The Delian League was a confederacy of Greek city-states, numbering between 150 and 330, founded in 478 BC under the leadership (hegemony) of Athens, whose purpose was to continue fighting the Persian Empire after the Greek victory in the Battle of Plataea at the end of the Second Persian invasion of Greece. The League functioned as a dual –offensive and defensive– alliance (symmachia) of autonomous states, similar to its rival association, the Peloponnesian League. The League's modern name derives from its official meeting place, the island of Delos, where congresses were held within the sanctuary of the Temple of Apollo; contemporary authors referred to the organization simply as "the Athenians and their Allies".

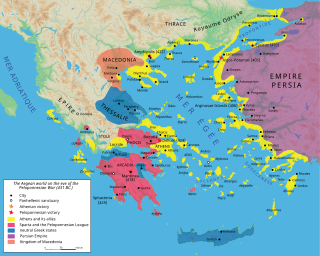
The Second Peloponnesian War, often called simply the Peloponnesian War, was an ancient Greek war fought between Athens and Sparta and their respective allies for the hegemony of the Greek world. The war remained undecided until the later intervention of the Persian Empire in support of Sparta. Led by Lysander, the Spartan fleet finally defeated Athens which began a period of Spartan hegemony over Greece.

The 5th century BC started the first day of 500 BC and ended the last day of 401 BC.
Year 447 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Macerinus and Iullus. The denomination 447 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

This is a timeline of ancient Greece from its emergence around 800 BC to its subjection to the Roman Empire in 146 BC.
Year 457 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time, it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Pulvillus and Augurinus or Cincinnatus and Vibulanus. The denomination 457 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.

Boeotia, sometimes Latinized as Boiotia or Beotia is one of the regional units of Greece. It is part of the region of Central Greece. Its capital is Livadeia, and its largest city is Thebes.

Plataea was an ancient Greek city-state situated in Boeotia near the frontier with Attica at the foot of Mt. Cithaeron, between the mountain and the river Asopus, which divided its territory from that of Thebes. Its inhabitants were known as the Plataeans.
The Peace of Callias is a purported peace treaty that supposedly was established around 449 BC between the Delian League and the Achaemenid Empire and ended the Greco-Persian Wars. The peace would then be the first compromise treaty between Achaemenid Persia and a Greek city.
The Battle of Oenophyta took place between Athens and the Boeotian city-states in 457 BC during the First Peloponnesian War.

The Battle of Delium took place in 424 BC, during the Peloponnesian War. It was fought between the Athenians and the Boeotians, who were allies of the Spartans, and ended with the siege of Delium in the following weeks.
In Archaic Greece, an amphictyony, or Amphictyonic League, was an ancient religious association of tribes formed before the rise of the Greek polis.

Pentecontaetia is the term used to refer to the period in Ancient Greek history between the defeat of the second Persian invasion of Greece at Plataea in 479 BC and the beginning of the Peloponnesian War in 431 BC. The term originated with a scholiast commenting on Thucydides, who used it in their description of the period. The Pentecontaetia was marked by the rise of Athens as the dominant state in the Greek world and by the rise of Athenian democracy, a period also known as Golden Age of Athens. Since Thucydides focused his account on these developments, the term is generally used when discussing developments in and involving Athens.
The First Peloponnesian War was fought between Sparta as the leaders of the Peloponnesian League and Sparta's other allies, most notably Thebes, and the Delian League led by Athens with support from Argos. This war consisted of a series of conflicts and minor wars, such as the Second Sacred War. There were several causes for the war including the building of the Athenian long walls, Megara's defection and the envy and concern felt by Sparta at the growth of the Athenian Empire.

Classical Greece was a period of around 200 years in Ancient Greece, marked by much of the eastern Aegean and northern regions of Greek culture gaining increased autonomy from the Persian Empire; the peak flourishing of democratic Athens; the First and Second Peloponnesian Wars; the Spartan and then Theban hegemonies; and the expansion of Macedonia under Philip II. Much of the early defining mathematics, science, artistic thought, theatre, literature, philosophy, and politics of Western civilization derives from this period of Greek history, which had a powerful influence on the later Roman Empire. Part of the broader era of classical antiquity, the classical Greek era ended after Philip II's unification of most of the Greek world against the common enemy of the Persian Empire, which was conquered within 13 years during the wars of Alexander the Great, Philip's son.

The Battle of the Eurymedon was a double battle, taking place both on water and land, between the Delian League of Athens and her Allies, and the Persian Empire of Xerxes I. It took place in either 469 or 466 BCE, in the vicinity of the mouth of the Eurymedon River in Pamphylia, Asia Minor. It forms part of the Wars of the Delian League, itself part of the larger Greco-Persian Wars.

The history of Sparta describes the history of the ancient Doric Greek city-state known as Sparta from its beginning in the legendary period to its incorporation into the Achaean League under the late Roman Republic, as Allied State, in 146 BC, a period of roughly 1000 years. Since the Dorians were not the first to settle the valley of the Eurotas River in the Peloponnesus of Greece, the preceding Mycenaean and Stone Age periods are described as well. Sparta went on to become a district of modern Greece. Brief mention is made of events in the post-classical periods.

The Wars of the Delian League were a series of campaigns fought between the Delian League of Athens and her allies, and the Achaemenid Empire of Persia. These conflicts represent a continuation of the Greco-Persian Wars, after the Ionian Revolt and the first and second Persian invasions of Greece.
Tolmides,, son of Tolmaeus, was a leading Athenian general of the First Peloponnesian War. He rivalled Pericles and Myronides for the military leadership of Athens during the 450s and early 440s BC.
Coroneia, or Coronea, was a town of ancient Boeotia, and a member of the Boeotian League. It is described by Strabo as situated upon a height near Mount Helicon; its territory was called Κορωνειακή. The town stood upon an insulated hill at the entrance of a valley leading southwards to Mt. Helicon, the principal summit of which is seen at the head of the valley. From this hill there was a fine view over the Lake Copais, and at its foot there was a broad plain extending as far as the marshes of the lake. On either side of the hill flowed two streams, one on the eastern or right hand side, called Coralius or Cuarius, and the other on the left, named Phalarus: a tributary of the latter was the Isomantus or Hoplias. Coroneia is said to have been founded by the Boeotians from Arne in Thessaly, after they had been driven out of their original homes by the Thessalians; and they appear to have called it Coroneia after the Thessalian town of this name. At the same time they built in the plain in front of the city a temple of Athena Itonica, also named after the one in Thessaly, and likewise gave to the river which flowed by the temple the name of Cuarius or Curalius, after the Thessalian river. In this temple was held the festival of the Pamboeotia, which was common to all the Boeotians. The Thessalian origin of Coroneia is also attested by Pausanias, who ascribes its foundation, as well as that of Haliartus, to Athamas and his descendants, who came from Thessaly.










