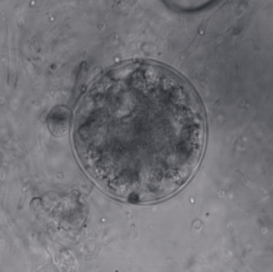
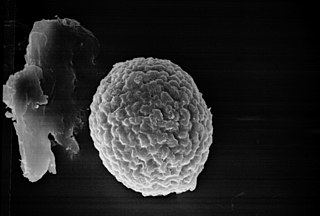
A ballistospore or ballistoconida is a spore that is discharged into the air from a living being, usually a species of fungus. With fungi, most types of basidiospores formed on basidia are discharged into the air from the tips of sterigmata. At least 30 thousand species of mushrooms, basidiomycete yeasts, and other fungal groups may discharge ballistospores, sometimes at initial accelerations exceeding 10 thousand times g. [1]

In biology, a spore is a unit of sexual or asexual reproduction that may be adapted for dispersal and for survival, often for extended periods of time, in unfavourable conditions. Spores form part of the life cycles of many plants, algae, fungi and protozoa. Bacterial spores are not part of a sexual cycle but are resistant structures used for survival under unfavourable conditions. Myxozoan spores release amoebulae into their hosts for parasitic infection, but also reproduce within the hosts through the pairing of two nuclei within the plasmodium, which develops from the amoebula.

A fungus is any member of the group of eukaryotic organisms that includes microorganisms such as yeasts and molds, as well as the more familiar mushrooms. These organisms are classified as a kingdom, fungi, which is separate from the other eukaryotic life kingdoms of plants and animals.

A basidiospore is a reproductive spore produced by Basidiomycete fungi, a grouping that includes mushrooms, shelf fungi, rusts, and smuts. Basidiospores typically each contain one haploid nucleus that is the product of meiosis, and they are produced by specialized fungal cells called basidia. Typically, four basidiospores develop on appendages from each basidium, out of these 2 are of one strain and other 2 of its opposite strain. In gills under a cap of one common species, there exist millions of basidia. Some gilled mushrooms in the order Agaricales have the ability to release billions of spores. The puffball fungus Calvatia gigantea has been calculated to produce about five trillion basidiospores. Most basidiospores are forcibly discharged, and are thus considered ballistospores. These spores serve as the main air dispersal units for the fungi. The spores are released during periods of high humidity and generally have a night-time or pre-dawn peak concentration in the atmosphere.