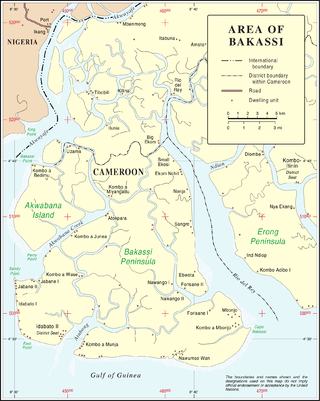
Bakassi is a peninsula on the Gulf of Guinea. It lies between the Cross River estuary, near the city of Calabar and the Rio del Ray estuary on the east. It is governed by Cameroon, following the transfer of sovereignty from neighbouring Nigeria as a result of a judgment by the International Court of Justice. On 22 November 2007, the Nigerian Senate rejected the transfer, since the Greentree Agreement ceding the area to Cameroon was contrary to Section 12(1) of the 1999 Constitution. Regardless, the territory was completely ceded to Cameroon on 14 August 2008, exactly two years after the first part of it was transferred.

Cameroon, officially the Republic of Cameroon, is a country in Central Africa. It shares boundaries with Nigeria to the west and north, Chad to the northeast, the Central African Republic to the east, and Equatorial Guinea, Gabon and the Republic of the Congo to the south. Its coastline lies on the Bight of Biafra, part of the Gulf of Guinea and the Atlantic Ocean. Due to its strategic position at the crossroads between West Africa and Central Africa, it has been categorized as being in both camps. Cameroon's population of nearly 31 million people speak 250 native languages, in addition to the national tongues of English and French, or both. Early inhabitants of the territory included the Sao civilisation around Lake Chad and the Baka hunter-gatherers in the southeastern rainforest. Portuguese explorers reached the coast in the 15th century and named the area Rio dos Camarões, which became Cameroon in English. Fulani soldiers founded the Adamawa Emirate in the north in the 19th century, and various ethnic groups of the west and northwest established powerful chiefdoms and fondoms.

Biafra, officially the Republic of Biafra, was a partially recognised state in West Africa that declared independence from Nigeria and existed from 1967 until 1970. Its territory consisted of the former Eastern Region of Nigeria, predominantly inhabited by the Igbo ethnic group. Biafra was established on 30 May 1967 by Igbo military officer and Eastern Region governor C. Odumegwu Ojukwu under his presidency, following a series of ethnic tensions and military coups after Nigerian independence in 1960 that culminated in the 1966 anti-Igbo pogrom. The Nigerian military proceeded in an attempt to reclaim the territory of Biafra, resulting in the start of the Nigerian Civil War. Biafra was officially recognised by Gabon, Haiti, Ivory Coast, Tanzania, and Zambia while receiving de facto recognition and covert military support from France, Portugal, Israel, South Africa and Rhodesia. After nearly three years of war, during which around two million Biafran civilians died, President Ojukwu fled into exile in Ivory Coast as the Nigerian military approached the capital of Biafra. Philip Effiong became the second president of Biafra, and he oversaw the surrender of Biafran forces to Nigeria.

Paul Biya is a Cameroonian politician who is the second president of Cameroon since 6 November 1982, having previously been the prime minister of Cameroon from 1975 to 1982. He is the second-longest-ruling president in Africa, the longest consecutively serving current non-royal national leader in the world and the oldest head of state in the world. He is regarded as an authoritarian leader and a dictator.
The Niger Delta is the delta of the Niger River sitting directly on the Gulf of Guinea on the Atlantic Ocean in Nigeria. It is located within nine coastal southern Nigerian states, which include: all six states from the South South geopolitical zone, one state (Ondo) from South West geopolitical zone and two states from South East geopolitical zone.

The Southern Cameroons was the southern part of the British League of Nations mandate territory of the British Cameroons in West Africa. Since 1961, it has been part of the Republic of Cameroon, where it makes up the Northwest Region and Southwest Region. Since 1994, pressure groups in the territory claim there was no legal document in accordance to UNGA RES 1608(XV) paragraph 5, and are seeking to restore statehood and independence from the Republic. They renamed the British Southern Cameroons as Ambazonia.

The Movement for the Emancipation of the Niger Delta (MEND) is a decentralised militant group in the Niger Delta region of Nigeria. MEND's actions – including sabotage, theft, property destruction, guerrilla warfare, and kidnapping – are part of the broader conflict in the Niger Delta and reduced Nigeria's oil production by 33% between 2006-07.

