Related Research Articles
E-commerce is the activity of electronically buying or selling products on online services or over the Internet. E-commerce draws on technologies such as mobile commerce, electronic funds transfer, supply chain management, Internet marketing, online transaction processing, electronic data interchange (EDI), inventory management systems, and automated data collection systems. E-commerce is the largest sector of the electronics industry and is in turn driven by the technological advances of the semiconductor industry.
Commerce is the large-scale organized system of activities, functions, procedures and institutions that directly or indirectly contribute to the smooth, unhindered distribution and transfer of goods and services on a substantial scale and at the right time, place, quantity, quality and price through various channels from the original producers to the final consumers within local, regional, national or international economies. The diversity in the distribution of natural resources, differences of human needs and wants, and division of labour along with comparative advantage are the principal factors that give rise to commercial exchanges.

The Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication (Swift), legally S.W.I.F.T. SC, is a Belgian banking cooperative providing services related to the execution of financial transactions and payments between limited banks worldwide. Its principal function is to serve as the main messaging network through which limited international payments are initiated. It also sells software and services to financial institutions, mostly for use on its proprietary "SWIFTNet", and assigns ISO 9362 Business Identifier Codes (BICs), popularly known as "Swift codes".

The International Chamber of Commerce is the largest, most representative business organization in the world. Its over 45 million members in over 100 countries have interests spanning every sector of private enterprise.
The Incoterms or International Commercial Terms are a series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC) relating to international commercial law. Incoterms define the responsibilities of exporters and importers in the arrangement of shipments and the transfer of liability involved at various stages of the transaction. They are widely used in international commercial transactions or procurement processes and their use is encouraged by trade councils, courts and international lawyers. A series of three-letter trade terms related to common contractual sales practices, the Incoterms rules are intended primarily to clearly communicate the tasks, costs, and risks associated with the global or international transportation and delivery of goods. Incoterms inform sales contracts defining respective obligations, costs, and risks involved in the delivery of goods from the seller to the buyer, but they do not themselves conclude a contract, determine the price payable, currency or credit terms, govern contract law or define where title to goods transfers.
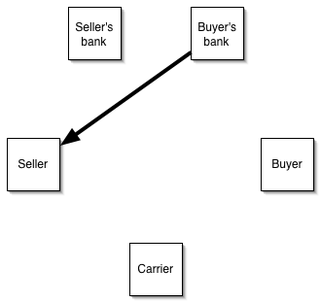
A letter of credit (LC), also known as a documentary credit or bankers commercial credit, or letter of undertaking (LoU), is a payment mechanism used in international trade to provide an economic guarantee from a creditworthy bank to an exporter of goods. Letters of credit are used extensively in the financing of international trade, when the reliability of contracting parties cannot be readily and easily determined. Its economic effect is to introduce a bank as an underwriter that assumes the counterparty risk of the buyer paying the seller for goods.
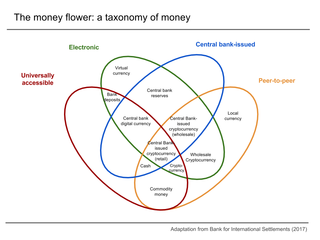
Digital currency is any currency, money, or money-like asset that is primarily managed, stored or exchanged on digital computer systems, especially over the internet. Types of digital currencies include cryptocurrency, virtual currency and central bank digital currency. Digital currency may be recorded on a distributed database on the internet, a centralized electronic computer database owned by a company or bank, within digital files or even on a stored-value card.
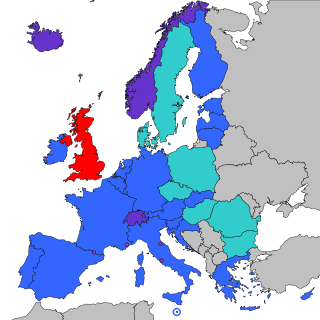
The Single Euro Payments Area (SEPA) is a payment integration initiative of the European Union for simplification of bank transfers denominated in euro. As of 2020, there were 36 members in SEPA, consisting of the 27 member states of the European Union, the four member states of the European Free Trade Association, and the United Kingdom. Some microstates participate in the technical schemes: Andorra, Monaco, San Marino, and Vatican City.

