Though the Ministry of Foreign Affairs (MOFA) is the government agency responsible for the conduct of foreign relations of Nepal, historically, it is the Office of Prime Minister (PMO) that has exercised the authority to formulate and conduct policies related to Nepal's foreign affairs. As a landlocked country wedged between two larger and far stronger powers, Nepal has tried to maintain good relations with both of its neighbors, People's Republic of China and Republic of India. Nepal's relationship with China, India, and the United States has remained utmost priority for successive Nepali governments. The relationship between Nepal and India however was significantly hampered during the 2015 Nepal blockade by pro-Indian anti-Nepal protestors, where the Government of Nepal accused India of using "Russia-Ukraine" tactics to cause unrest along Nepal's southern border using ethnically Indian residents of Nepal. India strictly denied the allegation and said the unrest were solely due to Madheshi protesters. For the most part though, Nepal has traditionally maintained a non-aligned policy and enjoys friendly relations with its neighboring countries and almost all the major countries of the world.
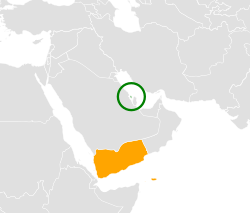
The foreign relations of Yemen are the relationships and policies that Yemen maintains with other countries. It is a member of the United Nations, the Arab League, and the Organisation of Islamic Cooperation. Yemen participates in the nonaligned movement. The Republic of Yemen accepted responsibility for all treaties and debts of its predecessors, the YAR and the PDRY. Additionally, Yemen has acceded to the Nuclear Non-Proliferation Treaty and has stressed the need to render the Middle East region free of nuclear and other weapons of mass destruction.

Brazil–Russia relations have seen a significant improvement in recent years, characterized by an increasing commercial trade and cooperation in military and technology segments. Today, Brazil shares an important alliance with Russia, with partnerships in areas such as space and military technologies as well as telecommunications.

Foreign relations between Argentina and Greece have existed for about half a century. Both countries are represented by an embassy in the other one's capital. At least 50,000 persons of Greek descent live in Argentina with about 5,000 with Greek passports. The majority of Greeks live in Buenos Aires.

Republic of the Congo–Russia relations refers to bilateral foreign relations between the Republic of the Congo and Russia. The Republic of the Congo has an embassy in Moscow. Russia has an embassy in Brazzaville.
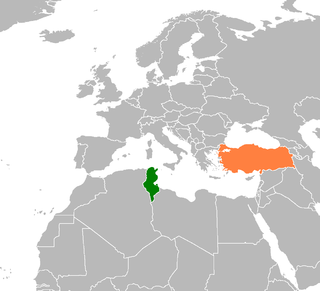
Tunisian–Turkish relations are foreign relations between Tunisia and Turkey. Tunisia has an embassy in Ankara and a consulate-general in Istanbul. Turkey has an embassy in Tunis. The diplomatic relations between Turkey and Tunisia were established in 1956 just after Tunisia gained its independence. Both countries are full members of the Union for the Mediterranean. The countries have had strong ethnic and cultural ties since the Ottoman colonization of Tunisia starting in the early 16th century. Due to several centuries of at least nominal Ottoman control of Tunisia, as much as 25% of Tunisians are at least partially of creole Turkish descent. Both countries signed The Treaty of Friendship and Cooperation on 15 September 2011. Turkey helped Tunisia after the Jasmine Revolution with financial and technical aid. Tunisia and Turkey have good economic ties. Many Tunisian merchants buy clothing (mostly) and other goods from Turkey. Also, Turkey is a very popular tourist destination for Tunisians. Citizens of both countries can travel visa-free between each other. Turkey and Tunisia are allies under the Major non-NATO ally agreement.

Croatia–India relations are the bilateral ties between Croatia and India. Diplomatic relations between two countries were officially established on 9 July 1992 following Croatia's independence from SFR Yugoslavia.

Extremely strong and cordial relations exist between Bahrain and Pakistan. Bahrain maintains an embassy in Islamabad and a Consulate-General in Karachi, whilst Pakistan maintains an embassy in Manama. Both countries are members of the OIC and of the G 77.

Bulgaria–India relations are the international relations that exist between the Republic of Bulgaria and the Republic of India.

