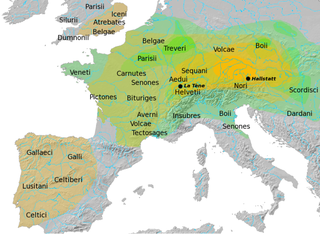
The Boii were a Celtic tribe of the later Iron Age, attested at various times in Cisalpine Gaul, Pannonia, present-day Bavaria, in and around present-day Bohemia, parts of present-day Slovakia and Poland, and Gallia Narbonensis.

Year 72 BC was a year of the pre-Julian Roman calendar. At the time it was known as the Year of the Consulship of Publicola and Lentulus. The denomination 72 BC for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years
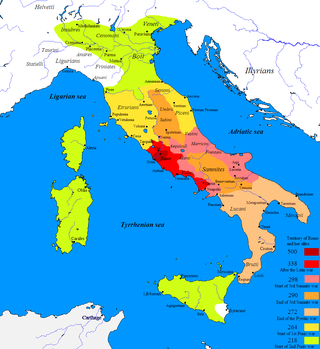
The First, Second, and Third Samnite Wars were fought between the Roman Republic and the Samnites, who lived on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains south of Rome and north of the Lucanian tribe.

Tullus Hostilius was the legendary third king of Rome. He succeeded Numa Pompilius and was succeeded by Ancus Marcius. Unlike his predecessor, Tullus was known as a warlike king who, according to the Roman historian Livy, believed the more peaceful nature of his predecessor had weakened Rome. It has been attested that he sought out war and was even more warlike than the first king of Rome, Romulus. Accounts of the death of Tullus Hostilius vary. In the mythological version of events Livy describes, he had angered Jupiter who then killed him with a bolt of lightning. Non-mythological sources on the other hand describe that he died of plague after a rule of 32 years.
The Third Macedonian War was a war fought between the Roman Republic and King Perseus of Macedon. In 179 BC, King Philip V of Macedon died and was succeeded by his ambitious son Perseus. He was anti-Roman and stirred anti-Roman feelings around Macedonia. In 172, a Roman commission visited Perseus and required of him concessions which meant the extinction of his independence. Upon his refusal to comply with the demands they returned home and Rome declared war.

Marcus Aemilius Lepidus was a Roman consul, Pontifex Maximus, Censor and Princeps Senatus. A scion of the ancient Patrician gens Aemilia, he was most likely the son of Marcus Aemilius Lepidus, with his brothers being Lucius and Quintus.

The Battle of Mutina took place on 21 April 43 BC between the forces loyal to the Senate under consuls Gaius Vibius Pansa and Aulus Hirtius, supported by the forces of Caesar Octavian, and the forces of Mark Antony which were besieging the troops of Decimus Brutus. The latter, one of Caesar's assassins, held the city of Mutina in Cisalpine Gaul.

The Battle of Placentia was fought in 194 BC, near Placentia, between the Roman Republic and the Boii. The Roman army won the battle. The following year, another battle with the Boii would take place in the same region; known as the Battle of Mutina, it would end the Boii threat.
Gaius Claudius Pulcher, consul in 177 BC, was the son of Appius Claudius Pulcher, consul in 212 BC, and he was the father of Appius Claudius Pulcher, consul in 143 BC.

