
Sedimentary rocks are types of rock that are formed by the deposition and subsequent cementation of mineral or organic particles on the floor of oceans or other bodies of water at the Earth's surface. Sedimentation is the collective name for processes that cause these particles to settle in place. The particles that form a sedimentary rock are called sediment, and may be composed of geological detritus (minerals) or biological detritus. Before being deposited, the geological detritus was formed by weathering and erosion from the source area, and then transported to the place of deposition by water, wind, ice, mass movement or glaciers, which are called agents of denudation. Biological detritus was formed by bodies and parts of dead aquatic organisms, as well as their fecal mass, suspended in water and slowly piling up on the floor of water bodies. Sedimentation may also occur as dissolved minerals precipitate from water solution.

Till or glacial till is unsorted glacial sediment.
Sedimentology encompasses the study of modern sediments such as sand, silt, and clay, and the processes that result in their formation, transport, deposition and diagenesis. Sedimentologists apply their understanding of modern processes to interpret geologic history through observations of sedimentary rocks and sedimentary structures.

The lithology of a rock unit is a description of its physical characteristics visible at outcrop, in hand or core samples, or with low magnification microscopy. Physical characteristics include colour, texture, grain size, and composition. Lithology may refer to either a detailed description of these characteristics, or a summary of the gross physical character of a rock. Lithology is the basis of subdividing rock sequences into individual lithostratigraphic units for the purposes of mapping and correlation between areas. In certain applications, such as site investigations, lithology is described using a standard terminology such as in the European geotechnical standard Eurocode 7.
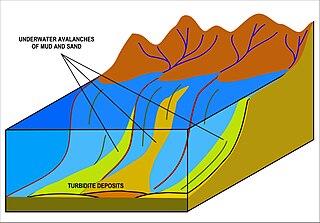
A turbidite is the geologic deposit of a turbidity current, which is a type of sediment gravity flow responsible for distributing vast amounts of clastic sediment into the deep ocean.

Flysch is a sequence of sedimentary rock layers that progress from deep-water and turbidity flow deposits to shallow-water shales and sandstones. It is deposited when a deep basin forms rapidly on the continental side of a mountain building episode. Examples are found near the North American Cordillera, the Alps, the Pyrenees and the Carpathians.

In geology, the term Torridonian is the informal name for the Torridonian Supergroup, a series of Mesoproterozoic to Neoproterozoic arenaceous and argillaceous sedimentary rocks, which occur extensively in the Northwest Highlands of Scotland. The strata of the Torridonian Supergroup are particularly well exposed in the district of upper Loch Torridon, a circumstance which suggested the name Torridon Sandstone, first applied to these rocks by James Nicol. Stratigraphically, they lie unconformably on gneisses of the Lewisian complex and their outcrop extent is restricted to the Hebridean Terrane.

In geology, cross-bedding is layering within a stratum and at an angle to the main bedding plane. The sedimentary structures which result are roughly horizontal units composed of inclined layers. The original depositional layering is tilted, such tilting not being the result of post-depositional deformation. Cross-beds or "sets" are the groups of inclined layers, which are known as cross strata.

A clastic dike is a seam of sedimentary material that fills an open fracture in and cuts across sedimentary rock strata or layering in other rock types. Clastic dikes form rapidly by fluidized injection or passively by water, wind, and gravity. Diagenesis may play a role in the formation of some dikes. Clastic dikes are commonly vertical or near-vertical. Centimeter-scale widths are common, but thicknesses range from millimetres to metres. Length is usually many times width.
Sedimentary structures include all kinds of features formed at the time of deposition. Sediments and sedimentary rocks are characterized by bedding, which occurs when layers of sediment, with different particle sizes are deposited on top of each other. These beds range from millimeters to centimeters thick and can even go to meters or multiple meters thick.

Mudcracks are sedimentary structures formed as muddy sediment dries and contracts. Crack formation also occurs in clay-bearing soils as a result of a reduction in water content.

In geology, lamination is a small-scale sequence of fine layers that occurs in sedimentary rocks. Laminae are normally smaller and less pronounced than bedding. Lamination is often regarded as planar structures one centimetre or less in thickness, whereas bedding layers are greater than one centimetre. However, structures from several millimetres to many centimetres have been described as laminae. A single sedimentary rock can have both laminae and beds.

