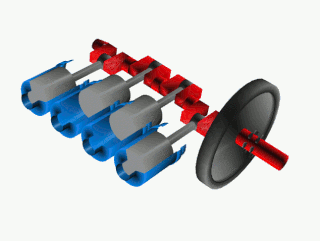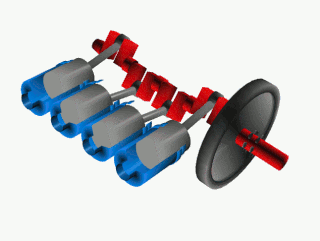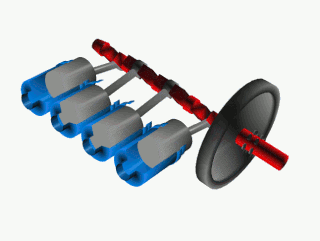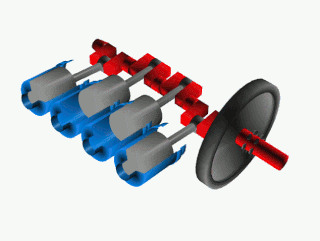
A crankshaft is a mechanical component used in a piston engine to convert the reciprocating motion into rotational motion. The crankshaft is a rotating shaft containing one or more crankpins, that are driven by the pistons via the connecting rods.

A reciprocating engine, also often known as a piston engine, is typically a heat engine that uses one or more reciprocating pistons to convert high temperature and high pressure into a rotating motion. This article describes the common features of all types. The main types are: the internal combustion engine, used extensively in motor vehicles; the steam engine, the mainstay of the Industrial Revolution; and the Stirling engine for niche applications. Internal combustion engines are further classified in two ways: either a spark-ignition (SI) engine, where the spark plug initiates the combustion; or a compression-ignition (CI) engine, where the air within the cylinder is compressed, thus heating it, so that the heated air ignites fuel that is injected then or earlier.

A cam is a rotating or sliding piece in a mechanical linkage used especially in transforming rotary motion into linear motion. It is often a part of a rotating wheel or shaft that strikes a lever at one or more points on its circular path. The cam can be a simple tooth, as is used to deliver pulses of power to a steam hammer, for example, or an eccentric disc or other shape that produces a smooth reciprocating motion in the follower, which is a lever making contact with the cam. A cam timer is similar, and were widely used for electric machine control before the advent of inexpensive electronics, microcontrollers, integrated circuits, programmable logic controllers and digital control.

The crankset or chainset is the component of a bicycle drivetrain that converts the reciprocating motion of the rider's legs into rotational motion used to drive the chain or belt, which in turn drives the rear wheel. It consists of one or more sprockets, also called chainrings or chainwheels attached to the cranks, arms, or crankarms to which the pedals attach. It is connected to the rider by the pedals, to the bicycle frame by the bottom bracket, and to the rear sprocket, cassette or freewheel via the chain.

The pedal is the part of a bicycle that the rider pushes with their foot to propel the vehicle. It provides the connection between the cyclist's foot or shoe and the crank allowing the leg to turn the bottom bracket spindle and propel the bicycle's wheels. A pedal usually consists of a spindle that threads into the end of the crank, and a body on which the foot rest is attached, that is free to rotate on bearings with respect to the spindle.

A crank is an arm attached at a right angle to a rotating shaft by which circular motion is imparted to or received from the shaft. When combined with a connecting rod, it can be used to convert circular motion into reciprocating motion, or vice versa. The arm may be a bent portion of the shaft, or a separate arm or disk attached to it. Attached to the end of the crank by a pivot is a rod, usually called a connecting rod (conrod).

The bottom bracket on a bicycle connects the crankset (chainset) to the bicycle and allows the crankset to rotate freely. It contains a spindle to which the crankset attaches, and the bearings that allow the spindle and crankset to rotate. The chainrings and pedals attach to the cranks. Bottom bracket bearings fit inside the bottom bracket shell, which connects the seat tube, down tube and chain stays as part of the bicycle frame.

The valve gear of a steam engine is the mechanism that operates the inlet and exhaust valves to admit steam into the cylinder and allow exhaust steam to escape, respectively, at the correct points in the cycle. It can also serve as a reversing gear. It is sometimes referred to as the "motion".

A single-speed bicycle is a type of bicycle with a single gear ratio. These bicycles are without derailleur gears, hub gearing or other methods for varying the gear ratio of the bicycle.

A fixed-gear bicycle is a bicycle that has a drivetrain with no freewheel mechanism such that the pedals always will spin together with the rear wheel. The freewheel was developed early in the history of bicycle design but the fixed-gear bicycle remained the standard track racing design. More recently the "fixie" has become a popular alternative among mainly urban cyclists, offering the advantage of simplicity compared with the standard multi-geared bicycle.

An automatic lubricator is a device fitted to a steam engine to supply lubricating oil to the cylinders and, sometimes, the bearings and axle box mountings as well. There are various types of automatic lubricator, which include various designs of displacement, hydrostatic and mechanical lubricators.

A fork end, fork-end, or forkend is a slot in a bicycle frame or bicycle fork where the axle of a bicycle wheel is attached. A dropout is a type of fork end that allows the rear wheel to be removed without first derailing the chain.

A linear actuator is an actuator that creates linear motion, in contrast to the circular motion of a conventional electric motor. Linear actuators are used in machine tools and industrial machinery, in computer peripherals such as disk drives and printers, in valves and dampers, and in many other places where linear motion is required. Hydraulic or pneumatic cylinders inherently produce linear motion. Many other mechanisms are used to generate linear motion from a rotating motor.

The sun and planet gear is a method of converting reciprocating motion to rotary motion and was used in the first rotative beam engines.

Reciprocating motion, also called reciprocation, is a repetitive up-and-down or back-and-forth linear motion. It is found in a wide range of mechanisms, including reciprocating engines and pumps. The two opposite motions that comprise a single reciprocation cycle are called strokes.

A straight-line mechanism is a mechanism that converts any type of rotary or angular motion to perfect or near-perfect straight-line motion, or vice versa. Straight-line motion is linear motion of definite length or "stroke", every forward stroke being followed by a return stroke, giving reciprocating motion. The first such mechanism, patented in 1784 by James Watt, produced approximate straight-line motion, referred to by Watt as parallel motion.

Precession is the process of a round part in a round hole, rotating with respect to each other, wherein the inner part begins rolling around the circumference of the outer bore, in a direction opposite of rotation. This is caused by too much clearance between them and a radial force on the part that constantly changes direction. The direction of rotation of the inner part is opposite to the direction of rotation of the radial force.

A quick release skewer is a mechanism for attaching a wheel to a bicycle. It consists of a rod threaded on one end and with a lever operated cam assembly on the other. The rod is inserted into the hollow axle of the wheel, a special nut is threaded on, and the lever is closed to tighten the cam and secure the wheel to the fork. Wheels equipped with quick release mechanisms can be removed from the bicycle frame and replaced without using tools by opening and closing the cam lever, thus more quickly than wheels with solid axles and nuts. On the negative side, a quick-release hub renders a wheel more vulnerable to theft and care must be taken to ensure that the mechanism is properly tightened.





















