassis and hydropneumatic suspension for airborne operations. Early prototypes received the designation ZLC-2000.