The Tamil people, also known as Tamilar, Thamizhar or simply Tamils, are speakers of the Tamil language and trace their ancestry to the Indian state of Tamil Nadu or Sri Lanka. Tamils constitute 5.9% of the population in India, 15% in Sri Lanka, 6% in Mauritius, 7% in Malaysia and 5% in Singapore. Tamils, with a population of around 76 million and with a documented history stretching back over 2,000 years, are one of the largest and oldest extant ethnolinguistic groups in the modern world.

Trincomalee also known as Gokanna/Gokarna, is the administrative headquarters of the Trincomalee District and major resort port city of Eastern Province, Sri Lanka. Located on the east coast of the island overlooking the Trincomalee Harbour, 237 kilometres (147 mi) north-east of Colombo, 182 kilometres (113 mi) south-east of Jaffna and 111 kilometres (69 mi) miles north of Batticaloa, Trincomalee has been one of the main centres of Sri Lankan Tamil language speaking culture on the island for over two millennia. With a population of 99,135, the city is built on a peninsula of the same name, which divides its inner and outer harbours. People from Trincomalee are known as Trincomalians and the local authority is Trincomalee Urban Council. Trincomalee city is home to the famous Koneswaram temple from where it developed and earned its historic Tamil name Thirukonamalai. The town is home to other historical monuments such as the Bhadrakali Amman Temple, Trincomalee, the Trincomalee Hindu Cultural Hall and, opened in 1897, the Trincomalee Hindu College. Trincomalee is also the site of the Trincomalee railway station and an ancient ferry service to Jaffna and the south side of the harbour at Muttur.

The Pandya dynasty, also known as the Pandyas of Madurai, was a dynasty of south India, one of the three ethnically Tamil lineages, the other two being the Chola and the Chera. The rulers of the three dynasties were referred to as "the three crowned rulers of the Tamil country". The Pandyas ruled extensive territories, at times including the large portions of present-day south India and Sri Lanka.

The Jaffna Kingdom, also known as Kingdom of Aryachakravarti, of modern northern Sri Lanka was a historic monarchy that came into existence around the town of Jaffna on the Jaffna peninsula traditionally thought to be established after the invasion of Magha, who is credited with the founding of the Jaffna kingdom and is said to have been from Kalinga, in India. Established as a powerful force in the north, north east and west of the island, it eventually became a tribute paying feudatory of the Pandyan Empire in modern South India in 1258, gaining independence in 1323, when the last Pandyan ruler of Madurai was defeated and expelled in 1323 by Malik Kafur, the army general of the Muslim Delhi Sultanate. For a brief period, in the early to mid-14th century, it was an ascendant power in the island of Sri Lanka when all regional kingdoms accepted subordination. However, the kingdom was eventually overpowered by the rival Kotte Kingdom, around 1450 when it was invaded by Prince Sapumal under the Kotte Kingdom's directive.

The Arya Chakravarti dynasty were kings of the Jaffna Kingdom in Sri Lanka. The earliest Sri Lankan sources, between 1277 and 1283, mention a military leader of this name as a minister in the services of the Pandyan Empire; he raided the western Sri Lankan coast and took the politically significant relic of the Buddha’s tooth from the Sinhalese capital city of Yapahuwa. Political and military leaders of the same family name left a number of inscriptions in the modern-day Tamil Nadu state, with dates ranging from 1272 to 1305, during the late Pandyan Empire. According to contemporary native literature, such as Cekaracecekaramalai, the family also claimed lineage from the Tamil Brahmins of the prominent Hindu pilgrimage temple of Rameswaram in the modern Ramanathapuram District of India. They ruled the Jaffna kingdom from the 13th until the 17th century, when the last of the dynasty, Cankili II, was ousted by the Portuguese.
The Madurai Nayaks were Tamil rulers from around 1529 until 1736, of a region comprising most of modern-day Tamil Nadu, India, with Madurai as their capital. The Nayak reign was an era noted for its achievement in arts, cultural and administrative reforms, revitalization of temples previously ransacked by the Delhi Sultans, and inauguration of a unique architectural style.
Most of the Pre modern coinage used in Sri Lanka or coins used in pre-Christian Sri Lanka can be categorised as Punch-marked coins, Tree and Swastika coins, Elephant and Swastika coins and Lakshmi plaques.

