
The Lordship of Ireland, sometimes referred to retrospectively as Anglo-Norman Ireland, was the part of Ireland ruled by the King of England and controlled by loyal Anglo-Norman Lords between 1177 and 1542. The lordship was created following the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland in 1169–1171. It was a papal fief, granted to the Plantagenet kings of England by the Holy See, via Laudabiliter. As the Lord of Ireland was also the King of England, he was represented locally by a governor, variously known as the Justiciar, Lieutenant, Lord Lieutenant or Lord Deputy.
This article concerns the Gaelic nobility of Ireland from ancient to modern times. It only partly overlaps with Chiefs of the Name because it excludes Scotland and other discussion. It is one of three groups of Irish nobility, the others being those nobles descended from the Hiberno-Normans and those granted titles of nobility in the Peerage of Ireland.

Baron Inchiquin is one of the older titles in the Peerage of Ireland. It was one of two titles created on 1 July 1543 for Murrough O'Brien, Prince of Thomond, who claimed descent from Brian Boru, a High King of Ireland. The English titles were granted under the policy of surrender and regrant, and therefore conditional upon the abandonment of any Irish titles, the adoption of English customs and laws, pledging of allegiance to the Crown, apostasy from the Catholic Church, and conversion to the Church of Ireland. Murrough was made both Earl of Thomond in the Peerage of Ireland, with remainder to his nephew Donough O'Brien and Baron Inchiquin, with remainder to his male heirs. Following the death of his cousin, Conor Myles John O' Brien in June 2023, Conor John Anthony O' Brien is currently the 19th Baron Inchiquin
Diarmait Mac Murchada, was King of Leinster in Ireland from 1127 to 1171. In 1167, he was deposed by the High King of Ireland, Ruaidrí Ua Conchobair. To recover his kingdom, Mac Murchada solicited help from King Henry II of England. His issue unresolved, he gained the military support of the Richard de Clare, 2nd Earl of Pembroke, thus initiating the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland.

The Tudor conquestof Ireland took place during the 16th century under the Tudor dynasty, which ruled the Kingdom of England. The Anglo-Normans had conquered swathes of Ireland in the late 12th century, bringing it under English rule. In the 14th century, the effective area of English rule shrank markedly, and from then most of Ireland was held by native Gaelic chiefdoms. Following a failed rebellion by the Earl of Kildare in the 1530s, the English Crown set about restoring its authority. Henry VIII of England was made "King of Ireland" by the Crown of Ireland Act 1542. The conquest involved assimilating the Gaelic nobility by way of "surrender and regrant"; the confiscation and colonisation ('plantation') of lands with settlers from Britain; imposing English law and language; banning Catholicism, dissolving the monasteries and making Anglican Protestantism the state religion.

Art Óg Mac Murchadha Caomhánach was an Irish king who is generally regarded as the most formidable of the later kings of Leinster. He revived not only the royal family's prerogatives, but also their lands and power. During his 42-year reign, he dominated the Anglo-Norman settlers of Leinster. His dominance of the province and its inhabitants, both Gaelic and Hiberno-Norman, was deemed sufficiently detrimental to the colony that Richard II of England spent much of the years 1394 and 1395 sparring with him. While MacMurrough-Kavanagh did eventually submit to Richard, he renounced this fealty on Richard's departure and made much of his kingdom a death trap for any invading English or Anglo-Irish forces. The Crown accordingly dealt with him cautiously and he was granted an amnesty in 1409.
During the Tudor conquest of Ireland (c.1540–1603), "surrender and regrant" was the legal mechanism by which Irish clans were to be converted from a power structure rooted in clan and kin loyalties, to a late-feudal system under the English legal system. The policy was an attempt to incorporate the clan chiefs into the English-controlled Kingdom of Ireland, and to guarantee their property under English common law, as distinct from the traditional Irish Brehon law system. This strategy was the primary non-violent method for Crown officials in the Dublin Castle administration to subjugate Irish clan leaders during the conquest. It was an unanticipated consequence to be required to pay fealty in currency instead of trade labor or commodities. The process of "surrender and regrant" thus created new, unfamiliar debt structures among the Irish, and these debts had social and political consequences.

The Ó h-Anluain family was an agnatic extended family comprising one of a string of dynasts along the Ulster-Leinster border. Depending on the advantage to the clan, the Chief of the Name—The O'Hanlon—supported either the Earl of Tyrone or authorities within the English Pale. During the 15th century, ties were close with the famed Earls of Kildare. Frequently, members of the clan would fight on both sides during a rebellion. Some would be outlawed; others pardoned; some ending up on the winning side.

Baron Upper Ossory was a title in the Peerage of Ireland. It was created on 11 June 1541 for Barnaby Fitzpatrick. This was in pursuance of the Surrender and regrant policy of King Henry VIII. Under the policy, Gaelic chiefs were actively encouraged to surrender their lands to the king and then have them regranted (returned) under a royal charter if they swore loyalty to him. Those who surrendered were also expected to speak English, wear English-style dress, remain loyal to the Crown, pay a rent and follow English laws and customs, abjure the Roman Catholic Church, and convert to Henry's new Anglican Church.