The Roman Republic conquered and occupied territories in the Iberian Peninsula that were previously under the control of native Celtic, Iberian, Celtiberian and Aquitanian tribes and the Carthaginian Empire. The Carthaginian territories in the south and east of the peninsula were conquered in 206 BC during the Second Punic War. Control was gradually extended over most of the peninsula without annexations. It was completed after the end of the Roman Republic, by Augustus, the first Roman emperor, who annexed the whole of the peninsula to the Roman Empire in 19 BC.
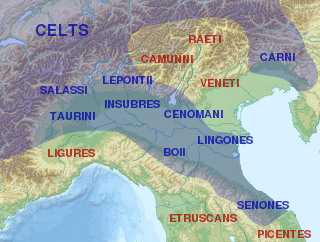
The Insubres or Insubri were an ancient Celtic population settled in Insubria, in what is now the Italian region of Lombardy. They were the founders of Mediolanum (Milan). Though completely Gaulish at the time of Roman conquest, they were the result of the fusion of pre-existing Ligurian and Celtic population with Gaulish tribes.
Lucius Cornelius L. f. Merula was consul of the Roman Republic, along with Quintus Minucius Thermus, in 193 BC. His province was Gallia Cisalpina. Merula closed an active predatory campaign by a total defeat of the Boian Gauls in the neighbourhood of Mutina. Since his staff officer Marcus Claudius Marcellus accused him of a delay in sending forward a reserve unit, resulting in several thousand unnecessary casualties and the escape of many enemy soldiers, the senate refused him a triumph.
Pontius Aquila was a Roman politician, military commander, and one of the assassins of Julius Caesar. In 45 BC, as tribune of the plebs, he annoyed Caesar by refusing to stand during his triumphal procession, and, in the following year, joined the conspiracy to kill the dictator. Aquila died fighting at the Second Battle of Mutina against Mark Antony in April 43 BC, before the formation of the Second Triumvirate later that year.

The Galatian War was a war between the Galatian Gauls and the Roman Republic supported by their allies Pergamum in 189 BC. The war was fought in Galatia in central Asia Minor, in present-day Turkey.
The gens Decia was a plebeian family of high antiquity, which became illustrious in Roman history by the example of its members sacrificing themselves for the preservation of their country. The first of the family known to history was Marcus Decius, chosen as a representative of the plebeians during the secession of 495 BC.

Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus was a Roman general and statesman, most notable as one of the main architects of Rome's victory against Carthage in the Second Punic War. Often regarded as one of the greatest military commanders and strategists of all time, his greatest military achievement was the defeat of Hannibal at the Battle of Zama in 202 BC. This victory in Africa earned him the honorific epithet Africanus, literally meaning "the African", but meant to be understood as a conqueror of Africa.

Over the course of nearly four centuries, the Roman Republic fought a series of wars against various Celtic tribes, whom they collectively described as Galli, or Gauls. Among the principal Gallic peoples described as antagonists by Greek and Roman writers were the Senones, Insubres, Boii, and Gaesatae.
The Roman-Aequian wars were a series of wars during the early expansion of ancient Rome in central Italy against their eastern neighbours, the Aequi.
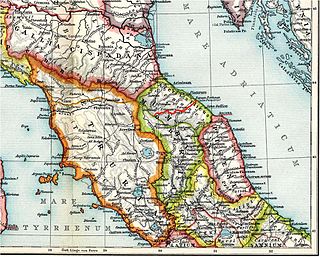
The Battle of Silva Litana was an ambush that took place in a forest 75 miles northwest of the Roman city of Ariminum during the Second Punic War in 216 BC. The Gallic Boii surprised and destroyed a Roman army under the consul-elect Lucius Postumius Albinus. Of 25,000 Romans, only 10 survived, with a few being taken prisoner by the Gauls. The corpse of Postumius was decapitated and his skull was made into a gilded ceremonial cup by the Boii. News of this military disaster probably reached Rome after the defeat at Cannae in the fall of 216 BC or the spring election of consuls for 215 BC, triggering a renewed panic. The Romans were compelled to postpone military operations against the Gauls until the conclusion of the Second Punic War, sending only two legions to guard against additional Gallic attacks. However, the Boii and Insubres did not attempt to exploit their victory. Cisalpine Gaul remained in relative peace until 207 BC, when Hasdrubal Barca arrived there with his army from Spain.
The siege of Mutina in 218 BC constitutes one of the first episodes of the Second Punic War. Hannibal's diplomacy in Cisalpine Gaul persuaded the Gallic Boii and Insubres tribes to revolt and drive the Roman colonists out of Piacenza (Placentia) and push them as far as Modena (Mutina), which was then besieged.











