Related Research Articles

Nagorno-Karabakh is a landlocked region in the South Caucasus, within the mountainous range of Karabakh, lying between Lower Karabakh and Syunik, and covering the southeastern range of the Lesser Caucasus mountains. The region is mostly mountainous and forested.

Caucasian Albania is a modern exonym for a former state located in ancient times in the Caucasus: mostly in what is now Azerbaijan. The modern endonyms for the area are Aghwank and Aluank, among the Udi people, who regard themselves as descended from the inhabitants of Caucasian Albania. However, its original endonym is unknown.
Azerbaijan is administratively divided into 66 districts and 7 cities that are subordinate to the Republic. Out of these, 7 districts and 1 city is located within the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic. The districts are further divided into municipalities.

The Aras is a river in the Caucasus. It rises in eastern Turkey and flows along the borders between Turkey and Armenia, between Turkey and the Nakhchivan exclave of Azerbaijan, between Iran and both Azerbaijan and Armenia, and, finally, through Azerbaijan where it is a tributary of the river Kura. It drains the south side of the Lesser Caucasus Mountains; after its confluence with the Kura, it drains the north side of the Lesser Caucasus Mountains. The river's total length is 1,072 kilometres (666 mi) and its watershed covers an area of 102,000 square kilometres (39,000 sq mi). The Aras is one of the longest rivers in the Caucasus.

Arran, also known as Aran, was a geographical name used in ancient and medieval times to signify an Iranian region which lay within the triangle of land, lowland in the east and mountainous in the west, formed by the junction of Kura and Aras rivers, including the highland and lowland Karabakh, Mil plain and parts of the Mughan plain, and in the pre-Islamic times, corresponded roughly to the territory of modern-day Republic of Azerbaijan. The term is the Middle Persian equivalent to the Greco-Roman Albania. It was known as Aghvania, Alvan-k in Armenian, and Al-ran in Arabic.

Bilasuvar District is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the south-east of the country and belongs to the Aran Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Imishli, Saatly, Sabirabad, Salyan, Neftchala, Jalilabad, and Ardabil Province of Iran. Its capital and largest city is Bilasuvar. As of 2020, the district had a population of 105,100.

Yardimli District is one of the 66 districts of Azerbaijan. It is located in the south-east of the country and belongs to the Lankaran Economic Region. The district borders the districts of Jalilabad, Masally, Lerik, and the Ardabil Province of Iran. Its capital and largest city is Yardimli. As of 2020, the district had a population of 68,000.
Iranian-Armenians, also known as Persian-Armenians, are Iranians of Armenian ethnicity who may speak Armenian as their first language. Estimates of their number in Iran range from 70,000 to 200,000. Areas with a high concentration of them include Tabriz, Tehran, Salmas and Isfahan's Jolfa quarter.

The Erivan Khanate, also known as Chokhur-e Sa'd, was a khanate that was established in Afsharid Iran in the 18th century. It covered an area of roughly 19,500 km2, and corresponded to most of present-day central Armenia, the Iğdır Province and the Kars Province's Kağızman district in present-day Turkey and the Sharur and Sadarak districts of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic of present-day Azerbaijan.

Paytakaran was the easternmost province of the Kingdom of Armenia. The province was located in the area of the lower courses of the rivers of Kura and Araks, adjacent to the Caspian sea. Today, the area is located in the territory of modern-day southeastern Azerbaijan and northwestern Iran.

Ordubad is the second largest town and a municipality of the Nakhchivan Autonomous Republic of Azerbaijan and is one of its three regions. It is the capital of the Ordubad District. Ordubad is a medieval city of the Caucasus and in its current capacity of a town was founded in the 18th century. The town is divided into five districts: Ambaras, Kurdtatal, Mingis, Sarshahar, and Uch.

Utik was a historic province of the Kingdom of Armenia and a region of Caucasian Albania after the splitting of Armenia in 387 AD by Sassanid Persia. Most of the region is located within present-day Azerbaijan immediately west of the Kura River while a part of it lies within the Tavush province of present-day northeastern Armenia.

Karabakh is a geographic region in present-day southwestern Azerbaijan and eastern Armenia, extending from the highlands of the Lesser Caucasus down to the lowlands between the rivers Kura and Aras.
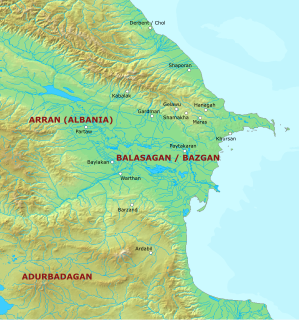
Balāsagān, also known as Bazgan, was a region located in the area of the Kura and Aras rivers, adjacent to the Caspian Sea. To the south, it bordered Atropatene/Adurbadagan and Gilan. It roughly corresponded to the Armenian province of Paytakaran, albeit extending farther into the north. It has been suggested that under the Sasanians the region extended as far as the stronghold of Derbent, albeit this remains disputed. The heartland of Balasagan was the Dasht i-Bałasakan which corresponds to the Mughan plain. During the late Sasanian era, Balasagan was included in the northern quadrant (kust) of Adurbadagan.

Chors is a village in Churs Rural District, in the Central District of Chaypareh County, West Azerbaijan Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its population was 2,367, in 636 families.

Tigranakert, also known as Tigranakert-Artsakh, is a ruined Armenian city dating back to the Hellenistic period, located in the Agdam District of what is today Azerbaijan.

Western Azerbaijan is an irredentist political concept that is used in the Republic of Azerbaijan mostly to refer to the territory of the Republic of Armenia. Azerbaijani statements claim that the territory of the modern Armenian republic were lands that once belonged to Azerbaijanis. Its claims are primarily hinged over the contention that the current Armenian territory was under the rule of various Turkic tribes, empires and khanates from the Late Middle Ages until the Treaty of Turkmenchay (1828) signed after the Russo-Persian War of 1826–1828. The concept has received official sanction by the government of Azerbaijan, and has been used by its current president, Ilham Aliyev, who, since around 2010, has made regular reference to "Irevan" (Yerevan), "Göyçə" and "Zangezur" (Syunik) as once and future "Azerbaijani lands". Also, after Aliyev was nominated in 2018 by the New Azerbaijan Party as presidential candidate, he called for "the return of Azerbaijanis" to these lands".

Bagavan was an ancient locality in the central part of Armenia in the principality of Bagrevand. The site is located in the village of Taşteker to the west of modern Diyadin, Turkey. Situated on a tributary of the Euphrates at the foothills of Mount Npat, to the north of Lake Van, Bagavan held one of the major temples of pre-Christian Armenia. After the Christianization of Armenia, Bagavan became the site of a large church and monastery. Pillaged in 1877 by the Kurds, it was completely destroyed after 1915 during the Armenian genocide.

Bagaran is a village in the Armavir Province of Armenia near the Armenia–Turkey border. Its name is derived from the nearby ancient Armenian city of Bagaran which was a large city and fortress that straddled both banks of the Akhurian River, and served as a former capital of medieval Armenia. A small Kurdish-populated village called Kılıttaşı now partially lies on the Turkish side of the closed border.

Bagaran was a city in Ancient Armenia founded during the reign of the Orontid Dynasty. It is one of the historical capitals of ancient Armenia.