The focal length of an optical system is a measure of how strongly the system converges or diverges light; it is the inverse of the system's optical power. A positive focal length indicates that a system converges light, while a negative focal length indicates that the system diverges light. A system with a shorter focal length bends the rays more sharply, bringing them to a focus in a shorter distance or diverging them more quickly. For the special case of a thin lens in air, a positive focal length is the distance over which initially collimated (parallel) rays are brought to a focus, or alternatively a negative focal length indicates how far in front of the lens a point source must be located to form a collimated beam. For more general optical systems, the focal length has no intuitive meaning; it is simply the inverse of the system's optical power.

Binoculars or field glasses are two refracting telescopes mounted side-by-side and aligned to point in the same direction, allowing the viewer to use both eyes when viewing distant objects. Most binoculars are sized to be held using both hands, although sizes vary widely from opera glasses to large pedestal-mounted military models.

The optical microscope, also referred to as a light microscope, is a type of microscope that commonly uses visible light and a system of lenses to generate magnified images of small objects. Optical microscopes are the oldest design of microscope and were possibly invented in their present compound form in the 17th century. Basic optical microscopes can be very simple, although many complex designs aim to improve resolution and sample contrast.

Forced perspective is a technique that employs optical illusion to make an object appear farther away, closer, larger or smaller than it actually is. It manipulates human visual perception through the use of scaled objects and the correlation between them and the vantage point of the spectator or camera. It has uses in photography, filmmaking and architecture.

A monocular is a compact refracting telescope used to magnify images of distant objects, typically using an optical prism to ensure an erect image, instead of using relay lenses like most telescopic sights. The volume and weight of a monocular are typically less than half of a pair of binoculars with similar optical properties, making it more portable and also less expensive. This is because binoculars are essentially a pair of monoculars packed together — one for each eye. As a result, monoculars only produce two-dimensional images, while binoculars can use two parallaxed images to produce binocular vision, which allows stereopsis and depth perception.

An optical telescope is a telescope that gathers and focuses light mainly from the visible part of the electromagnetic spectrum, to create a magnified image for direct visual inspection, to make a photograph, or to collect data through electronic image sensors.

Depth perception is the ability to perceive distance to objects in the world using the visual system and visual perception. It is a major factor in perceiving the world in three dimensions

In optical engineering, an objective is an optical element that gathers light from an object being observed and focuses the light rays from it to produce a real image of the object. Objectives can be a single lens or mirror, or combinations of several optical elements. They are used in microscopes, binoculars, telescopes, cameras, slide projectors, CD players and many other optical instruments. Objectives are also called object lenses, object glasses, or objective glasses.
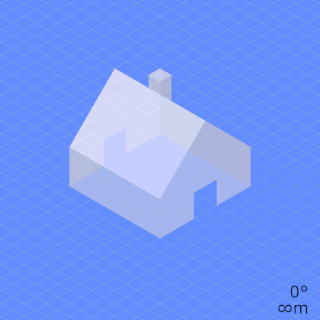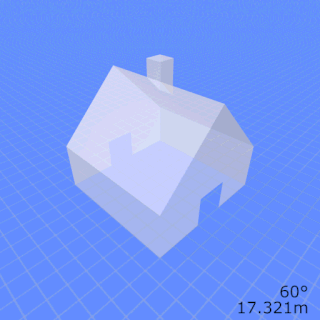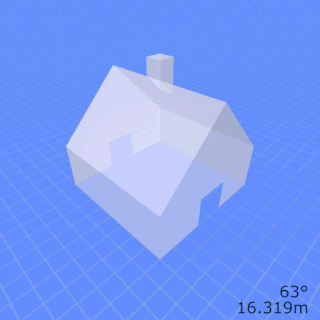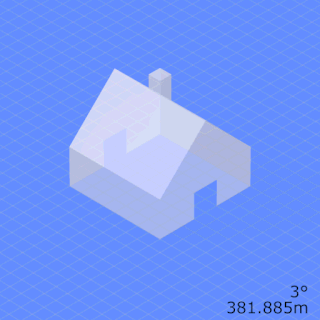
In photography and cinematography, perspective distortion is a warping or transformation of an object and its surrounding area that differs significantly from what the object would look like with a normal focal length, due to the relative scale of nearby and distant features. Perspective distortion is determined by the relative distances at which the image is captured and viewed, and is due to the angle of view of the image being either wider or narrower than the angle of view at which the image is viewed, hence the apparent relative distances differing from what is expected. Related to this concept is axial magnification – the perceived depth of objects at a given magnification.