Piracy in the Gulf of Guinea affects a number of countries in West Africa as well as the wider international community. By 2011, it had become an issue of global concern. Pirates in the Gulf of Guinea are often part of heavily armed criminal enterprises, who employ violent methods to steal oil cargo. In 2012, the International Maritime Bureau (IMB), Oceans Beyond Piracy and the Maritime Piracy Humanitarian Response Program reported that the number of vessels attacks by West African pirates had reached a world high, with 966 seafarers attacked during the year. According to the Control Risks Group, pirate attacks in the Gulf of Guinea had by mid-November 2013 maintained a steady level of around 100 attempted hijackings in the year, a close second behind the Strait of Malacca in Southeast Asia.
This article is about the particular significance of the year 2006 to Nigeria and its people. See also Timeline of Nigerian history
Since 2006, militant groups in Nigeria's Niger Delta, especially the Movement for the Emancipation of the Niger Delta (MEND), have resorted to taking foreign employees of oil companies hostage as part of the conflict in the Niger Delta. More than 200 foreigners have been kidnapped since 2006, though most were released unharmed.
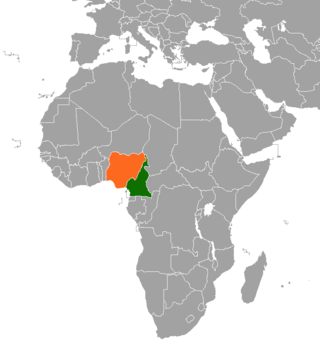
Relations between Cameroon and Nigeria were established in 1960, the same year that each country obtained its independence. Since then, their relationship has revolved in large part around their extensive shared border, as well as the legacy of colonial arrangements under which areas of Cameroon were administered as part of British Nigeria. The countries came close to war in the 1990s in the culmination of a long-running dispute over the sovereignty of the Bakassi peninsula. In the 21st century, however, a return to conviviality has been achieved, partly because the demarcation of their border has been formalised, and partly because the Boko Haram insurgency in the Lake Chad basin has necessitated increasingly close cooperation in regional security matters.
The following lists events that happened in 2013 in Nigeria.
Starting in late January 2015, a coalition of West African troops launched an offensive against the Boko Haram insurgents in Nigeria.
The 2016Niger Delta conflict is an ongoing conflict around the Niger Delta region of Nigeria in a bid for the secession of the region, which was a part of the breakaway state of Biafra. It follows on-and-off conflict in the Christian-dominated southern Niger Delta in the preceding years, as well as an insurgency in the Muslim-dominated northeast.

The Bakassi conflict is an ongoing armed dispute over the Bakassi Peninsula of Cameroon. Originally subject to a border conflict between Cameroon and Nigeria, Bakassi later became affected by insurgencies waged by local separatists against Cameroonian government forces.

The insurgency in Southeastern Nigeria is a military conflict that broke out in the city of Orlu, Imo State, Nigeria on 16 January 2021, when the Nigerian Army moved to crush the paramilitary wing of the Indigenous People of Biafra (IPOB), the Eastern Security Network (ESN). The conflict escalated after the ESN managed to repulse the initial push by the Nigerian Army, but IPOB ended the initial crisis by unilaterally withdrawing the ESN from Orlu. After a few weeks of quiet, Nigeria launched a military offensive in the area to destroy the ESN. On 19 February 2021, IPOB declared that as of the day before, a state of war existed between Nigeria and Biafra. Three weeks later, another separatist group declared the formation of a Biafran interim government which was subsequently endorsed by IPOB. Since then, the Biafran separatists have begun to form alliances with other separatist groups in Nigeria and Cameroon. Despite these developments, the separatists claimed that their militant operations were mainly aimed at defending local communities from armed herders and bandits instead of fighting the Nigerian government. In late June, IPOB leader Nnamdi Kanu was arrested by Interpol and handed over to Nigerian authorities.
As a practice of piracy, petro-piracy, also sometimes called oil piracy or petrol piracy, is defined as “illegal taking of oil after vessel hijacks, which are sometimes executed with the use of motorships” with huge potential financial rewards. Petro-piracy is mostly a practice that is connected to and originates from piracy in the Gulf of Guinea, but examples of petro-piracy outside of the Gulf of Guinea is not uncommon. At least since 2008, the Gulf of Guinea has been home to pirates practicing petro-piracy by targeting the region's extensive oil industry. Piracy in the Gulf of Guinea has risen in the last years to become the hot spot of piracy globally with 76 actual and attempted attacks, according to the International Maritime Bureau (IMB). Most of these attacks in the Gulf of Guinea take place in inland or territorial waters, but recently pirates have been proven to venture further out to sea, e.g. crew members were kidnapped from the tanker David B. 220 nautical miles outside of Benin. Pirates most often targets vessels carrying oil products and kidnappings of crew for ransom. IMB reports that countries in the Gulf of Guinea, Angola, Benin, Cameroon, Equatorial Guinea, Ghana, Guinea, Ivory Coast, Togo, Congo, and, especially, Nigeria, have experienced petro-piracy and kidnappings of crew as the most common trends of piracy attacks in the Gulf of Guinea.
Separatist movements of Nigeria want to achieve state secession, which is the withdrawal of one or more of the states of Nigeria from the multinational state of the Federal Republic of Nigeria. The only act of secession in Nigeria occurred from 1967 to 1970 during the Nigerian Civil War, when the breakaway republic of Biafra declared its independence from Nigeria and was eventually defeated. Ever since then, Nigeria has experienced the emergence of separatist movements seeking the independence of Biafra as well as other proposed states.

The Biafra Nations League, initially known as the Biafra Nations Youth League, is a secessionist group in Nigeria's eastern region with operational headquarters in the Bakassi Peninsula. The group was established in Port Harcourt, Rivers State on 3 August 2013.