The Early Pandyas of the Sangam period were one of the three main kingdoms of the ancient Tamil country, the other two being the Cholas, and Cheras Dynasty. As with many other kingdoms around this period, most of the information about the Early Pandyas come to modern historians mainly through literary sources and some epigraphic, archaeological and numismatic evidence. The capital of the Early Pandyan kingdom was initially Korkai, Thoothukudi and was later moved to Koodal during the reign of Nedunjeliyan I. The kingdom lay to the south of the Maurya Empire of India.

There are literary, archaeological, epigraphic and numismatic sources of ancient Tamil history. The foremost among these sources is the Sangam literature, generally dated to 5th century BCE to 3rd century CE. The poems in Sangam literature contain vivid descriptions of the different aspects of life and society in Tamilakam during this age; scholars agree that, for the most part, these are reliable accounts. Greek and Roman literature, around the dawn of the Christian era, give details of the maritime trade between Tamilakam and the Roman empire, including the names and locations of many ports on both coasts of the Tamil country.

The Flag of the Jaffna Kingdom of the Aryacakravarti line of kings of Jaffna kingdom in northern Sri Lanka consisted of the couchant bull, the silver crescent moon with a golden sun. The single sacred conch shell, which spiral open to the right, and in the centre above the sacred bull, is a white parasol with golden tassels and white pearls. The color of the Royal Flag is saffron. The flag symbols are similar to number of flags found in India especially belonging to the Eastern Ganga dynasty. The Setu coins minted by the Aryacakravarti kings also have a similar symbol.

Setu coins or Setu bull coins are found in large quantities in the northern part of Sri Lanka and in Southern India. Codrington in his book Ceylon Coins and Currency published in 1924 and Mitchiner in his book Oriental Coins published in 1978 have clearly pointed out that the traditional design of Sri Lanka standing King Type Copper Massa (coins) of the Jaffna Kingdoms belongs to the Aryacakravarti dynasty from 1284 AD to 1410 AD. Setu coins were previously attributed to the Setupati Princes of Ramanathapuram in South India. There are two series one in the issued from the 13th to the 15th centuries and the other after the brief loss of sovereignty to the rival Kotte kingdom from 1450 to 1467 and reconstitution of the Kingdom. Even during the rule of Sapumal Kumaraya coins were issued in Jaffna that was distinct. Three types of this series are illustrated below. The obverse of these coins have a human figure flanked by lamps and the reverse has the Nandi (bull) symbol, the legend Sethu in Tamil with a crescent moon above.

The Anuradhapura period was a period in the history of Sri Lanka of the Anuradhapura Kingdom from 377 BC to 1017 AD. The period begins when Pandukabhaya, King of Upatissa Nuwara moved the administration to Anuradhapura, becoming the kingdom's first monarch. Anuradhapura is heralded as an ancient cosmopolitan citadel with diverse populations.
Savakanmaindan was a monarch of the kingdoms of Tambralinga and Jaffna. He was the son of the Savakan king Chandrabhanu of Tambralinga who usurped the Tamil throne in 1255 AD. During his rule of Jaffna, the Venetian traveller Marco Polo visited the northeastern Tamil country.
When to date the start of the history of the Jaffna kingdom is debated among historians.
Mittasena was King of Anuradhapura in the 5th century, whose reign lasted from 435 to 436. He succeeded Chattagahaka Jantu as King of Anuradhapura. During his reign, the kingdom was invaded by Pandu of The Six Dravidians.
Sena II was King of Anuradhapura in the 9th century, whose reign lasted from 866 to 901. He succeeded his uncle Sena I as King of Anuradhapura and was succeeded by his brother Udaya I.

Manthai is a coastal town and an ancient harbor situated in the Mannar district, of the Northern Province of Sri Lanka. Manthai functioned as the main port of the Anuradhapura Kingdom throughout its history.

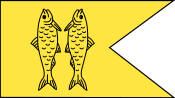
The Flag of Pandya was used by Pandyan Dynasty consisted of the single fish or twin fish. There is no reference or description about the flag. Therefore, any Pandya flags used in media are created for the purpose of illustration. There are flags with double fish or single fish as per archaeological findings and historians's illustration.

The Polonnaruwa period was a period in the history of Sri Lanka from 1017, after the Chola conquest of Anuradhapura and when the center of administration was moved to Polonnaruwa, to the end of the Kingdom of Polonnaruwa in 1232.

Kadurugoda Viharaya is an ancient Buddhist temple situated in Chunnakam, Jaffna District, Sri Lanka. The temple is located in a small hamlet called Kandarodai and it is one of the few Buddhist temples remaining in Jaffna today. Currently this temple has been declared as an archaeological site in Sri Lanka and is maintained by the Sri Lankan army.