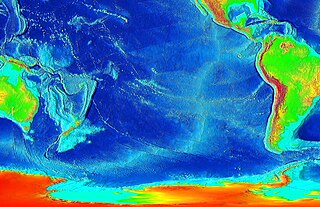
The Pacific-Antarctic Ridge (PAR) is a divergent tectonic plate boundary located on the seafloor of the South Pacific Ocean, separating the Pacific Plate from the Antarctic Plate. It is regarded as the southern section of the East Pacific Rise in some usages, generally south of the Challenger Fracture Zone and stretching to the Macquarie Triple Junction south of New Zealand.

In geology, hotspots are volcanic locales thought to be fed by underlying mantle that is anomalously hot compared with the surrounding mantle. Examples include the Hawaii, Iceland, and Yellowstone hotspots. A hotspot's position on the Earth's surface is independent of tectonic plate boundaries, and so hotspots may create a chain of volcanoes as the plates move above them.
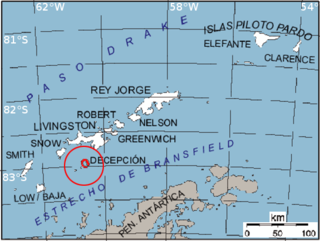
Bransfield Strait or Fleet Sea is a body of water about 100 kilometres (60 mi) wide extending for 300 miles (500 km) in a general northeast – southwest direction between the South Shetland Islands and the Antarctic Peninsula.

The Kermadec Trench is a linear ocean trench in the south Pacific Ocean. It stretches about 1,000 km (620 mi) from the Louisville Seamount Chain in the north (26°S) to the Hikurangi Plateau in the south (37°S), north-east of New Zealand's North Island. Together with the Tonga Trench to the north, it forms the 2,000 km (1,200 mi)-long, near-linear Kermadec-Tonga subduction system, which began to evolve in the Eocene when the Pacific Plate started to subduct beneath the Australian Plate. Convergence rates along this subduction system are among the fastest on Earth, 80 mm (3.1 in)/yr in the north and 45 mm (1.8 in)/yr in the south.

Monasterio de la Sierra is a municipality and town located in the province of Burgos, Castile and León, Spain. According to the 2004 census (INE), the municipality has a population of 43 inhabitants.

The Hawaiʻi hotspot is a volcanic hotspot located near the namesake Hawaiian Islands, in the northern Pacific Ocean. One of the best known and intensively studied hotspots in the world, the Hawaii plume is responsible for the creation of the Hawaiian–Emperor seamount chain, a 6,200-kilometer (3,900 mi) mostly undersea volcanic mountain range. Four of these volcanoes are active, two are dormant; more than 123 are extinct, most now preserved as atolls or seamounts. The chain extends from south of the island of Hawaiʻi to the edge of the Aleutian Trench, near the eastern coast of Russia.

Penguin Bank is the name given to a now-submerged shield volcano of the Hawaiian Islands. Its coral-capped remains lie immediately west of the island of Molokaʻi, under relatively shallow water.

Borceguí Island is an ice-free island in the South Shetland Islands, midway between Cape Yelcho and the Gibbous Rocks, 2 kilometres (1 nmi) off the north coast of Elephant Island. The name was applied by the command of the Argentine sea-going tug Chiriguano in the 1954–55 cruise; in Spanish "borceguí" means half-boot and describes the shape of the island.
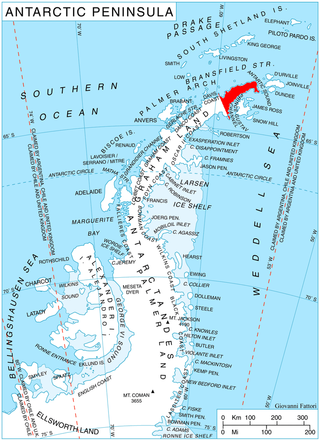
Diplock Glacier is a narrow straight glacier, 10 miles (16 km) long, flowing eastward from Detroit Plateau, on Trinity Peninsula in Graham Land, into Prince Gustav Channel 5 miles (8 km) south of Alectoria Island. It is situated south of Marla Glacier and north of Zavera Snowfield. The feature was mapped from surveys by the Falkland Islands Dependencies Survey (1960–61), and was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee for Bramah Joseph Diplock, a British engineer who made considerable advances in the design of chain-track tractors (1885–1913).
Fenton Glacier is a glacier that drains south into Mosby Glacier just east of Mount Adkins in Palmer Land, Antarctica. It was mapped by the United States Geological Survey from ground surveys and U.S. Navy air photos, 1961–1967, and was named by the Advisory Committee on Antarctic Names for Lieutenant Ernest R. Fenton, U.S. Navy, Officer-in-Charge of Palmer Station in 1971.

Hektoria Glacier is a glacier flowing south from the area around Mount Johnston between Mount Quandary and Zagreus Ridge into Vaughan Inlet next west of Brenitsa Glacier and east of Green Glacier, on the east coast of the Antarctic Peninsula.

Highton Glacier is a glacier on the east coast of Clarence Island in the South Shetland Islands, south of Sugarloaf Island, flowing northeast to the sea. Called "Stamina Glacier" from the stamina needed to cross it by the Joint Services Expedition to the Elephant Island Group, 1976–77, it was named by the UK Antarctic Place-Names Committee in 1980 after Commander John E. Highton, Royal Navy, Deputy Leader of the expedition and in charge of the group on Clarence Island.

Wordie Seamount is a seamount located in Bransfield Strait, Antarctica. The feature is named after James Wordie, geologist on Ernest Shackleton's 1914 expedition to Antarctica.
Barsukov or Barsukova is a Russian surname. Notable people with the surname include:

Arago hotspot is a hotspot in the Pacific Ocean, presently located below the Arago seamount close to the island of Rurutu, French Polynesia.
Ngatemato seamounts are a series of seamounts in the southern Pacific Ocean.
Foundation Seamounts are a series of seamounts in the southern Pacific Ocean. Discovered in 1992, these seamounts form a 1,350 kilometres (840 mi) long chain which starts from the Pacific-Antarctic Ridge. Some of these seamounts may have once emerged from the ocean.

Musicians Seamounts are a chain of seamounts in the Pacific Ocean, north of the Hawaiian Ridge. There are about 65 seamounts, some of which are named after musicians. These seamounts exist in two chains, one of which has been attributed to a probably now-extinct hotspot called the Euterpe hotspot. Others may have formed in response to plate tectonics associated with the boundary between the Pacific Plate and the former Farallon Plate.












