
Combined arms is an approach to warfare that seeks to integrate different combat arms of a military to achieve mutually complementary effects—for example, using infantry and armour in an urban environment in which each supports the other.

A pike is a long thrusting spear formerly used in European warfare from the Late Middle Ages and most of the early modern period, and wielded by foot soldiers deployed in pike square formation, until it was largely replaced by bayonet-equipped muskets. The pike was particularly well known as the primary weapon of Swiss mercenary, German Landsknecht units and French sans-culottes. A similar weapon, the sarissa, had been used in antiquity by Alexander the Great's Macedonian phalanx infantry.

The Battle of Mormant was fought during the War of the Sixth Coalition between an Imperial French army under Emperor Napoleon I and a division of Russians under Count Peter Petrovich Pahlen near the town of Mormant, some 50 km (31 mi) southeast of Paris. Pahlen's outnumbered force was enveloped by cavalry and infantry, and nearly destroyed, with only about a third of its soldiers escaping.
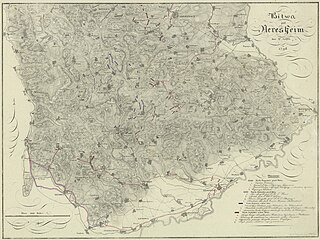
The Battle of Neresheim was fought by the Republican French army under Jean Victor Marie Moreau against the army of the Habsburg monarchy of Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen. Pursued by Moreau's Army of Rhin-et-Moselle, Charles launched an attack against the French. While the Austrian left wing saw some success, the battle degenerated into a stalemate and the archduke withdrew further into the Electorate of Bavaria. Neresheim is located in the state of Baden-Württemberg in Germany a distance of 57 kilometres (35 mi) northeast of Ulm. The action took place during the War of the First Coalition, part of a larger conflict called the French Revolutionary Wars.

The Battle of New Market was fought on May 15, 1864, in Virginia during the Valley Campaigns of 1864 in the American Civil War. A makeshift Confederate army of 4,100 men defeated the larger Army of the Shenandoah under Major General Franz Sigel, delaying the capture of Staunton by several weeks.

The First Battle of Winchester, fought on May 25, 1862, in and around Frederick County, Virginia, and Winchester, Virginia, was a major victory in Confederate Army Maj. Gen. Thomas J. "Stonewall" Jackson's Campaign through the Shenandoah Valley during the American Civil War. Jackson enveloped the right flank of the Union Army under Maj. Gen. Nathaniel P. Banks and pursued it as it fled across the Potomac River into Maryland. Jackson's success in achieving force concentration early in the fighting allowed him to secure a more decisive victory which had escaped him in previous battles of the campaign.

The Swiss mercenaries were a powerful infantry force constituted by professional soldiers originating from the cantons of the Old Swiss Confederacy. They were notable for their service in foreign armies, especially among the military forces of the kings of France, throughout the early modern period of European history, from the Late Middle Ages into the Renaissance. Their service as mercenaries was at its peak during the Renaissance, when their proven battlefield capabilities made them sought-after mercenary troops. There followed a period of decline, as technological and organizational advances counteracted the Swiss' advantages. Switzerland's military isolationism largely put an end to organized mercenary activity; the principal remnant of the practice is the Pontifical Swiss Guard at the Vatican.

The Battle of Maida, fought on 4 July 1806 was a battle between the British expeditionary force and a French force outside the town of Maida in Calabria, Italy during the Napoleonic Wars. John Stuart led 5,236 Anglo-Sicilian troops to victory over about 5,400 Franco-Italian-Polish troops under the command of French general Jean Reynier, inflicting significant losses while incurring relatively few casualties. Maida is located in the toe of Italy, about 30 kilometres (19 mi) west of Catanzaro.

Antoine-Charles-Louis, Comte de Lasalle was a French cavalry general during the French Revolutionary and Napoleonic Wars. Often called "The Hussar General," he first gained fame for his role in the Capitulation of Stettin. Throughout his short career, he became known as a daring adventurer and was credited with many exploits, fighting on every front. He was killed at the Battle of Wagram.

The Battle of Novara was a battle of the War of the League of Cambrai fought on 6 June 1513, near Novara, in Northern Italy. A French attacking force was routed by allied Milanese–Swiss troops. As a consequence, France was forced to withdraw entirely from Italy.

The Battle of Bicocca or La Bicocca was fought on 27 April 1522, during the Italian War of 1521–26. A combined French and Venetian force under Odet de Foix, Vicomte de Lautrec, was decisively defeated by an Imperial–Spanish and Papal army under the overall command of Prospero Colonna. Lautrec then withdrew from Lombardy, leaving the Duchy of Milan in Imperial hands.