Seismites are sedimentary beds and structures deformed by seismic shaking. The German paleontologist Adolf Seilacher first used the term in 1969 to describe earthquake-deformed layers. Today, the term is applied to both sedimentary layers and soft sediment deformation structures formed by shaking. This subtle change in usage accommodates structures that may not remain within a layer.

Load casts are bulges, lumps, and lobes that can form on the bedding planes that separate the layers of sedimentary rocks. The lumps "hang down" from the upper layer into the lower layer, and typically form with fairly equal spacing. These features form during soft-sediment deformation shortly after sediment burial, before the sediments lithify. They can be created when a denser layer of sediment is deposited on top of a less-dense sediment. This arrangement is gravitationally unstable, which encourages formation of a Rayleigh-Taylor instability if the sediment becomes liquefied. Once the sediments can flow, the instability creates the "hanging" lobes and knobs of the load casts as plumes of the denser sediment descend into the less-dense layer.

Vegetation-induced sedimentary structures (VISS) are primary sedimentary structures formed by the interaction of detrital sediment with in situ plants. VISS provide physical evidence of vegetation's fundamental role in mediating sediment accumulation and erosion in clastic depositional environments. VISS can be broken into seven types, five being hydrodynamic and two being decay-related. The simple hydrodynamic VISS are categorized by centroclinal cross strata, scratch semicircles and upturned beds. The complex hydrodynamic VISS are categorized by coalesced scour fills and scour-and-mound beds. The decay-related VISS are categorized by mudstone-filled hollows and downturned beds.

Soft-sediment deformation structures develop at deposition or shortly after, during the first stages of the sediment's consolidation. This is because the sediments need to be "liquid-like" or unsolidified for the deformation to occur. These formations have also been put into a category called water-escape structures by Lowe (1975). The most common places for soft-sediment deformations to materialize are in deep water basins with turbidity currents, rivers, deltas, and shallow-marine areas with storm impacted conditions. This is because these environments have high deposition rates, which allows the sediments to pack loosely.

Growth faults are syndepositional or syn-sedimentary extensional faults that initiate and evolve at the margins of continental plates. They extend parallel to passive margins that have high sediment supply. Their fault plane dips mostly toward the basin and has long-term continuous displacement. Figure one shows a growth fault with a concave upward fault plane that has high updip angle and flattened at its base into zone of detachment or décollement. This angle is continuously changing from nearly vertical in the updip area to nearly horizontal in the downdip area.
The Angola Basin is located along the West African South Atlantic Margin which extends from Cameroon to Angola. It is characterized as a passive margin that began spreading in the south and then continued upwards throughout the basin. This basin formed during the initial breakup of the supercontinent Pangaea during the early Cretaceous, creating the Atlantic Ocean and causing the formation of the Angola, Cape, and Argentine basins. It is often separated into two units: the Lower Congo Basin, which lies in the northern region and the Kwanza Basin which is in the southern part of the Angola margin. The Angola Basin is famous for its "Aptian Salt Basins," a thick layer of evaporites that has influenced topography of the basin since its deposition and acts as an important petroleum reservoir.
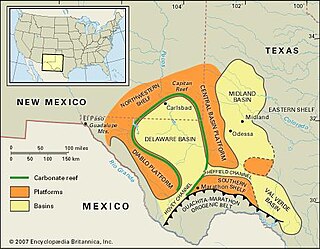
The Val Verde Basin is a marginal foreland basin located between West Texas and southeastern New Mexico, just southeast of the Midland Basin. The Val Verde is a sub-basin of the larger Permian Basin and is roughly 24–40 km wide by 240 km long. It is an unconventional system and its sediments were deposited during a long period of flooding during the Middle to Late Cretaceous. This flooding event is referred to as the Western Interior Seaway, and many basins in the Western United States can attribute their oil and gas producing basins to carbonate deposition during this time period.
The geology of South Korea includes rocks dating to the Archean and two large massifs of metamorphic rock as the crystalline basement, overlain by thick sedimentary sequences, younger metamorphic rocks and volcanic deposits.
























