Related Research Articles

Indonesia is an archipelagic country located in Southeast Asia and Oceania, lying between the Indian Ocean and the Pacific Ocean. It is located in a strategic location astride or along major sea lanes connecting East Asia, South Asia and Oceania. Indonesia is the largest archipelago in the world. Indonesia's various regional cultures have been shaped—although not specifically determined—by centuries of complex interactions with its physical environment.

The Eurasian plate is a tectonic plate that includes most of the continent of Eurasia, with the notable exceptions of the Indian subcontinent, the Arabian subcontinent and the area east of the Chersky Range in eastern Siberia. It also includes oceanic crust extending westward to the Mid-Atlantic Ridge and northward to the Gakkel Ridge.
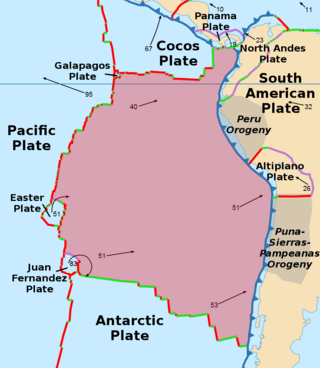
The Nazca plate or Nasca plate, named after the Nazca region of southern Peru, is an oceanic tectonic plate in the eastern Pacific Ocean basin off the west coast of South America. The ongoing subduction, along the Peru–Chile Trench, of the Nazca plate under the South American plate is largely responsible for the Andean orogeny. The Nazca plate is bounded on the west by the Pacific plate and to the south by the Antarctic plate through the East Pacific Rise and the Chile Rise, respectively. The movement of the Nazca plate over several hotspots has created some volcanic islands as well as east–west running seamount chains that subduct under South America. Nazca is a relatively young plate in terms of the age of its rocks and its existence as an independent plate, having been formed from the breakup of the Farallon plate about 23 million years ago. The oldest rocks of the plate are about 50 million years old.
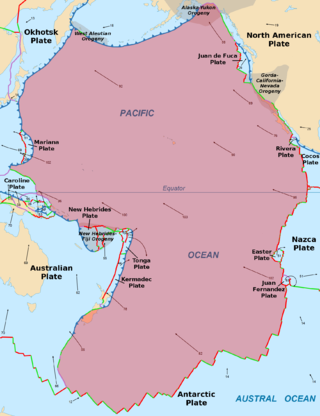
The Pacific plate is an oceanic tectonic plate that lies beneath the Pacific Ocean. At 103 million km2 (40 million sq mi), it is the largest tectonic plate.

The Banda Sea is one of four seas that surround the Maluku Islands of Indonesia, connected to the Pacific Ocean, but surrounded by hundreds of islands, including Timor, as well as the Halmahera and Ceram Seas. It is about 1000 km (600 mi) east to west, and about 500 km (300 mi) north to south.

The Australian plate is a major tectonic plate in the eastern and, largely, southern hemispheres. Originally a part of the ancient continent of Gondwana, Australia remained connected to India and Antarctica until approximately 100 million years ago when India broke away and began moving north. Australia and Antarctica had begun rifting by 96 million years ago and completely separated a while after this, some believing as recently as 45 million years ago, but most accepting presently that this had occurred by 60 million years ago.

A triple junction is the point where the boundaries of three tectonic plates meet. At the triple junction each of the three boundaries will be one of three types – a ridge (R), trench (T) or transform fault (F) – and triple junctions can be described according to the types of plate margin that meet at them. Of the ten possible types of triple junctions only a few are stable through time. The meeting of four or more plates is also theoretically possible, but junctions will only exist instantaneously.

The Sunda plate is a minor tectonic plate straddling the equator in the Eastern Hemisphere on which the majority of Southeast Asia is located.

The Phoenix plate was a tectonic plate that existed during the early Paleozoic through late Cenozoic time. It formed a triple junction with the Izanagi and Farallon plates in the Panthalassa Ocean as early as 410 million years ago, during which time the Phoenix plate was subducting under eastern Gondwana.
The 1938 Banda Sea earthquake occurred on February 2 at 04:04 local time with an estimated magnitude of 8.5-8.6 on the moment magnitude scale. Shaking was intense with an assigned Rossi–Forel intensity of VII and intensity of VI (Strong) on the Modified Mercalli intensity scale. This oblique-slip event generated a destructive tsunami of up to 1.5 metres in the Banda Sea region, but there were no deaths.