The Battle of Ceresole took place on 14 April 1544, during the Italian War of 1542–1546, outside the village of Ceresole d'Alba in the Piedmont region of Italy. A French army, commanded by François de Bourbon, Count of Enghien, defeated the combined forces of the Holy Roman Empire and Spain, commanded by Alfonso d'Avalos d'Aquino, Marquis del Vasto. Despite having inflicted substantial casualties on the Imperial troops, the French subsequently failed to exploit their victory by taking Milan.

The Battle of Mór took place during the Hungarian Revolution of 1848 on 30 December 1848 between Austria and Hungarian Revolutionary Army. The Austrians were led by Croatian Ban Lieutenant General Josip Jelačić, while the Hungarians were led by Major General Mór Perczel. The Austrians were victorious and, subsequently, the Hungarian main army led by Artúr Görgei lost the last chance to stop the Austrian armies which were threatening the Hungarian capitals Pest and Buda. As a result of this, the Austrian army led by Field Marshal Alfred I, Prince of Windisch-Grätz occupied on 5 January 1849 Pest and Buda.

The Battle of Gujrat was a decisive battle in the Second Anglo-Sikh War, fought on 21 February 1849, between the forces of the East India Company, and a Sikh army in rebellion against the company's control of the Sikh Empire, represented by the child Maharaja Duleep Singh who was in British custody in Lahore. The Sikh army was defeated by the British regular and Bengal Army forces of the British East India Company. After it capitulated a few days later, the Punjab was annexed to the East India Company's territories and Duleep Singh was deposed.

The Battle of Kápolna was one of the decisive battles of the Hungarian war of Independence of 1848–1849, fought on 26 and 27 February 1849 between the Hungarian revolutionary army led by Lieutenant General Henryk Dembiński and the Austrian main army operating in Hungary Field Marshal Alfred I, Prince of Windisch-Grätz. After the Austrian offensive from the winter of 1848-1849, which resulted in losing the Western part of the country, the Hungarian army tried its first major counter-attack, but due to the disastrous leadership of the Polish Henryk Dembiński, the battle ended with an Austrian victory, and this did not influence only the military situation, but also the politics of central Europe: Franz Joseph I announced the March Constitution of Austria on 4 March 1849.

Despite the rise of knightly cavalry in the 11th century, infantry played an important role throughout the Middle Ages on both the battlefield and in sieges. From the 14th century onwards, it has been argued that there was a rise in the prominence of infantry forces, sometimes referred to as an "infantry revolution", but this view is strongly contested by some military historians.

The Battle of Schwechat was a battle in the Hungarian war of Independence of 1848-1849, fought on 30 October 1848 between the revolutionary Hungarian Army led by Lieutenant General János Móga against the army of the Austrian Empire led by Lieutenant General Josip Jelačić, at Schwechat, near Vienna. This was the last battle of 1848 in the Transdanubian campaign. The Hungarian Army wanted to relieve the revolutionaries from Vienna, besieged by the Austrian imperial army, but they were defeated. Vienna fell on the next day.

At the Battle of Schliengen, the French Army of the Rhine and Moselle under the command of Jean-Victor Moreau and the Austrian army under the command of Archduke Charles of Austria both claimed victories. The village of Schliengen lies in the present-day Kreis Lörrach close to the border of present-day Baden-Württemberg (Germany), the Haut-Rhin (France), and the Canton of Basel-Stadt (Switzerland).

At the Battle of Emmendingen, on 19 October 1796, the French Army of Rhin-et-Moselle under Jean Victor Marie Moreau fought the First Coalition Army of the Upper Rhine commanded by Archduke Charles, Duke of Teschen. Emmendingen is located on the Elz River in Baden-Württemberg, Germany, 9 miles (14 km) north of Freiburg im Breisgau. The action occurred during the War of the First Coalition, the first phase of the larger French Revolutionary Wars.

The First Battle of Bar-sur-Aube was fought during the War of the Sixth Coalition when Marshal Édouard Mortier, duc de Trévise's corps of French Imperial Guards defended against an Austrians corps under Ignaz Gyulai and a Württemberger corps led by Crown Prince Frederick William of Württemberg. After holding his main defensive positions in stiff fighting, Mortier withdrew his elite troops during the night and retreated to Troyes. Bar-sur-Aube is located 53 kilometres (33 mi) east of Troyes.




