The Foreign Ministry is the government body in the Sultanate of Oman responsible for organising and directing Oman's relations with other countries and with regional and international organisations.

Czech Republic–Philippines relations refer to foreign relations between the Czech Republic and the Philippines. The Czech Republic has an embassy in Manila and the Philippines has an embassy in Prague.
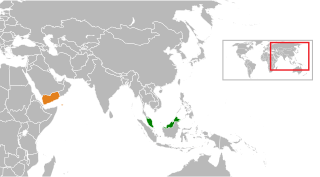
Malaysia–Yemen relations are foreign relations between Malaysia and Yemen. Malaysia formerly had an embassy in Sana'a, of which its operations had been relocated to Muscat, Oman and Yemen has an embassy in Kuala Lumpur.

Indonesia–Yemen relations are current and historical bilateral relations between Indonesia and Yemen. Indonesia and Yemen shared similarity as the Muslim majority countries, Indonesia is the most popular Muslim country in the world, while Yemen also a Muslim majority nation. Indonesia has an embassy in Sana'a, while Yemen has an embassy in Jakarta. Both the countries have many cultural proximities and similar view on international issues and these nations are members of the Non-Aligned Movement and Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (OIC).

Bangladesh–Yemen relations are the bilateral relations between Bangladesh and Yemen. In 2014 Mohammad Ashab Uddin was named Bangladeshi ambassador to Yemen.

Historic and current bilateral relationship exist between Bahrain and Japan. Diplomatic relations were first established in 1972, and since then they have had increasing economic, cultural, and military cooperation, with Japan becoming one of the major trading partners of Bahrain. Several high-level official visits have taken place, including by King Hamad bin Isa Al Khalifa to Japan in 2012, Crown Prince Salman in 2013, and Prime Minister Shinzo Abe to Bahrain in 2013, with the governments of both countries expressing their intent to continue to increase their bilateral relations.
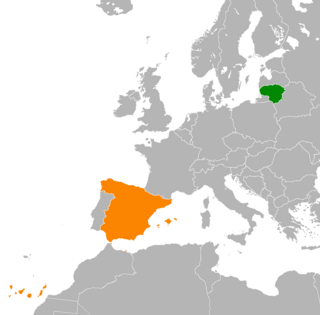
Lithuania–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Relationships are mainly defined by the membership of both countries to the European Union and to NATO. Lithuania has an embassy in Madrid and honorary consulates in La Coruña, Albacete, almería, Barcelona, Bilbao, santa Cruz de Tenerife, Valencia. Spain have an embassy in Vilnius since December 2013.

Bilateral and diplomatic relations exist between these two countries. Bahrain does not have an embassy in Spain, it relates its diplomatic activities in this country through its embassy in Paris. Spain also has no embassy in Bahrain, but its embassy in Kuwait is accredited to this country, Spain has an Honorary Consulate in Manama (Bahrain).

Spain–Yemen relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Yemen has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Sana'a.
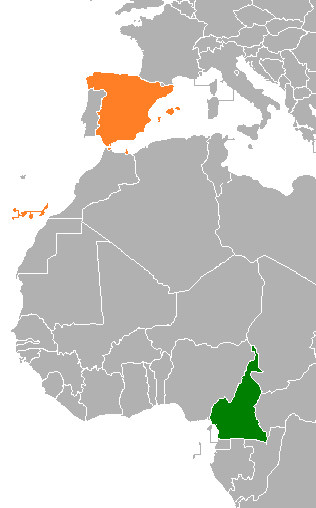
Cameroon–Spain relations are the bilateral and diplomatic relations between these two countries. Cameroon has an embassy in Madrid. Spain has an embassy in Yaoundé.
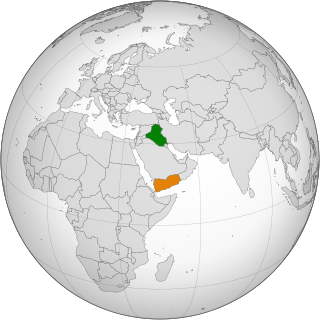
Diplomatic relations between the Republic of Yemen and the Republic of Iraq are old, religious and ethnic relations that began before the establishment of republics in the two countries.