History
The previous battle was fought in 310 BC during the Second Samnite War (327-304 BC) between the Romans and a large coalition of Etruscan city-states. It was said to have been the largest battle between the two nations.
Unfortunately, this battle occurred in a period for which the books in The History of Rome by Livy, the most thorough ancient historian who wrote Roman history, have been lost and we do not have his thorough coverage. The best text is by Polybius, but this lacks important details. A fragment from Appian is confusing. There are many details about how the battle was fought.
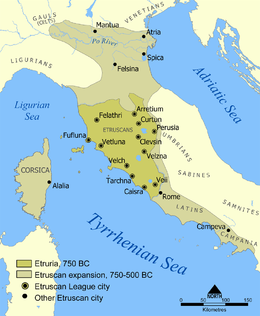
According to Polybius, the battle followed events which started with the siege of Arretium (Arezzo, in north-eastern Tuscany). Unspecified Gauls besieged Arretium and defeated the Romans who came to the aid of the city. The praetor Lucius Caecilius Metellus Denter died in the battle and was replaced by Manius Curius Dentatus. This places the event in 283 BC because Lucius Caecilius was a consul in 284 BC. Dentatus sent envoys to negotiate the release of Roman hostages, but they were killed. As a result, the Romans marched on Gaul and they were met by the Senones who were defeated in a pitched battle. The Senones were one of the Gallic tribes which lived in northern Italy. Polybius used the highly generic term Gaul. He meant Gallia Cisalpina (Gaul this side of the Alp from the Roman geographical viewpoint) which was the name the Romans gave the area of the Gauls of northern Italy (as opposed to Gallia Transalpina, Gaul the other side of the Alps, which referred to what is now southern France). It can be assumed that this clash with the Senones occurred in the ager Gallicus (the name the Romans gave to the area which had been conquered by the Senones), on the Adriatic coast (in modern Marche) as Polybius wrote that “the Romans invaded the territory of the Senones, killed most of them and drove the rest out of the country and founded the colony of Sena Gallia (Senigalia). Polybius did not specify who led this Roman campaign. [1]
Polybius wrote that “[h]ereupon the Boii, seeing the Senones expelled from their territory, and fearing a like fate for themselves and their own land, implored the aid of the Etruscans and marched out in full force. The united armies gave battle to the Romans near Lake Vadimon, and in this battle most of the Etruscans were cut to pieces while only quite a few of the Boii escaped." He also wrote that the next year the Boii and the Etruscans engaged the Romans in battle again and “were utterly defeated and it was only now that their courage at length gave way and that they sent an embassy to sue for terms and made a treaty with the Romans." [2]
Appian wrote about the wars between Rome and the Gauls in Italy and Gaul and Julius Caesar’s conquest of Gaul (Gallic Wars 1, 2, and 3 of his Roman History). However, his work has survived only in fragments which are often short and sometimes do not shed enough light on events. He wrote about events in 283 BC and mentioned the battle fought against the Romans by a Gallic and Etruscan force without mentioning where it was. This fragment concentrates on an incident which involved Roman ambassadors and Roman actions in the ager Gallicus (the land of the Senones).
According to Appian, the Romans sent their ambassadors specifically to the Senones and for a different reason. The Senones had provided mercenaries to forces which had fought against Rome despite the fact that they had a treaty with Rome. The Romans sent ambassadors to remonstrate against this. Appian wrote that “Britomaris, the Gaul, being incensed against them on account of his father, who had been killed by the Romans while fighting on the side of the Etruscans in this very war, slew the ambassadors” while they were still holding the herald’s staff. He added some details which are most probably fictive and reflections of prejudice towards barbarians. He wrote that Britomaris wore their official garments and “cut their bodies in small pieces and scattered them in the fields." Then Publius Cornelius Dolabella, (the consul for 283 BC) “while he was on the march, moved with great speed” to the ager Gallicus “by way of the Sabine country and Picenum” and laid it to waste: "He ravaged them all [the Senones] with fire and sword. He reduced the women and children to slavery, killed all the adult males without exception, devastated the country in every possible way, and made it uninhabitable for anybody else." Appian added that [a] little later the Senones (who were serving as mercenaries), having no longer any homes to return to, fell boldly upon the consul Domitius, and being defeated by him killed themselves in despair.” [3]
Appian’s text is unclear and confusing. He does not link the ambassadors’ event to the siege and battle at Arretium. He does not mention where the ambassadors met Britomaris either. The fact his father was killed by the Romans while fighting on the side of the Etruscans in the same war could suggest that this previous fighting was the battle of Lake Vadimon, which involved a combined Etruscan and Gallic army (the Battle of Arretium involved Gauls only). The second battle mentioned by Polybius, in which the Etruscans and Gauls were defeated again and sued for peace, may well correspond with the second battle mentioned by Appian. However, while Polybius places this second battle against an Etrusco-Gallic force in the next year (284 BC), Appian claims that it was won by Gnaeus Domitius Calvinus Maximus, who was the other consul for 283 BC. Appian did not mention the Boii Gauls in the second battle. It does not seem that there is a reference to the battle of Arretium as there is no mention of a siege, of a battle between Romans and Gauls only, or Roman prisoners, and the purpose of the Roman embassy was different. The lack of mention of where the battles were fought compounds the problem. There also may be a discrepancy between the sequence of events presented by Polybius and the sequence which may be inferred from Appian's text:
Polybius: Battle of Arretium - devastation of the ager Gallicus - Battle of Lake Vadimon - final battle.
Appian: Battle of Lake Vadimon - devastation of the ager Gallicus - final battle (no reference to a battle of Arretium).