
A loom is a device used to weave cloth and tapestry. The basic purpose of any loom is to hold the warp threads under tension to facilitate the interweaving of the weft threads. The precise shape of the loom and its mechanics may vary, but the basic function is the same.
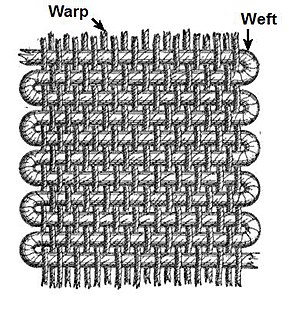
Weaving is a method of textile production in which two distinct sets of yarns or threads are interlaced at right angles to form a fabric or cloth. Other methods are knitting, crocheting, felting, and braiding or plaiting. The longitudinal threads are called the warp and the lateral threads are the weft, woof, or filling. The method in which these threads are interwoven affects the characteristics of the cloth. Cloth is usually woven on a loom, a device that holds the warp threads in place while filling threads are woven through them. A fabric band that meets this definition of cloth can also be made using other methods, including tablet weaving, back strap loom, or other techniques that can be done without looms.

A satin weave is a type of fabric weave that produces a characteristically glossy, smooth or lustrous material, typically with a glossy top surface and a dull back. It is one of three fundamental types of textile weaves alongside plain weave and twill weave.
Ikat is a dyeing technique originating from Indonesia used to pattern textiles that employs resist dyeing on the yarns prior to dyeing and weaving the fabric.

A Persian carpet or Persian rug, also known as Iranian carpet, is a heavy textile made for a wide variety of utilitarian and symbolic purposes and produced in Iran, for home use, local sale, and export. Carpet weaving is an essential part of Persian culture and Iranian art. Within the group of Oriental rugs produced by the countries of the "rug belt", the Persian carpet stands out by the variety and elaborateness of its manifold designs.

A kilim is a flat tapestry-woven carpet or rug traditionally produced in countries of the former Persian Empire, including Iran, the Balkans and the Turkic countries. Kilims can be purely decorative or can function as prayer rugs. Modern kilims are popular floor coverings in Western households.

Jamdani is a fine muslin textile produced for centuries in South Rupshi of Narayanganj district in Bangladesh on the bank of Shitalakhwa river. The historic production of jamdani was patronized by imperial warrants of the Mughal emperors. Under British colonialism, the Bengali jamdani and muslin industries rapidly declined due to colonial import policies favoring industrially manufactured textiles. In more recent years, the production of jamdani has witnessed a revival in Bangladesh. Jamdani is typically woven using a mixture of cotton and gold thread.

Pile weave is a form of textile created by weaving. This type of fabric is characterized by a pile—a looped or tufted surface that extends above the initial foundation, or 'ground' weave. The pile is formed by supplemental yarn running in the direction of the length of the fabric or the width of the fabric. Pile weaves include velvet and corduroy fabrics and machine-woven Berber carpets.

Songket is a Tenun fabric that belongs to the brocade family of textiles of the Malay world. It is hand-woven in silk or cotton, and intricately patterned with gold or silver threads. The metallic threads stand out against the background cloth to create a shimmering effect. In the weaving process the metallic threads are inserted in between the silk or cotton weft (latitudinal) threads in a technique called supplementary weft weaving technique.

Cloth of gold or gold cloth is a fabric woven with a gold-wrapped or spun weft—referred to as "a spirally spun gold strip". In most cases, the core yarn is silk wrapped (filé) with a band or strip of high content gold. In rarer instances, fine linen and wool have been used as the core.

A selvage or selvedge is a "self-finished" edge of a piece of fabric which keeps it from unraveling and fraying. The term "self-finished" means that the edge does not require additional finishing work, such as hem or bias tape, to prevent fraying.

Silk in the Indian subcontinent is a luxury good. In India, about 97% of the raw mulberry silk is produced in the Indian states of Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and West Bengal. Mysore and North Bangalore, the upcoming site of a US$20 million "Silk City", contribute to a majority of silk production. Another emerging silk producer is Tamil Nadu where mulberry cultivation is concentrated in Salem, Erode and Dharmapuri districts. Hyderabad, Andhra Pradesh and Gobichettipalayam, Tamil Nadu were the first locations to have automated silk reeling units.
The manufacture of textiles is one of the oldest of human technologies. To make textiles, the first requirement is a source of fiber from which a yarn can be made, primarily by spinning. The yarn is processed by knitting or weaving, which turns yarn into cloth. The machine used for weaving is the loom. For decoration, the process of colouring yarn or the finished material is dyeing. For more information of the various steps, see textile manufacturing.

A bamboo wife is a bolster (pillow) made from a woven bamboo cylinder that may be as large as the size of the human body. It goes by names such as, also known as a Dutch wife, in Tagalog as kawil ; in Burmese as ဖက်လုံး and in Indonesian as guling.

A knotted-pile carpet is a carpet containing raised surfaces, or piles, from the cut off ends of knots woven between the warp and weft. The Ghiordes/Turkish knot and the Senneh/Persian knot, typical of Anatolian carpets and Persian carpets, are the two primary knots. A flat or tapestry woven carpet, without pile, is a kilim. A pile carpet is influenced by width and number of warp and weft, pile height, knots used, and knot density.

Pile is the raised surface or nap of a fabric, consisting of upright loops or strands of yarn. Examples of pile textiles are carpets, corduroy, velvet, plush, and Turkish towels. The word is derived from Latin pilus for "hair".

Soumak is a tapestry technique of weaving sturdy, decorative fabrics used for rugs, domestic bags and bedding, with soumak fabrics used for bedding known as soumak mafrash.
Venkatagiri Sari is a sari style woven in Venkatagiri of Nellore district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It was registered as one of the geographical indication from Andhra Pradesh by Geographical Indications of Goods Act, 1999. Venkatagiri saris are known for their fine weaving. These style of saris can also be found in the villages of Sengunthapuram, Variyankaval, Elaiyur, Kallathur, Andimadam and Marudhur villages.
Bamboo weaving is a form of bambooworking and a traditional craft of Taiwan.

Supplementary weaving is a decorative technique in which additional threads are woven into a textile to create an ornamental pattern in addition to the ground pattern. The supplementary weave can be of the warp or of the weft. Supplementary weave is commonly used in many of thetextiles of Southeast Asia such as in Balinese textiles, the textiles of Sumba and the songket of Sumatra, Malaysia and Brunei.















