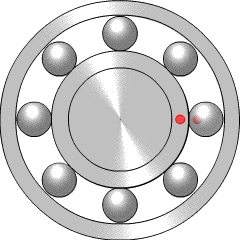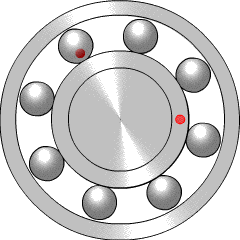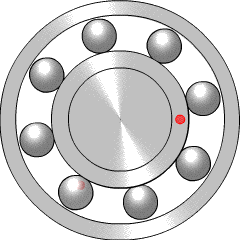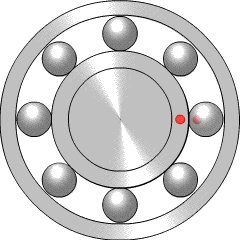
A ball bearing is a type of rolling-element bearing that uses balls to maintain the separation between the bearing races.
Fluid bearings are bearings in which the load is supported by a thin layer of rapidly moving pressurized liquid or gas between the bearing surfaces. Since there is no contact between the moving parts, there is no sliding friction, allowing fluid bearings to have lower friction, wear and vibration than many other types of bearings. Thus, it is possible for some fluid bearings to have near-zero wear if operated correctly.

A bearing is a machine element that constrains relative motion to only the desired motion and reduces friction between moving parts. The design of the bearing may, for example, provide for free linear movement of the moving part or for free rotation around a fixed axis; or, it may prevent a motion by controlling the vectors of normal forces that bear on the moving parts. Most bearings facilitate the desired motion by minimizing friction. Bearings are classified broadly according to the type of operation, the motions allowed, or the directions of the loads (forces) applied to the parts.

A caster is an undriven wheel that is designed to be attached to the bottom of a larger object to enable that object to be moved.

A variable-frequency drive is a type of AC motor drive that controls speed and torque by varying the frequency of the input electricity. Depending on its topology, it controls the associated voltage or current variation.

A sprag clutch is a one-way freewheel clutch. It resembles a roller bearing but, instead of cylindrical rollers, non-revolving asymmetric figure-eight shaped sprags, or other elements allowing single direction rotation, are used. When the unit rotates in one direction the rollers slip or free-wheel, but when a torque is applied in the opposite direction, the sprags tilt slightly, producing a wedging action and binding because of friction.

A bucket-wheel excavator (BWE) is a large heavy equipment machine used in surface mining.

Tapered roller bearings are rolling element bearings that can support axial forces as well as radial forces.

An automated guided vehicle (AGV), different from an autonomous mobile robot (AMR), is a portable robot that follows along marked long lines or wires on the floor, or uses radio waves, vision cameras, magnets, or lasers for navigation. They are most often used in industrial applications to transport heavy materials around a large industrial building, such as a factory or warehouse. Application of the automatic guided vehicle broadened during the late 20th century.

In an automobile, ball joints are spherical bearings that connect the control arms to the steering knuckles, and are used on virtually every automobile made. They bionically resemble the ball-and-socket joints found in most tetrapod animals.

Omni wheels or poly wheels, similar to Mecanum wheels, are wheels with small discs around the circumference which are perpendicular to the turning direction. The effect is that the wheel can be driven with full force, but will also slide laterally with great ease. These wheels are often employed in holonomic drive systems.
An idler-wheel is a wheel which serves only to transmit rotation from one shaft to another, in applications where it is undesirable to connect them directly. For example, connecting a motor to the platter of a phonograph, or the crankshaft-to-camshaft gear train of an automobile.
Automotive suspension design is an aspect of automotive engineering, concerned with designing the suspension for cars and trucks. Suspension design for other vehicles is similar, though the process may not be as well established.

Material handling equipment (MHE) is mechanical equipment used for the movement, storage, control, and protection of materials, goods and products throughout the process of manufacturing, distribution, consumption, and disposal. The different types of equipment can be classified into four major categories: transport equipment, positioning equipment, unit load formation equipment, and storage equipment.

