
A lathe is a machine tool that rotates a workpiece about an axis of rotation to perform various operations such as cutting, sanding, knurling, drilling, deformation, facing, threading and turning, with tools that are applied to the workpiece to create an object with symmetry about that axis.

Metalworking is the process of shaping and reshaping metals in order to create useful objects, parts, assemblies, and large scale structures. As a term, it covers a wide and diverse range of processes, skills, and tools for producing objects on every scale: from huge ships, buildings, and bridges, down to precise engine parts and delicate jewelry.

A machinist is a tradesperson or trained professional who operates machine tools, and has the ability to set up tools such as milling machines, grinders, lathes, and drilling machines.
G-code is the most widely used computer numerical control (CNC) and 3D printing programming language. It is used mainly in computer-aided manufacturing to control automated machine tools, as well as for 3D-printer slicer applications. The G stands for geometry. G-code has many variants.

Woodturning is the craft of using a wood lathe with hand-held tools to cut a shape that is symmetrical around the axis of rotation. Like the potter's wheel, the wood lathe is a mechanism that can generate a variety of forms. The operator is known as a turner, and the skills needed to use the tools were traditionally known as turnery. In pre-industrial England, these skills were sufficiently difficult to be known as "the mysteries of the turners' guild." The skills to use the tools by hand, without a fixed point of contact with the wood, distinguish woodturning and the wood lathe from the machinist's lathe, or metal-working lathe.

A grinding machine, often shortened to grinder, is any of various power tools or machine tools used for grinding. It is a type of material removal using an abrasive wheel as the cutting tool. Each grain of abrasive on the wheel's surface cuts a small chip from the workpiece via shear deformation.

A drawknife is a traditional woodworking hand tool used to shape wood by removing shavings. It consists of a blade with a handle at each end. The blade is much longer than it is deep. It is pulled or "drawn" toward the user.

A collet is a segmented sleeve, band or collar. One of the two radial surfaces of a collet is usually tapered and the other is cylindrical. The term collet commonly refers to a type of chuck that uses collets to hold either a workpiece or a tool, but collets have other mechanical applications.

A chuck is a specialized type of clamp used to hold an object with radial symmetry, especially a cylinder. In a drill, a mill and a transmission, a chuck holds the rotating tool; in a lathe, it holds the rotating workpiece.

Turning is a machining process in which a cutting tool, typically a non-rotary tool bit, describes a helix toolpath by moving more or less linearly while the workpiece rotates.

In machining, a metal lathe or metalworking lathe is a large class of lathes designed for precisely machining relatively hard materials. They were originally designed to machine metals; however, with the advent of plastics and other materials, and with their inherent versatility, they are used in a wide range of applications, and a broad range of materials. In machining jargon, where the larger context is already understood, they are usually simply called lathes, or else referred to by more-specific subtype names. These rigid machine tools remove material from a rotating workpiece via the movements of various cutting tools, such as tool bits and drill bits.

A plasterer is a tradesman who works with plaster, such as forming a layer of plaster on an interior wall or plaster decorative moldings on ceilings or walls. The process of creating plasterwork, called plastering, has been used in building construction for centuries. A plasterer is someone who does a full 4 or 2 years apprenticeship to be fully qualified.

A turret lathe is a form of metalworking lathe that is used for repetitive production of duplicate parts, which by the nature of their cutting process are usually interchangeable. It evolved from earlier lathes with the addition of the turret, which is an indexable toolholder that allows multiple cutting operations to be performed, each with a different cutting tool, in easy, rapid succession, with no need for the operator to perform set-up tasks in between or to control the toolpath. The latter is due to the toolpath's being controlled by the machine, either in jig-like fashion, via the mechanical limits placed on it by the turret's slide and stops, or via digitally-directed servomechanisms for computer numerical control lathes.
A banjo is a stringed instrument common in folk and popular music.

Segmented turning, also known as polychromatic turning, is a form of woodturning on a lathe where the initial workpiece is composed of multiple parts glued together. The process involves gluing several pieces of wood to create patterns and visual effects in turned projects.
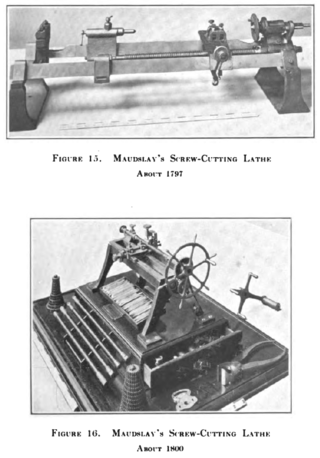
A screw-cutting lathe is a machine capable of cutting very accurate screw threads via single-point screw-cutting, which is the process of guiding the linear motion of the tool bit in a precisely known ratio to the rotating motion of the workpiece. This is accomplished by gearing the leadscrew to the spindle with a certain gear ratio for each thread pitch. Every degree of spindle rotation is matched by a certain distance of linear tool travel, depending on the desired thread pitch.
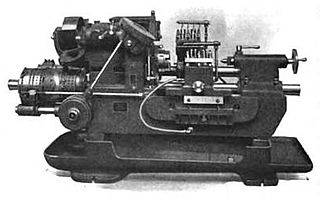
In metalworking and woodworking, an automatic lathe is a lathe with an automatically controlled cutting process. Automatic lathes were first developed in the 1870s and were mechanically controlled. From the advent of NC and CNC in the 1950s, the term automatic lathe has generally been used for only mechanically controlled lathes, although some manufacturers market Swiss-type CNC lathes as 'automatic'.

Okuma Corporation is a machine tool builder based in Ōguchi, Aichi Prefecture, Japan. It has global market share in CNC machine tools such as CNC lathes, machining centers, and turn-mill machining centers. The company also offers FA products and servomotors.

Milling is the process of machining using rotary cutters to remove material by advancing a cutter into a workpiece. This may be done by varying directions on one or several axes, cutter head speed, and pressure. Milling covers a wide variety of different operations and machines, on scales from small individual parts to large, heavy-duty gang milling operations. It is one of the most commonly used processes for machining custom parts to precise tolerances.

A workpiece is a piece, often made of a single material, that is being processed into another desired shape.















