
A Linux distribution is an operating system that includes the Linux kernel for its kernel functionality. Although the name does not imply product distribution per se, a distro, if distributed on its own, is often obtained via a website intended specifically for the purpose. Distros have been designed for a wide variety of systems ranging from personal computers to servers and from embedded devices to supercomputers.

Ubuntu is a Linux distribution derived from Debian and composed mostly of free and open-source software. Ubuntu is officially released in multiple editions: Desktop, Server, and Core for Internet of things devices and robots. The operating system is developed by the British company Canonical and a community of other developers, under a meritocratic governance model. As of October 2024, the latest interim release is 24.10, with most-recent long-term support release is 24.04.

A tablet computer, commonly shortened to tablet, is a mobile device, typically with a mobile operating system and touchscreen display processing circuitry, and a rechargeable battery in a single, thin and flat package. Tablets, being computers, have similar capabilities, but lack some input/output (I/O) abilities that others have. Modern tablets largely resemble modern smartphones, the only differences being that tablets are relatively larger than smartphones, with screens 7 inches (18 cm) or larger, measured diagonally, and may not support access to a cellular network. Unlike laptops, tablets usually run mobile operating systems, alongside smartphones.
A mobile operating system is an operating system used for smartphones, tablets, smartwatches, smartglasses, or other non-laptop personal mobile computing devices. While computers such as typical/mobile laptops are "mobile", the operating systems used on them are usually not considered mobile, as they were originally designed for desktop computers that historically did not have or need specific mobile features. This "fine line" distinguishing mobile and other forms has become blurred in recent years, due to the fact that newer devices have become smaller and more mobile, unlike the hardware of the past. Key notabilities blurring this line are the introduction of tablet computers, light laptops, and the hybridization of the two in 2-in-1 PCs.

ChromeOS, sometimes styled as chromeOS and formerly styled as Chrome OS, is a Linux distribution developed and designed by Google. It is derived from the open-source ChromiumOS operating system and uses the Google Chrome web browser as its principal user interface.

Joli OS was an Ubuntu-based Linux distribution created by Tariq Krim and Romain Huet co-founders of the French company Jolicloud. Joli OS is now an open source project, with source code hosted on GitHub.

Unity is a graphical shell for the GNOME desktop environment originally developed by Canonical Ltd. for its Ubuntu operating system. It debuted in 2010 in the netbook edition of Ubuntu 10.10 and was used until Ubuntu 17.10. Since 2017, its development was taken over by the Unity7 Maintainers (Unity7) and UBports.

A 2-in-1 laptop, also known as 2-in-1 PC, 2-in-1 tablet, laplet, tabtop, laptop tablet, or simply 2-in-1, is a portable computer that has features of both tablets and laptops.
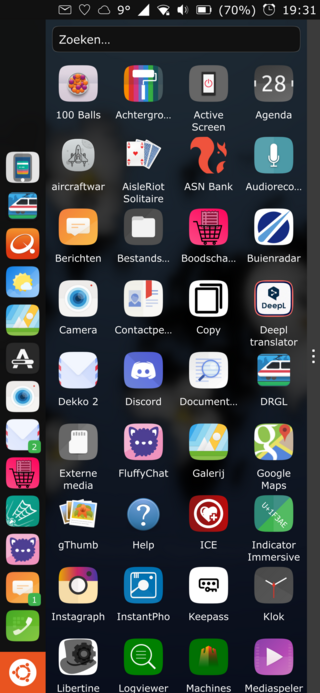
Ubuntu Touch is a mobile version of the Ubuntu operating system, developed by the UBports community. Its user interface is written in Qt, and is designed primarily for touchscreen mobile devices such as smartphones and tablet computers. However, the original goal of convergence was intended to bring Ubuntu Touch to laptops, desktops, IOT devices and TVs for a complete unified user experience.
Besides the Linux distributions designed for general-purpose use on desktops and servers, distributions may be specialized for different purposes including computer architecture support, embedded systems, stability, security, localization to a specific region or language, targeting of specific user groups, support for real-time applications, or commitment to a given desktop environment. Furthermore, some distributions deliberately include only free software. As of 2015, over four hundred Linux distributions are actively developed, with about a dozen distributions being most popular for general-purpose use.
Laptop–tablet convergence describes the tendency in recent years for laptops and tablet computers to converge technologically.
The following article is about Adobe Acrobat's version history.

The BQ Aquaris E4.5 is an Android smartphone from the Spanish manufacturer BQ that was released to market in June 2014 as a budget dual-SIM phone. The device shipped with Android versions starting from v4.0 and can be updated to Android 4.4.2 (KitKat). BQ elected not to skin the operating system and as such it retains the unmodified "Google Experience".
The Aquaris E5 and Aquaris E5 FHD are dual-SIM Android smartphones from the Spanish manufacturer BQ that were released to market in July 2014. The devices shipped with Android 4.4 (KitKat). BQ elected not to skin the operating system and as such it retains the unmodified "Google Experience", such as found on the Google Nexus.

The Meizu MX4 Ubuntu Edition is a smartphone designed and produced by the Chinese manufacturer Meizu, which runs on Ubuntu Touch. It is a previous phablet model of the MX series, representing an alternative edition of the MX4. It is Meizu's first commercially available Ubuntu Touch device and the second commercially available phone with Ubuntu Touch overall. It was unveiled at the Mobile World Congress in March 2015.
Ubuntu is a Debian-based Linux distribution for personal computers, tablets and smartphones, where the Ubuntu Touch edition is used; and also runs network servers, usually with the Ubuntu Server edition, either on physical or virtual servers or with containers, that is with enterprise-class features.

postmarketOS is an operating system primarily for smartphones, based on the Alpine Linux distribution.

BQ was a Spanish company brand of user electronics devices, such as smartphones, tablets, e-readers and 3D printers among other products.
Comparison of user features of operating systems refers to a comparison of the general user features of major operating systems in a narrative format. It does not encompass a full exhaustive comparison or description of all technical details of all operating systems. It is a comparison of basic roles and the most prominent features. It also includes the most important features of the operating system's origins, historical development, and role.












