
A seamount is a mountain rising from the ocean seafloor that does not reach to the water's surface, and thus is not an island, islet or cliff-rock. Seamounts are typically formed from extinct volcanoes that rise abruptly and are usually found rising from the seafloor to 1,000–4,000 m (3,300–13,100 ft) in height. They are defined by oceanographers as independent features that rise to at least 1,000 m (3,281 ft) above the seafloor, characteristically of conical form. The peaks are often found hundreds to thousands of meters below the surface, and are therefore considered to be within the deep sea. During their evolution over geologic time, the largest seamounts may reach the sea surface where wave action erodes the summit to form a flat surface. After they have subsided and sunk below the sea surface such flat-top seamounts are called "guyots" or "tablemounts"

In geology, the places known as hotspots or hot spots are volcanic regions thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Their position on the Earth's surface is independent of tectonic plate boundaries. There are two hypotheses that attempt to explain their origins. One suggests that hotspots are due to mantle plumes that rise as thermal diapirs from the core–mantle boundary. The other hypothesis is that lithospheric extension permits the passive rising of melt from shallow depths. This hypothesis considers the term "hotspot" to be a misnomer, asserting that the mantle source beneath them is, in fact, not anomalously hot at all. Well-known examples include the Hawaii, Iceland and Yellowstone hotspots.

Sabrina Coast is that portion of the coast of Wilkes Land, Antarctica, lying between Cape Waldron, at 115° 33' E, and Cape Southard, at 122° 05' E. John Balleny has long been credited with having seen land in March 1839 at about 117° E.

Bransfield Strait is a body of water about 100 kilometres (60 mi) wide extending for 300 miles (500 km) in a general northeast – southwest direction between the South Shetland Islands and the Antarctic Peninsula.
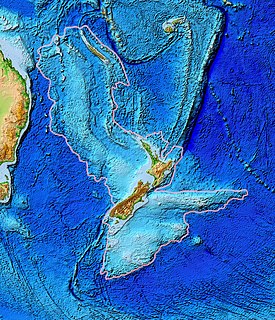
The Lord Howe Rise is a deep sea plateau which extends from south west of New Caledonia to the Challenger Plateau, west of New Zealand in the south west of the Pacific Ocean. To its west is the Tasman Basin and to the east is the New Caledonia Basin. Lord Howe Rise has a total area of about 1,500,000 square km, and generally lies about 750 to 1,200 metres under water. It is part of Zealandia, a much larger continent that is now mostly submerged, and so is composed of continental crust.
The South Tasman Rise is an area of seafloor that lies 550 km south of Hobart, Tasmania in the Southern Ocean where water depths are about 1,500 metres. The South Tasman Rise is also known as the Tasmania Ridge or South Tasmania Ridge.

The Balleny hotspot is a volcanic hotspot located in the Southern Ocean. The hotspot created the Balleny Islands, which forms a chain that extends for about 160 km (99 mi) in a northwest-southeast direction. Due to plate tectonics the hot spot was under different parts of the ocean bed in the past, and this has resulted in a chain of seamounts extending from the East Tasman Plateau. Isotopes and trace elements in the volcanic rocks indicated a high U/Pb mantle source. The same pattern is seen in basalt from Tasmania, but not from Victoria.

Detroit Seamount, which was formed around 76 million years ago, is one of the oldest seamounts of the Hawaiian-Emperor seamount chain. It lies near the northernmost end of the chain and is south of Aleutian Islands, at 51°28.80′N167°36′E It is a seamount in the chain, located north of the hinge of the "V" in the image at right.

Adare Seamounts, also known as Adare Mountains, are the seamounts in Balleny Basin named in association with Adare Peninsula and Cape Adare. Name approved by the Advisory Committee on Undersea Features, June 1988.

The Macquarie Triple Junction is a geologically active tectonic boundary located at 61°30′S161°0′E at which the Indo-Australian Plate, Pacific Plate, and Antarctic Plate collide and interact. The term Triple Junction is given to particular tectonic boundaries at which three separate tectonic plates meet at a specific, singular location. The Macquarie Triple Junction is located on the seafloor of the southern region of the Pacific Ocean, just south of New Zealand. This tectonic boundary was named in respect to the nearby Macquarie Island, which is located southeast of New Zealand.
The East Tasman Plateau is a submerged microcontinent south east of Tasmania. Its area is 50,000 square kilometres (19,000 sq mi), and it is mostly from 2,500 to 3,000 metres deep. It is a circular piece of continental rocks surrounded by oceanic crust. Volcanism occurred there 36 million years ago. The East Tasman Plateau is separated from the island of Tasmania by 100 kilometres (62 mi) of deeper water, and the East Tasman Saddle is a higher ridge connecting the plateau to the Freycinet Peninsula region of the Tasmanian East Coast. This ridge runs north west from the plateau. South-west of the plateau is the L'Atalante Depression.

Borradaile Island is one of the Balleny Islands. It was the site of the first landing south of the Antarctic Circle, and features the "remarkable pinnacle" called Beale Pinnacle, near Cape Beale on its south-eastern coast, and Cape Scoresby on its north-western coast.
De Gerlache Seamounts are seamounts in Antarctica, named for Lieutenant Adrien Victor Joseph de Gerlache, Commander of the Belgica during the first Belgian Antarctic Expedition, 1896–1899.

Vaughan Bank is a submarine bank in the Balleny Islands area. It was named for V. J. Vaughan, Commanding Officer, USS Glacier used in the U.S./New Zealand Balleny Island Expedition (1965). Name approved 4/80.

Foundation Seamounts are a series of seamounts in the southern Pacific Ocean. Discovered in 1992, these seamounts form a 1,350 kilometres (840 mi) long chain which starts from the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge. Some of these seamounts may have once emerged from the ocean.

Musicians Seamounts are a chain of seamounts in the Pacific Ocean, north of the Hawaiian Ridge. There are about 65 seamounts, some of which are named after musicians. These seamounts exist in two chains, one of which has been attributed to a probably now-extinct hotspot called the Euterpe hotspot. Others may have formed in response to plate tectonics associated with the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the former Farallon Plate.
Vesteris Seamount is a seamount in the North Atlantic Ocean between Greenland and Norway. It lies north of Jan Mayen and rises from 41–43 million years old ocean crust. The reasons for the volcanic activity at Vesteris are unclear and may involve lithospheric processes.

Pako Guyot is a guyot in the Pacific Ocean, which reaches a depth of 1,210 metres (3,970 ft). It has dimensions of 40 by 65 kilometres and features a summit plateau 2,056 square kilometres (794 sq mi) wide with a shape corresponding to an irregular rectangle-triangle. It is part of the Magellan Seamounts. The seamount was volcanically active 91.3 million years ago and may have formed on a hotspot together with Ioah Guyot and Vlinder Guyot; a late phase of volcanism may have taken place in the Paleocene-Eocene.
















