
Cotabato or North Cotabato, officially the Province of Cotabato, is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the Soccsksargen region in Mindanao. Its capital is the city of Kidapawan. Some of its barangays are under the jurisdiction of the nearby Bangsamoro Autonomous Region.

The Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao was an autonomous region of the Philippines, located in the Mindanao island group of the Philippines, that consisted of five predominantly Muslim provinces: Basilan, Lanao del Sur, Maguindanao, Sulu, and Tawi-Tawi. It was the only region that had its own government. The region's de facto seat of government was Cotabato City, although this self-governing city was outside its jurisdiction.

The Moro people or Bangsamoro people are the 13 Muslim-majority ethnolinguistic Austronesian groups of Mindanao, Sulu, and Palawan, native to the region known as the Bangsamoro. As Muslim-majority ethnic groups, they form the largest non-Christian population in the Philippines, and comprise about 5% of the country's total population, or 5 million people.

Cotabato Airport ; also known as Awang Airport, is an airport serving the general area of Cotabato City, North Cotabato, Maguindanao del Norte, and Maguindanao del Sur. Located in the province of Maguindanao del Norte in the Philippines. It is classified as a Class 1 principal airport by the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines, a body of the Department of Transportation that is responsible for the operations of all airports in the Philippines except the major international airports.

Sanga-Sanga Airport, also known as Tawi-Tawi Airport, is an airport serving the general area of Bongao, the capital of the province of Tawi-Tawi in the Philippines. The airport is classified as a Class 2 principal airport by the Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines (CAAP), a body of the Department of Transportation (DOTr) that is responsible for the operations of not only the airport but also of all other airports in the Philippines except the major international airports. It is not an international airport, contrary to its classification by the Tawi-Tawi provincial government. It is located in Sanga-Sanga Island. The airport was formerly referred by the IATA with the code SGS until the end of 2011, when its IATA code was finally changed to TWT.
Cagayan de Sulu Airport is an airport serving the island municipality of Mapun, Tawi-Tawi, Philippines. The Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines classifies this facility as a community airport.

Bangsamoro, officially the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao is an autonomous region in the Philippines, located in the southwestern portion of the island of Mindanao.

The Iranun language, also known as Iranon or Illanun, is an Austronesian language belonging to the Danao languages spoken in the provinces of Maguindanao del Norte and other part of Lanao del Sur and Lanao del Norte, coastal municipalities of Zamboanga del Sur from Tukuran to Dumalinao and Cotabato in southern Philippines and the Malaysian state of Sabah. It is the second most spoken language in Maguindanao after the Maguindanao language.
Malabang Airport is an airport located in the town of Malabang, Lanao del Sur, Philippines. The Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines classifies this 16.05-hectare facility as a community airport.

An autonomous region of the Philippines is a first-level administrative division that has the authority to control a region's culture and economy. The Constitution of the Philippines allows for two autonomous regions: in the Cordilleras and in Muslim Mindanao. Currently, Bangsamoro, which largely consists of the Muslim-majority areas of Mindanao, is the only autonomous region in the country.
Wao Airport is an airport serving the general area of Wao, located in the province of Lanao del Sur, Philippines. The Civil Aviation Authority of the Philippines classifies this recently constructed facility as a community airport.

The 2019 Bangsamoro autonomy plebiscite was a two-part plebiscite held in Mindanao, Philippines, that ratified the Bangsamoro Organic Law (BOL) and replaced the Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) with the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM), as well as the scope of the said region.

The Special Geographic Area (SGA) is a loose collection of 63 barangays in six municipalities of the province of Cotabato in the Philippines. It is part of the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, despite the province of Cotabato itself being part of a separate neighboring region, Soccsksargen.

The Police Regional Office Bangsamoro Autonomous Region, also known as the Bangsamoro Police, is the regional office of the Philippine National Police meant to cover the whole Bangsamoro autonomous region.

The transition period of the now-defunct Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (ARMM) into the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao (BARMM) began when the Bangsamoro Organic Law was ratified in a two-part plebiscite held in January and February 2019. It is set to end after the first set of regular officials are elected in 2025.

The flag of Bangsamoro is the flag which represents the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, an autonomous region of the Philippines.

The Emblem of Bangsamoro is the official insignia of the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao, an autonomous region in the Philippines.
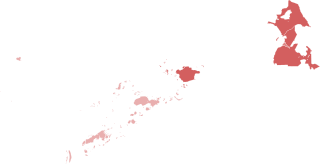
The COVID-19 pandemic in Bangsamoro is part of the worldwide pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2. The virus reached the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao on March 11, 2020, when the first case of the disease was confirmed in Lanao del Sur. Cases has been confirmed in Lanao del Sur, Maguindanao, and the independent city of Cotabato.
Dickson Peñas Hermoso is a Filipino government official and former military official who serves as the head of the Ministry of Transportation and Communications of Bangsamoro. He was also known for being part of the Philippine Army's 6th Infantry Division which was involved in the Moro conflict.

Maguindanao del Norte, officially the Province of Maguindanao del Norte, is a province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao in Mindanao. Its capital is the municipality of Datu Odin Sinsuat. It borders Cotabato province to the east, Lanao del Sur to the north, Maguindanao del Sur to the south-east, and Sultan Kudarat to the south.