Magennis, also spelled Maguiness or McGuinness, is an Irish surname, meaning the "son of Angus", which in eastern Ulster was commonly pronounced in Irish as Mag/Mac Aonghusa. A prominent branch of the Uíbh Eachach Cobha, the Magennises would become chiefs of the territory of Iveagh, which by the 16th century comprised over half of modern County Down. By the end of the 17th century, their territory had been divided up between them, the McCartan chiefs and English prospectors.

Caomhánach is an Irish-language surname first assumed by Domhnall Caomhánach, eldest son of the 12th-century Diarmait Mac Murchada, king of Leinster. A considerable number of anglicised variations of Caomhánach exist; some of the most common are Kavanagh, Cavanagh, Kavanaugh and Cavanaugh.
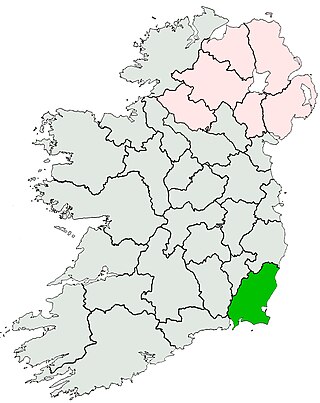
County Wexford is a county located in the south-east of Ireland, in the province of Leinster. It takes its name from the principal town, Wexford, named 'Waesfjord' by the Vikings – meaning 'inlet (fjord) of the mud-flats' in the Old Norse language. In pre-Norman times it was part of the Kingdom of Uí Cheinnselaig, with its capital at Ferns.

MacGorman, also known as McGorman, Gorman, or O'Gorman, is an Irish Gaelic clan based most prominently in what is today County Clare. The paternal ancestors of the clan are of the Laigin and emerged in what is today County Waterford. As leaders of the Uí Bairrche, they competed with the Uí Cheinnselaig in the 5th century for the Kingship of Leinster, ultimately losing out in that specific arena, but holding on to significant lands in the Leinster area.
Elizabeth le Veel, also known as Elizabeth Calf, was an Anglo-Irish noblewoman, and wife of Art mac Art MacMurrough-Kavanagh, King of Leinster. Her marriage to Art violated the Statutes of Kilkenny, and resulted in her property being forfeited to the English crown. This caused her husband to declare war in Ireland against the forces of King Richard II of England.

Umhaill or Umhall was a Gaelic territory around Clew Bay in the west of what is now County Mayo, Ireland, comprising the baronies of Burrishoole and Murrisk. By the 12th century, its ruling dynasty were known as the Uí Máille (O'Malleys). Originally an autonomous part of the kingdom of Connacht, it later became one of the vassal territories of the Mac William Íochtar. Umhaill's last and most famous ruler was Grace O'Malley, nicknamed "the pirate queen". In 1576, during the Tudor conquest of Ireland, she agreed to the surrender and regrant policy, accepting English inheritance law in return for official title deeds to her lands. On her death the lands were inherited by her son Tibbot "na Long". Umhaill had a strong seafaring culture. Important sites associated with it include Carrickkildavnet Castle, Carrickahowley Castle, Granuaile's Castle and Clare Island Abbey.

The siege of Wexford took place in early May 1169 and was the first major clash of the Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland. The town was besieged by a combined force of Normans under Robert Fitz-Stephen and soldiers loyal to Diarmait mac Murchadha. After being ousted as King of Leinster, Diarmait had recruited the Normans to help him regain control of Leinster and the semi-independent Norse-Gaelic seaport of Wexford. Although the attackers did not breach the town's walls, Wexford surrendered after almost two days and came under Norman control.
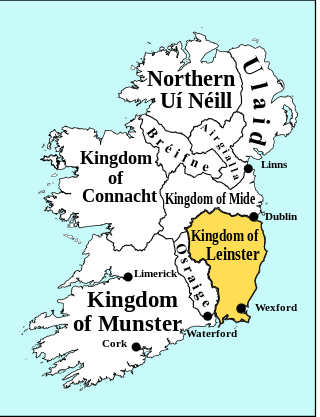
The Kingdom of Leinster was a kingdom of Gaelic Ireland which existed in the east of the island from the Irish Iron Age until the 17th century Early Modern Ireland. According to traditional Irish history found in the Annals of the Four Masters, the kingdom was founded as the territory of the Laighin, a Heremonian tribe of Irish Gaels. Some of the early kings of Leinster were also High Kings of Ireland and Kings of Tara, such as Úgaine Mór, Labraid Loingsech and Cathair Mór.
Cahir mac Art Kavanagh, "The MacMurrough" and King of Leinster, also Lord of St. Molyns, and baron of Ballyann, was an Irish magnate of the Tudor period.
Domhnall Caomhánach is the ancestor of the Caomhánach line of the Uí Ceinnselaig dynasty and was King of Leinster from 1171 to 1175. Domhnall was the eldest son of the 12th century King of Leinster, Diarmait Mac Murchada in Ireland.

Iveagh is the name of several historical territorial divisions in what is now County Down, Northern Ireland. Originally it was a Gaelic Irish territory, ruled by the Uí Echach Cobo and part of the overkingdom of Ulaid. From the 12th century the Magennises were chiefs of Iveagh. They were based at Rathfriland and were inaugurated at Knock Iveagh. Following the Nine Years' War, the rulers of Iveagh submitted to the English Crown and the territory was divided between them. Iveagh became a barony, which was later split into Iveagh Lower and Iveagh Upper. The territory of Iveagh was also the basis of the Roman Catholic Diocese of Dromore.













