
Christian IV was King of Denmark and Norway and Duke of Holstein and Schleswig from 1588 until his death in 1648. His reign of 59 years and 330 days is the longest in Scandinavian history.

Frederick III was King of Denmark and Norway from 1648 until his death in 1670. He also governed under the name Frederick II as diocesan administrator of the Prince-Bishopric of Verden, and the Prince-Archbishopric of Bremen (1635–45).

The Battle of Copenhagen of 1801, also known as the First Battle of Copenhagen to distinguish it from the Second Battle of Copenhagen in 1807, was a naval battle in which a British fleet fought and defeated a smaller force of the Dano-Norwegian Navy anchored near Copenhagen on 2 April 1801. The battle came about over British fears that the powerful Danish fleet would ally with France, and a breakdown in diplomatic communications on both sides.

Eric Magnusson was the King of Norway from 1280 until 1299.

The Second Battle of Copenhagen was a British bombardment of the Danish capital, Copenhagen, in order to capture or destroy the Dano-Norwegian fleet during the Napoleonic Wars. The incident led to the outbreak of the Anglo-Russian War of 1807, which ended with the Treaty of Örebro in 1812. The attack on Denmark, a neutral country, was heavily criticized internationally.

Sverre Sigurdsson was the king of Norway from 1184 to 1202.

The Battle of Öland was a naval battle between an allied Danish-Dutch fleet and the Swedish navy in the Baltic Sea, off the east coast of Öland on 1 June 1676. The battle was a part of the Scanian War (1675–79) fought for supremacy over the southern Baltic. Sweden was in urgent need of reinforcements for its north German possessions; Denmark sought to ferry an army to Scania in southern Sweden to open a front on Swedish soil.

The Battle of Møn, also known as the Battle of Fehmarn, took place 31 May–1 June 1677, as part of the Scanian War. A smaller Swedish squadron under Admiral Erik Sjöblad attempted to sail from Gothenburg to join the main Swedish fleet in the Baltic Sea. It was intercepted by a superior Danish-Norwegian force under Niels Juel and decimated over the course of two days. The Swedes lost 8 ships and over 1,500 men dead, injured or captured, including Admiral Sjöblad himself, while the Danish losses were insignificant.

The Gunboat War was a naval conflict between Denmark–Norway and Great Britain supported by Sweden during the Napoleonic Wars. The war's name is derived from the Danish tactic of employing small gunboats against the materially superior Royal Navy. In Scandinavia it is seen as the later stage of the English Wars, whose commencement is accounted as the First Battle of Copenhagen in 1801.

The Battle of the Sound was a naval engagement which took place on 8 November 1658 during the Second Northern War, near the Sound or Øresund, just north of the Danish capital, Copenhagen. Sweden had invaded Denmark and an army under Charles X of Sweden had Copenhagen itself under siege. The Dutch fleet was sent to prevent Sweden from gaining control of both sides of the Sound and thereby controlling access to the Baltic Sea as well as of its trade.

The Battle of Køge Bay was a naval battle between Denmark-Norway and Sweden that took place in the bay off of Køge 1–2 July 1677 during the Scanian War. The battle was a major success for Admiral Niels Juel and is regarded as the greatest naval victory in Danish naval history.
Swedish military history encompasses the military engagements and strategic developments of Sweden from prehistoric times to the present day. As a significant European power during the 17th and early 18th centuries, Sweden played a major role in shaping the political landscape of Northern Europe. The country's military history is marked by periods of expansionism, particularly during the Swedish Empire era, followed by a long-standing policy of armed neutrality. Key phases include the Viking Age, the rise of the Swedish Empire, involvement in the Thirty Years' War, the Great Northern War, and more recent participation in United Nations peacekeeping operations. Sweden's military strategies have evolved from aggressive expansion to a focus on territorial defense and international cooperation, reflecting changes in its geopolitical position and global security landscape. Despite maintaining official neutrality through both World Wars, Sweden has continued to adapt its military capabilities and policies in response to regional and global security challenges, including its recent decision to join NATO in response to changing European security dynamics.

Jens Eriksen Munk was a Danish-Norwegian navigator and explorer. He entered into the service of King Christian IV of Denmark-Norway and is most noted for his attempts to find the Northwest Passage.

The Dano-Swedish War of 1658–1660 was a war between Denmark–Norway and Sweden, with the former backed by the Dutch Republic and Poland. It is known in Denmark as the Second Karl Gustav War, in Norway as Bjelkes Feud in Sweden as Karl Gustav's Second Danish War, and in the Netherlands as the Swedish-Dutch War.

The English Wars were a series of conflicts pitting the United Kingdom and Sweden against Denmark-Norway as part of the Napoleonic Wars. It is named after England, the common name in Scandinavia for the United Kingdom, which declared war on Denmark-Norway due to disagreements over the neutrality of Danish trade and to prevent the Danish fleet falling into the hands of the First French Empire. It began with the Battle of Copenhagen (1801) and its latter stage from 1807 onwards was followed by the Gunboat War, the Dano-Swedish War of 1808–09 and the Swedish invasion of Holstein in 1814.

Jochum Nicolay Müller was a Norwegian naval officer who, as a midshipman, excelled at mathematics. As a junior lieutenant he met Horatio Nelson, and as a captain commanded the Finnmark squadron. He finally rose to the rank of Vice Admiral in the independent Royal Norwegian Navy.

The Landing at Humlebæk took place on August 4, 1700, in the Swedish invasion of Denmark during the Great Northern War 1700-1721. It was the first offensive during the war by the Swedish army, and it was directly led by Charles XII of Sweden commanding the right flank and Arvid Horn together with Carl Gustav Rehnskiöld at the left. The Swedes were victorious and routed the Danish forces led by Jens Rostgaard.
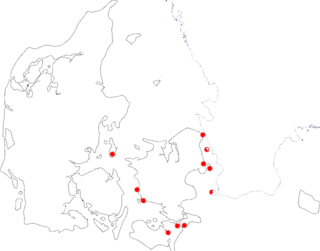
The War of the Outlaws also known as the Outlaw War, the Outlaw Revenge War, the Danish-Norwegian War, the Revenge War and in Denmark as the war with Norway over the archbishop's election, took place from 1289 to 1296. It was a conflict between two royal families over hereditary demands and special interests and was triggered by the murder of Eric V of Denmark.

The battle of Skanör was fought during the War of the Outlaws on 9 July 1289.
Events from the 13th century in Denmark.

