The Azores triple junction (ATJ) is a geologic triple junction where the boundaries of three tectonic plates intersect: the North American plate, the Eurasian plate and the African plate. This triple junction is located along the Mid-Atlantic Ridge (MAR) amidst the Azores islands, nearly due west of the Strait of Gibraltar. It is classified as an R-R-R triple junction of the T type, as it is an intersection of the Mid-Atlantic Ridge running north–south and the Terceira Rift which runs east-southeast.

The Macquarie triple junction is a geologically active tectonic boundary located at 61°30′S161°0′E at which the historic Indo-Australian Plate, Pacific Plate, and Antarctic Plate collide and interact. The term triple junction is given to particular tectonic boundaries at which three separate tectonic plates meet at a specific, singular location. The Macquarie triple junction is located on the seafloor of the southern region of the Pacific Ocean, just south of New Zealand. This tectonic boundary was named in respect to the nearby Macquarie Island, which is located southeast of New Zealand.

The Galápagos triple junction (GTJ) is a geological area in the eastern Pacific Ocean several hundred miles west of the Galápagos Islands where three tectonic plates – the Cocos plate, the Nazca plate, and the Pacific plate – meet. It is an unusual type of triple junction in which the three plates do not meet at a simple intersection. Instead, the junction includes two small microplates, the Galápagos microplate and the northern Galápagos microplate, caught in the junction, turning synchronously with respect to each other and separated by the Hess Deep rift.

The Banda Sea plate is a minor tectonic plate underlying the Banda Sea in southeast Asia. This plate also carries a portion of Sulawesi Island, the entire Seram Island, and the Banda Islands. Clockwise from the east it is bounded by the Bird's Head plate of western New Guinea, Australian plate, Timor plate, Sunda plate, and the Molucca Sea Collision Zone. The western border is a convergent boundary largely responsible for the mountains in western Sulawesi, subduction zones also exist on the eastern border near Seram and the southern border with the Timor plate. A small rift is located in the middle of Sulawesi. It is a very seismically active area home to many volcanoes and the site of many large earthquakes, the largest of which was the 1938 Banda Sea earthquake which measured around 8.4 on the moment magnitude scale.

The Juan Fernandez plate is a small tectonic plate (microplate) in the Pacific Ocean. With a surface area of approximately 105 km2, the microplate is located between 32° and 35°S and 109° and 112°W. The plate is located at a triple junction between the Antarctic plate, the Nazca plate, and the Pacific plate. Approximately 2,000 km to the west of South America, it is, on average, 3,000 meters deep with its shallowest point coming to approximately 1,600 meters, and its deepest point reaching 4,400 meters.

Located in the western Pacific Ocean near Indonesia, the Molucca Sea plate has been classified by scientists as a fully subducted microplate that is part of the Molucca Sea Collision Complex. The Molucca Sea plate represents the only known example of divergent double subduction (DDS), which describes the subduction on both sides of a single oceanic plate.
This is a list of articles related to plate tectonics and tectonic plates.

The Boso triple junction is a triple junction off the coast of Japan; it is one of two known examples of a trench-trench-trench triple junction on the Earth. It is the meeting point of the North American plate to the north, the Pacific plate to the east and the Philippine Sea plate to the south.

The Banda Arc is a dual chain of islands in eastern Indonesia that is around 2,300 km long. It is the result of the collision of a continent and an intra-oceanic island arc.
References
- Hinschberger, F; Malod, J.-A; Dyment, J; Honthaas, C; Réhault, J.-P; Burhanuddin, S (2001), "Magnetic lineations constraints for the back-arc opening of the Late Neogene South Banda Basin (eastern Indonesia)", Tectonophysics, 333 (1–2): 47–59, Bibcode:2001Tectp.333...47H, doi:10.1016/S0040-1951(00)00266-3
- Tectonics of Indonesia – University of North Dakota