The Central Bank of Iran (CBI), also known as Bank Markazi, officially the Central Bank of the Islamic Republic of Iran is the central bank of Iran.

Mobile banking is a service provided by a bank or other financial institution that allows its customers to conduct financial transactions remotely using a mobile device such as a smartphone or tablet. Unlike the related internet banking it uses software, usually called an app, provided by the financial institution for the purpose. Mobile banking is usually available on a 24-hour basis. Some financial institutions have restrictions on which accounts may be accessed through mobile banking, as well as a limit on the amount that can be transacted. Mobile banking is dependent on the availability of an internet or data connection to the mobile device.
The Uniform Customs and Practice for Documentary Credits (UCP) is a set of rules on the issuance and use of letters of credit. The UCP is utilized by bankers and commercial parties in more than 175 countries in trade finance. Some 11-15% of international trade utilizes letters of credit, totaling over a trillion dollars (US) each year.
The Revised Payment Services Directive (PSD2, Directive (EU) 2015/2366, which replaced the Payment Services Directive (PSD), Directive 2007/64/EC) is an EU Directive, administered by the European Commission (Directorate General Internal Market) to regulate payment services and payment service providers throughout the European Union (EU) and European Economic Area (EEA). The PSD's purpose was to increase pan-European competition and participation in the payments industry also from non-banks, and to provide for a level playing field by harmonizing consumer protection and the rights and obligations for payment providers and users. The key objectives of the PSD2 directive are creating a more integrated European payments market, making payments more secure and protecting consumers.

Westpac Banking Corporation, known simply as Westpac, is an Australian multinational banking and financial services company headquartered at Westpac Place in Sydney, New South Wales.
Trade finance is a phrase used to describe different strategies that are employed to make international trade easier. It signifies financing for trade, and it concerns both domestic and international trade transactions. A trade transaction requires a seller of goods and services as well as a buyer. Various intermediaries such as banks and financial institutions can facilitate these transactions by financing the trade. Trade finance manifest itself in the form of letters of credit (LOC), guarantees or insurance and is usually provided by intermediaries.

Ajaypal Singh Banga is an Indian-born American business executive. He is currently the president of the World Bank Group. He was vice chairman at General Atlantic, and was before that executive chairman of Mastercard, after having previously served as president and chief executive officer (CEO) of the company from July 2010 until December 31, 2020. He retired from this position on December 31, 2021, to join General Atlantic. He is also the chairman of Netherlands-based investment holding company Exor and chairman of the public-private Partnership for Central America with U.S. Vice President Kamala Harris.

The Institute of International Banking Law & Practice is a non-profit American educational and research organization that studies banking law and practice. It was founded in 1987.
The Arab Chamber of Commerce and Industry (ARABCCI) or (ArabCham) in Hong Kong was established in 2006 to promote commercial ties between Hong Kong and Greater China with the Arab world. The Arab Chamber of Commerce is a not for profit organisation, The President is Edwin Hitti.

Dhaka Chamber of Commerce & Industry (DCCI), established in 1958, is a large organization for businesspeople in Dhaka, Bangladesh.
EBA Clearing is a provider of pan-European payment infrastructure wholly owned by shareholders that consist of major European banks.
The UNCITRAL Model Law on Electronic Transferable Records (“MLETR”) is a uniform model law that has been adopted by the United Nations Commission on International Trade Law (UNCITRAL) in 2017. Its scope is to allow the use of transferable documents and instruments in electronic form. Transferable documents and instruments typically include bills of lading, warehouse receipts, bills of exchange, promissory notes and cheques. National law qualifies a document or instrument as transferable.
References
- ↑ "Dubai Chamber and ICC regional launch of BPO rules". ICC. 24 June 2013. Archived from the original on 10 November 2014. Retrieved 10 November 2014.