A conveyor system is a common piece of mechanical handling equipment that moves materials from one location to another. Conveyors are especially useful in applications involving the transport of heavy or bulky materials. Conveyor systems allow quick and efficient transport for a wide variety of materials, which make them very popular in the material handling and packaging industries. They also have popular consumer applications, as they are often found in supermarkets and airports, constituting the final leg of item/ bag delivery to customers. Many kinds of conveying systems are available and are used according to the various needs of different industries. There are chain conveyors as well. Chain conveyors consist of enclosed tracks, I-Beam, towline, power & free, and hand pushed trolleys.

The rolling-elements of a rolling-element bearing ride on races. The large race that goes into a bore is called the outer race, and the small race that the shaft rides in is called the inner race.
Brinelling is the permanent indentation of a hard surface. It is named after the Brinell scale of hardness, in which a small ball is pushed against a hard surface at a preset level of force, and the depth and diameter of the mark indicates the Brinell hardness of the surface. Brinelling is permanent plastic deformation of a surface, and usually occurs while two surfaces in contact are stationary and the material yield strength has been exceeded.

A drum motor is a geared motor drive enclosed within a steel shell providing a single component driving pulley for conveyor belts.
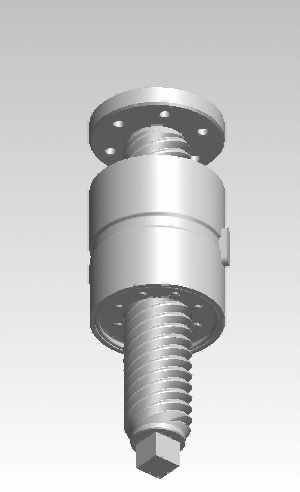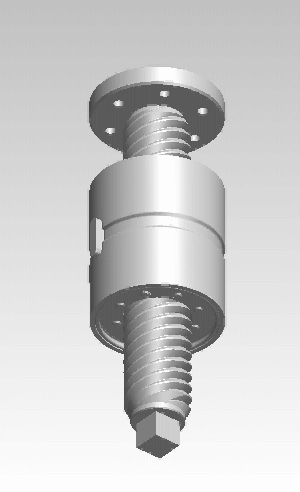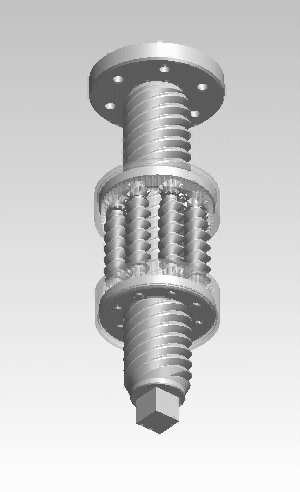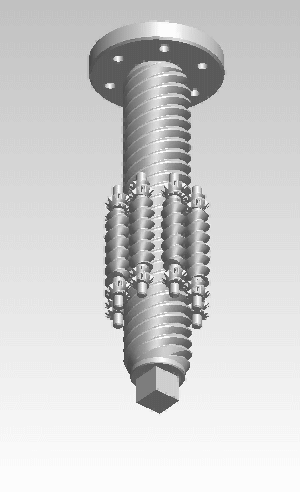
A roller screw, also known as a planetary roller screw or satellite roller screw, is a low-friction precision screw-type actuator, a mechanical device for converting rotational motion to linear motion, or vice versa. Planetary roller screws are used as the actuating mechanism in many electromechanical linear actuators. Due to its complexity, the roller screw is a relatively expensive actuator, but may be suitable for high-precision, high-speed, heavy-load, long-life, and heavy-use applications.

A scenery wagon, also known as a stage wagon, is a mobile platform that is used to support and transport movable, three-dimensional theatrical scenery on a theater stage. In most cases, the scenery is constructed on top of the wagon such that the wagon, and the scenery it supports, forms a single, integrated structure. Heavy duty casters are mounted to the underside of the platform so that the entire assembly can be quickly moved onstage or offstage, so as to facilitate rapid scenery changes during live productions. Scenery wagons are built in a wide range of sizes, ranging from less than one square foot up to the size of the playing area of the stage.

