Magnification is the process of enlarging the apparent size, not physical size, of something. This enlargement is quantified by a size ratio called optical magnification. When this number is less than one, it refers to a reduction in size, sometimes called de-magnification.

A magnifying glass is a convex lens that is used to produce a magnified image of an object. The lens is usually mounted in a frame with a handle. Beyond its primary function of magnification, this simple yet ingenious tool serves a variety of purposes. It can be employed to focus sunlight, harnessing the Sun's rays to create a concentrated hot spot at the lens's focus, which is often used for starting fires.

An eyepiece, or ocular lens, is a type of lens that is attached to a variety of optical devices such as telescopes and microscopes. It is named because it is usually the lens that is closest to the eye when someone looks through an optical device to observe an object or sample. The objective lens or mirror collects light from an object or sample and brings it to focus creating an image of the object. The eyepiece is placed near the focal point of the objective to magnify this image to the eyes. The amount of magnification depends on the focal length of the eyepiece.

A telescopic sight, commonly called a scope informally, is an optical sighting device based on a refracting telescope. It is equipped with some form of a referencing pattern – known as a reticle – mounted in a focally appropriate position in its optical system to provide an accurate point of aim. Telescopic sights are used with all types of systems that require magnification in addition to reliable visual aiming, as opposed to non-magnifying iron sights, reflector (reflex) sights, holographic sights or laser sights, and are most commonly found on long-barrel firearms, particularly rifles, usually via a scope mount. Similar devices are also found on other platforms such as artillery, tanks and even aircraft. The optical components may be combined with optoelectronics to add night vision or smart device features.

In optics, the exit pupil is a virtual aperture in an optical system. Only rays which pass through this virtual aperture can exit the system. The exit pupil is the image of the aperture stop in the optics that follow it. In a telescope or compound microscope, this image is the image of the objective element(s) as produced by the eyepiece. The size and shape of this disc is crucial to the instrument's performance, because the observer's eye can see light only if it passes through the aperture. The term exit pupil is also sometimes used to refer to the diameter of the virtual aperture. Older literature on optics sometimes refers to the exit pupil as the Ramsden disc, named after English instrument-maker Jesse Ramsden.
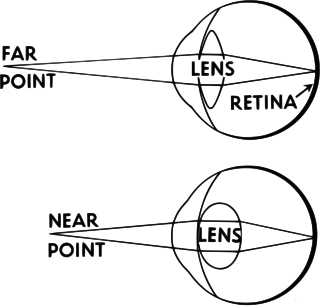
Accommodation is the process by which the vertebrate eye changes optical power to maintain a clear image or focus on an object as its distance varies. In this, distances vary for individuals from the far point—the maximum distance from the eye for which a clear image of an object can be seen, to the near point—the minimum distance for a clear image. Accommodation usually acts like a reflex, including part of the accommodation-convergence reflex, but it can also be consciously controlled.

A finderscope is an accessory sighting device used in astronomy and stargazing, typically a small auxiliary refracting telescope/monocular mounted parallelly on a larger astronomical telescope along the same line of sight. The finderscope usually has a much smaller magnification than the main telescope, thus providing a larger field of view, useful for manually pointing the main telescope into a roughly correct direction that can easily place a desired astronomical object in view when zooming in. Some finderscopes have sophisticated reticles to more accurately aim the main telescope and/or even perform stadiametric measurements.
Monocular vision is vision using only one eye. It is seen in two distinct categories: either a species moves its eyes independently, or a species typically uses two eyes for vision, but is unable to use one due to circumstances such as injury.

A loupe is a simple, small magnification device used to see small details more closely. They generally have higher magnification than a magnifying glass, and are designed to be held or worn close to the eye. A loupe does not have an attached handle, and its focusing lens(es) are contained in an opaque cylinder or cone. On some loupes this cylinder folds into an enclosing housing that protects the lenses when not in use.
In photography, a long-focus lens is a camera lens which has a focal length that is longer than the diagonal measure of the film or sensor that receives its image. It is used to make distant objects appear magnified with magnification increasing as longer focal length lenses are used. A long-focus lens is one of three basic photographic lens types classified by relative focal length, the other two being a normal lens and a wide-angle lens. As with other types of camera lenses, the focal length is usually expressed in a millimeter value written on the lens, for example: a 500 mm lens. The most common type of long-focus lens is the telephoto lens, which incorporate a special lens group known as a telephoto group to make the physical length of the lens shorter than the focal length.

The chameleon is among the most highly visually-oriented lizards, using this sense in prey capture, mating behavior, and predator avoidance. Unique features of chameleon vision include a negative lens, a positive cornea, and monocular focusing. The development of the chameleon visual system could have evolved to aid in prey capture and/or in predator avoidance.


















