Related Research Articles

The Kuwait Armed Forces are the military forces of the State of Kuwait. They consist of the Kuwait Air Force, the Kuwait Army, the Kuwait Navy & the Kuwait National Guard. The governing bodies are the Kuwait Ministry of Defense, the Kuwait Ministry of Interior, and the Kuwait Fire Service Directorate. The Emir of Kuwait is the commander-in-chief of all defense forces while the Crown Prince is the deputy commander.
A diploma mill or degree mill is a business that sells illegitimate diplomas or academic degrees, respectively. The term diploma mill is also used pejoratively to describe any educational institution with low standards for admission and graduation, low career placement rate, or low average starting salaries of its graduates.

The Kuwait National Petroleum Company (KNPC) is the national oil refining company of Kuwait. Established in October 1960, KNPC has the mandate for oil refining, gas liquefaction, and distribution of petroleum goods within the local market. KNPC also handles CFP.
Education in Oman is provided free of charge up to end of secondary education, though attendance is not mandatory at any level. In 1970 there were only three formal schools with 900 students in the whole state. Oman's national educational program expanded rapidly during the 1970s and the 1980s, with the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia sending teachers on its own expense during that time period. In 2006–2007 about 560,000 students attended 1053 public schools. The number of students in private schools is about 65,000. There are also extensive programmes to combat adult illiteracy. Sultan Qaboos University, the only national university near Muscat, was founded in 1986, and in 2006 it had 13,500 students. The Human Development Report found the literacy rate to be 93.0% in adults, up from 54.7% in 1990. For the same period, the youth literacy rate increased from 85.6 to 97.3%. Public expenditure on education was reported to be 4.6% of GDP and 26.1% of total government spending.

Education in Rwanda has undergone considerable changes throughout Rwanda's recent history, and has faced major disruptions due to periods of conflict. Education was divided by gender whereby women and men had a different education relevant to their responsibilities in day-to-day life. Women were mostly taught housekeeping while men were mainly taught how to hunt, raise animals, and fish. This is because Rwanda was a community-based society where every member had a specific contribution to the overall development of the community. Older family members like grandparents usually took on the role of educators.

Ministry of Education and Science of the Russian Federation existed from March 2004 till May 2018. It oversaw scientific institutions, education and school accreditation in the Russian Federation. The agency had its headquarters in Tverskoy District, Central Administrative Okrug, Moscow.
Hamdan Bin Mohammad e-University formerly e-TQM College. in Dubai is the world's first online school for the field of Total Quality Management (TQM), and the first "virtual" university in the Middle East. The college was founded in 2002 by the Dubai Police, and by 2004 had 50,000 students.
Adailiya is an area and a suburb of Kuwait City; it is located in the Capital Governorate in Kuwait. It had a population of 21,996 in 2022. Adailiya houses a campus of Kuwait's Public Authority for Applied Education and Training (PAAET) and, temporarily, the colleges of Architecture and Life Sciences at Kuwait University as well as the Kazma Sport Club and religious, cultural, and commercial places. It also has a Water Towers Park.
Provision of education in the UAE began shortly after the establishment of the federation with the inception of the first university, the United Arab Emirates University, located in Al Ain, Abu Dhabi. Since then, the country has progressed with efforts of ensuring high literacy rates, modern programs and women's share in education. It works on improving its youth's education which is why the agenda 2021 has been set. The UAE currently devotes approximately 16 percent of total federal government spending to education. In 2019, the overall literacy rate was 96%, and in the year 2022, the literacy rate increased to 98.29.

The State of Kuwait, located at the head of the Persian Gulf, supports an educational policy that seeks to provide an opportunity to all children, irrespective of their social class, including children with special needs. Kuwait was ranked 63rd on the Human Development Index report for 2011 by the United Nations Development Programme, placing Kuwait above the regional average.

Higher education in Ontario includes postsecondary education and skills training regulated by the Ministry of Colleges and Universities and provided by universities, colleges of applied arts and technology, and private career colleges. The current minister is Jill Dunlop who was appointed in June 2021. The ministry administers laws covering 22 public universities, 24 public colleges, 17 privately funded religious universities, and over 500 private career colleges. 18 of the top 50 research universities in Canada are in Ontario.
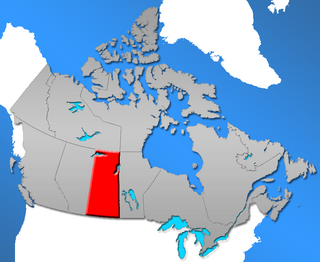
Historically, Saskatchewan's higher education system has been "significantly shaped" by demographics. In 1901, six years prior to the 1907 founding of a university in Saskatchewan, the urban population in Saskatchewan was 14,266 (16%) while the rural population was 77,013 (84%). One hundred years later, the proportions had changed significantly: urban population in 2001 was 629,036 (64%) while the rural population was 349,897 (36%). Over time the province's higher education system has changed significantly in response both to this demographic shift and to provincial politics.

Higher education in New Brunswick refers to education provided by higher education institutions in the Canadian province of New Brunswick. Higher education has a rich history in New Brunswick. The first English-language university in Canada was the University of New Brunswick. Mount Allison University was the first in the British Empire to award a baccalaureate to a woman, Grace Annie Lockhart, B.Sc. in 1875. Education is the responsibility of the provinces in Canada and there is no federal ministry governing it.
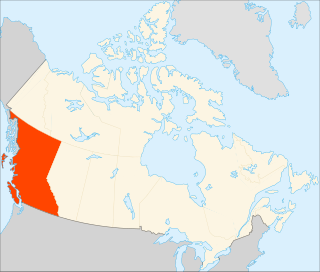
Higher education in British Columbia is delivered by 25 publicly funded institutions that are composed of eleven universities, eleven colleges, and three institutes. This is in addition to three private universities, five private colleges, and six theological colleges. There are also an extensive number of private career institutes and colleges. Over 297,000 students were enrolled in post-secondary institutions in British Columbia in the 2019-2020 academic year.

The Public Authority for Applied Education and Training (PAAET) is an academic institute in Kuwait. It is considered one of the largest institutes offering associate degrees in the Middle East in terms of the number of enrolled students. The PAAET offers a wide variety of vocational programs across its different colleges and training institutes.
Higher education accreditation is a type of quality assurance process under which services and operations of post-secondary educational institutions or programs are evaluated to determine if applicable standards are met. If standards are met, accredited status is granted by the agency.

Dr. Soliman Abdel-hady Soliman was an Egyptian professor of electrical engineering focusing on power and machines sector. Since 1997, he has been Professor of Electric Power System Analysis, Electrical Power & Machines Department, at Ain Shams University in Cairo, Egypt,

The Kuwait Police is an agency of the Ministry of Interior of Kuwait, which maintains the national security envelope, defense of land border, coastal and the rule of law in the State of Kuwait. The Kuwait Police Agency was established in 1938 by Ahmad Al-Jaber Al-Sabah as the Directorate of Public Security Force.
References
- ↑ "The Public Authority for Applied Education and Training (PAAET)" Archived September 17, 2008, at the Wayback Machine , Ministry of Information, Kuwait
- ↑ "Higher Education in Kuwait", Arab International Women's Conference, 22 October 2003
- ↑ "e-TQM, Kuwait college sign education deal", Gulf News, 16 March 2003
- ↑ "Ministry assures better education" Archived July 26, 2011, at the Wayback Machine , Kuwait Times, September 17, 2008