Related Research Articles

Kanishka I, Kanishka or Kanishka the Great, was an emperor of the Kushan dynasty, under whose reign the empire reached its zenith. He is famous for his military, political, and spiritual achievements. A descendant of Kujula Kadphises, founder of the Kushan empire, Kanishka came to rule an empire extending from Central Asia and Gandhara to Pataliputra on the Gangetic plain. The main capital of his empire was located at Puruṣapura (Peshawar) in Gandhara, with another major capital at Mathura. Coins of Kanishka were found in Tripuri.
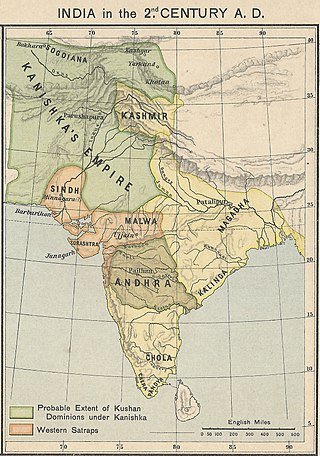
The Kushan Empire was a syncretic empire formed by the Yuezhi in the Bactrian territories in the early 1st century. It spread to encompass much of what is now Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Pakistan, and Northern India, at least as far as Saketa and Sarnath, near Varanasi, where inscriptions have been found dating to the era of the Kushan emperor Kanishka the Great.

The Gurjara-Pratihara was a dynasty that ruled much of Northern India from the mid-8th to the 11th century. They ruled first at Ujjain and later at Kannauj.

Rajuvula was an Indo-Scythian Great Satrap (Mahākṣatrapa), one of the "Northern Satraps" who ruled in the area of Mathura in the northern Indian Subcontinent in the years around 10 CE. The Mathura lion capital was consecrated under the reign of Rajuvula. In central India, the Indo-Scythians had conquered the area of Mathura from Indian kings around 60 BCE. Some of their satraps were Hagamasha and Hagana, who were in turn followed by Rajuvula.
The Aśvaka, also known as the Ashvakan, Aśvakayana, or Asvayana and sometimes Latinised as Assacenii, Assacani, or Aspasii or Aspii, were a people who lived in what is now northern Pakistan. The region in which they lived was also called Aśvaka. In the modern day, Asvaka is believed to have been preserved in the modern day Pashtun, with the term Afghan also being derived from Asvakan.
Nagabhata I was the founder of the imperial Gurjara Pratihara dynasty in northern India. He ruled the Avanti region in present-day Madhya Pradesh, from his capital at Ujjain. He may have extended his control over Gurjaradesa, which includes parts of present-day Gujarat and Rajasthan. He repulsed an Arab invasion from Sindh, probably led by Junayd ibn Abd al-Rahman al-Murri or Al Hakam ibn Awana.
Kharavela was a monarch of Kalinga in present-day Odisha, India, who ruled during the second or first century BCE. The primary source for Kharavela is his rock-cut Hathigumpha inscription. The inscription is undated, only four of its 17 lines are completely legible, others unclear, variously interpreted and disputed by scholars. The inscription written with Jainism-related phrases recites a year by year record of his reign and panegyrically credits him with public infrastructure projects, welfare activities, patronage of the arts, and many military victories. Historians agree that it is best and most complete biography of Kharavela available. He was a follower of Jainism.

Govind Chandra Pande was a well-known Indian scholar, philosopher and historian of the Vedic and the Buddhist periods. He served as professor of ancient history and vice-chancellor at Jaipur and Allahabad universities. He was also the chairman of the Indian Institute of Advanced Study, Simla for several years, the Chairman of Allahabad Museum Society and the Chairman of Central Tibetan Society, Sarnath Varanasi.
Duggal is a Punjabi Khatri surname.

The Traikutakas were a dynasty of Indian kings who ruled between 388 and 456. The name "Traikutakas" seems to be derived from the words for a three-peaked mountain ("Tri-kuta"). The Traikutakas are mentioned in Kalidasa's Raghuvamsa, in which they are located in the area of northern Konkan. The dominions of the Traikutakas further included Aparanta and northern Maharashtra.
Gurjar is an Indo-Aryan agricultural ethnic community, residing mainly in India, Pakistan and Afghanistan, divided internally into various clan groups. They were traditionally involved in agriculture, pastoral and nomadic activities and formed a large heterogeneous group. The historical role of Gurjars has been quite diverse in society: at one end they have been founders of several kingdoms and dynasties and, at the other end, some are still nomads with no land of their own.
The Khukhrain or Khokhrain is a clan composed of eight septs of the Khatri caste that originally hailed from the areas of the Salt Range.

Radha Kumud Mukherjee, also known as Radha Kumud Mukhopadhyaya, was an Indian historian and a noted Indian nationalist during the period of British colonial rule. He was the brother of the sociologist Radhakamal Mukerjee.
The origin of the Gurjara-Pratihara dynasty of India is a topic of debate among historians. The rulers of this dynasty used the self-designation "Pratihara" for their clan, but have been described as "Gurjara" by their neighbouring kingdoms. Only one particular inscription of a feudatory ruler named Mathanadeva mentions him as a "Gurjara-Pratihara".
Merutuṅga was a medieval scholar from present-day Gujarat in India and was a Śvētāmbara Jain monk of the Añcala Gaccha. He is presently most well-known for his Sanskrit text, the Prabandhacintāmaṇi, composed in 1306 CE. He also wrote Vicāraśreṇī in 1350 CE which describes the chronology of Chāvḍā, Chaulukya and Vāghelā dynasties.

The Bengal Sultanate–Kamata Kingdom War was a late 15th century conflict between the Kamata Kingdom and the Bengal Sultanate. As a result of the conflict the Khen dynasty was overthrown and the Bengal Sultanate extended its domain up to the Hajo in what is present day western Assam by 1502. Nevertheless, the Sultanate administration was removed in about ten years by the Assamese Bhuyans led by Harup Narayan.

Bhavani Narayanrao Krishnamurti Sharma, commonly known as B. N. K. Sharma or B. N. Krishnamurti Sharma, was an Indian writer, scholar, professor, and Indologist. Sharma was a professor and Head of the Department of Sanskrit in Ruparel College, Bombay from (1953–1969). Sharma was one of the foremost exponents of Madhvacharya's school of Dvaita Vedanta. B. N. K. Sharma learned the art of debates under Satyadhyana Tirtha of Uttaradi Math. Sharma travelled along with Satyadhyana Tirtha from, learned all philosophical knowledge from him and also used to rectify his doubts from Satyadhyana Tirtha.
Upanah (Sanskrit) is an ancient form of footwear from India. The term is used to refer to several types of strapped sandals and shoes employed by common people, in contrast to monks and mendicants who would use paduka instead. The word comes from the Sansakrit root nah, meaning "to tie", "to bind", to "fasten", as well as pad, meaning "foot". Combined words like charan-upanah might have originated modern words like "chappal".

Kumāralāta was an Indian founder of the Sautrāntika school of Buddhism. He was a native of Taxila, in modern day Pakistan.
References
- 1 2 Baij Nath Puri (1987). Buddhism In Central Asia. Motilal Banarsidass Publ. ISBN 8120803728.
- ↑ Baij Nath Puri Open Library
- ↑ Puri, Baij Nath WorldCat.
- Sarva Daman Singh (1996). Culture Through the Ages: Prof. B.N. Puri Felicitation Volume. Agam Kala Prakashan. ISBN 817320019X.