Related Research Articles
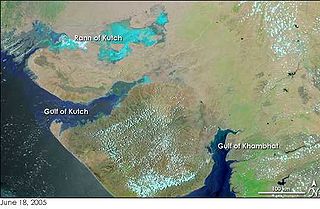
The Great Rann of Kutch is a salt marsh in the Thar Desert in the Kutch District of Gujarat, India. It is about 7500 km2 in the area and is reputed to be one of the largest salt deserts in the world. This area has been inhabited by the Kutchi people.

Sivapithecus is a genus of extinct apes. Fossil remains of animals now assigned to this genus, dated from 12.2 million years old in the Miocene, have been found since the 19th century in the Siwalik Hills of the Indian subcontinent as well as in Kutch. Any one of the species in this genus may have been the ancestor to the modern orangutans.

Lakhpat is a sparsely populated town and sub-district in the Kachchh district in the Indian state of Gujarat located at the mouth of the Kori Creek. The town is enclosed by 7km-long, 18th-century fort walls.

The kori bustard is arguably the largest flying bird native to Africa. It is a member of the bustard family, which all belong to the order Otidiformes and are restricted in distribution to the Old World. It is one of the four species in the large-bodied genus Ardeotis. In fact, the male kori bustard may be the heaviest living animal capable of flight.

The Hyderabadi Rupee was the currency of the Hyderabad State from 1918 to 1959. It coexisted with the Indian rupee from 1950. Like the Indian rupee, it was divided into 16 annas, each of 12 pai. Coins were issued in copper for denominations of 1 and 2 pai and ½ anna, in cupro-nickel for 1 anna and in silver for 2, 4 and 8 annas and 1 rupee.

The Kori was the currency of Kutch State until 1948. It was subdivided into 24 Dokda, each of 2 Trambiyo. Only coins were issued. Other copper coins in use were called Dhabbu and Dhinglo. The Kori was replaced by the Indian rupee.
Kori may refer to:

The Kori Creek is a tidal creek in the Kutch region of the Indian state of Gujarat. It lies just to the west of the Great Rann of Kutch area of India. This region belonging to India is a part of the Indus River Delta which lies across Gujarat state in India and Sindh in Pakistan.
The Standard Catalog of World Paper Money is a well-known catalogue of banknotes that is published by Krause Publications in three volumes. These catalogues are commonly known in the numismatic trade as the Pick catalogues, as the numbering system was originally compiled by Albert Pick, but are also referred to as "Krause" or "SCWPM." Since the mid-1980s the titles have been owned by Krause Publications, and from 1994–2016 were under the editorship of George S. Cuhaj, and subsequently by Tracy L. Schmidt.

The Rann of Kutch is a large area of salt marshes that span the border between India and Pakistan. It is located mostly in Gujarat, India and in some parts of Sindh, Pakistan. It is divided into the Great Rann and Little Rann.

Koteshwar is a small village and the location of an ancient Shiva temple. It located near the mouth of Kori Creek, in the west of Kutch district of Gujarat, India.

Kutch Museum in Bhuj is the oldest museum of Gujarat. It is located opposite Hamirsar Lake in Bhuj, Kutch, Gujarat, India. The museum was earlier known as Fergusson Museum.

Cutch, also spelled Kutch or Kachchh also historically known as Kingdom of Kutch, was a kingdom in the Kutch region from 1147 to 1819 and a princely state under British rule from 1819 to 1947. Its territories covered the present day Kutch region of Gujarat north of the Gulf of Kutch. Bordered by Sindh in the north, Cutch State was one of the few princely states with a coastline.

Shakoor Lake is a lake, comprising 300 km2, located on the border between the Indian state of Gujarat and the Sindh province on the southern edge of Pakistan. About 90 km2 of the lake comes under Pakistan, whilst the majority of the lake i.e. 210 km2, lies within India. The Indian built Indo-Pak Border Road runs across the Shakoor Lake and it is joined by the Indian GJ SH 45 State Highway just east of the lake, at the Kanjarkot Fort.
Tejara is a historical place in Kutch district of Gujarat, India.
Rao Deshalji I was the Rao of Cutch belonging to Jadeja Rajput dynasty, who ruled Princely State of Cutch as a regent from 1718 1752. His son Lakhpatji confined him in 1741 and ruled as a regent until death of Deshalji in 1752.
The 200 yen note (二百円紙幣) was a denomination of Japanese yen issued from 1927 to 1946. These issues were broken up into three different designs including one which has two different varieties. For whatever reason two-hundred yen banknotes were not issued when they were first authorized. The first issuance came as the result of a financial emergency that took place in 1927. Second series notes were also printed for the emergency, but were placed in storage until the end of World War II. By the time these were released along with a third series of notes, things were changing in Japan's monetary system. Currency could no longer be converted into gold coins making the messages on the long unreleased second series notes obsolete. An end to the series ultimately came in 1946, when all 200 yen bills were demonetized. These notes are now collectables which trade on the marketplace for amounts dependent on condition and rarity.
A yen was a colloquial term used to refer to a form of military scrip used in post-war US-Occupied Japan, Korea, and Okinawa from September 7, 1945, to July 21, 1948. They are notable for being the first "Military Payment Certificates" given after World War II had ended.

Meruda Takkar is a geological feature located north of Khadir Bet in the Great Rann of Kutch, Kutch district, Gujarat, India. It has a presence of Syenite rocks. It is described as a hill, an island, an outcrop as well as a monadnock.

Edward VIII coins are a series of coins that were produced upon the ascension of King Edward VIII. Because of his short reign of just 326 days and eventual abdication many never entered circulation and remained only as pattern pieces.
References
- Cuhaj, George S. (editor) (2006). Standard Catalog of World Paper Money: Specialized Issues (10th ed.). Krause Publications. ISBN 0-89689-161-5.CS1 maint: extra text: authors list (link)