Bajirao I, born as Visaji, was the 7th Peshwa of the Maratha Confederacy.

The Maratha Empire, also referred to as the Maratha Confederacy, was an early modern Indian empire and later a confederation that controlled large portions of the Indian subcontinent in the 18th century. Maratha rule formally began in 1674 with the coronation of Shivaji of the Bhonsle dynasty as the Chhatrapati. Although Shivaji came from the Maratha caste, the Maratha empire also included warriors, administrators, and other nobles from the Maratha and several other castes from what is known today as Maharashtra. The Maratha Kingdom was expanded into a full-fledged Empire in the 18th Century C.E under the leadership of Peshwa Bajirao I.

Mir Qamar-ud-din Khan Siddiqi also known as Chin Qilich Qamaruddin Khan, Nizam-ul-Mulk, Asaf Jah and Nizam I, was the first Nizam of Hyderabad. He was married to the daughter of a Syed nobleman of Gulbarga. He began his career as a favourite of the Mughal emperor Aurangzeb, who made him a general. Following the death of Aurangzeb in 1707, Asaf Jah refused to favour any one of Aurangzeb's warring sons and as such remained neutral. When Aurangzeb's third son Bahadur Shah ultimately emerged victorious, Asaf Jah was rotated as governor of multiple Mughal provinces until 1714, when he was created Viceroy of the Deccan with authority over six Mughal provinces in southern India from 1714 to 1719. From 1719 onwards he was involved in combating the intrigues of the Sayyid brothers. From 1720 to 1722 he helped the new Mughal emperor Muhammad Shah eliminate the Sayyid brothers and was rewarded by being elevated to the grand viziership from 1722 to 1724. He also engaged in military conflict against BajiRao Peshwa in Battle of Palkhed and Battle of Bhopal.

The Third Anglo-Maratha War (1817–1819) was the final and decisive conflict between the British East India Company and the Maratha Empire in India. The war left the Company in control of most of India. It began with an invasion of Maratha territory by British East India Company troops, and although the British were outnumbered, the Maratha army was decimated. The troops were led by Governor General Hastings, supported by a force under General Thomas Hislop. Operations began against the Pindaris, a band of Muslim mercenaries and Marathas from central India.

Balaji Baji Rao, often referred to as Nana Saheb I, was the 8th Peshwa of the Maratha Confederacy. He was appointed as Peshwa in 1740 upon the death of his father, the Peshwa Bajirao I.

Mirza Aziz-ud-Din Muhammad, better known by his regnal name Alamgir II, was the fifteenth Mughal emperor from 1754 to 1759. He was the son of Jahandar Shah.

Ahmad Shah Bahadur, also known as Mirza Ahmad Shah or Mujahid-ud-Din Ahmad Shah Ghazi, was the fourteenth Mughal emperor, born to Emperor Muhammad Shah. He succeeded his father to the throne in 1748, at the age of 22. When Ahmed Shah Bahadur came to power, the Mughal Empire started to decline. Furthermore, his administrative weakness eventually led to the rise of the usurping Imad-ul-Mulk.
The Treaty of Mungi-Shevgaon was signed on March 6, 1728, between Bajirao I of the Maratha Empire and the Nizam of Hyderabad, Asaf Jah I, in what is present-day Shevgaon. According to the terms of the treaty, the Nizam granted the Marathas the authority to collect Chauth, a type of tax, from the six Subahs located in the Deccan region. Additionally, the treaty recognized Shahu I as the Emperor of the Maratha Empire, and in return, the Maratha Emperor agreed not to apprehend Sambhaji II, who had allied himself with the Nizam against the Emperor.

The Carnatic wars were a series of military conflicts in the middle of the 18th century in India's coastal Carnatic region, a dependency of Hyderabad State, India. The first Carnatic wars were fought between 1740 to 1748

Mirza Nizam Ali Khan Siddiqi, Asaf Jah II was the 5th Nizam of Hyderabad State in South India between 1762 and 1803. He was born on 7 March 1734 as fourth son to Asaf Jah I and Umda Begum. His official name is Asaf Jah II, Nizam ul-Mulk, Nizam ud-Daula, Nawab Mir Nizam 'Ali Khan Siddiqi, Fateh Jang, Sipah Salar, Nawab Subedar of the Deccan. Sawānih-i-Deccan, a Persian work compiled by Munim Khan, a military commander during the era of Asaf Jah II gave more insight about administration of Asaf Jahis.

The Mughal–Maratha Wars was a conflict between the Mughal Empire and the descendants of the Maratha ruler Shivaji from the time of Shivaji's death in 1680 until the death of Emperor Aurangzeb in 1707. Shivaji was a central figure in what has been called "the Maratha insurgency" against the Mughal state. Both he and his son, Sambhaji, or Shambuji, typically, alternated between rebellion against the Mughal state and service to the Mughal sovereign in an official capacity. It was common practice in late 17th-century India for members of a ruling family of a small principality to both collaborate with the Mughals and rebel.

Malhar Rao Holkar was a noble subedar of the Maratha Empire, in present-day India. He was one of the early officers along with Ranoji Scindia to help spread the Maratha rule to northern states and was given the estate of Indore to rule by the Peshwas, during the reign of the Maratha emperor Shahu I. He was founder of the Holkar dynasty that ruled Malwa.

Salabat Jung, born as Mir Sa'id Muhammad Khan Siddiqi Bayafandi on 24 November 1718, was the 3rd son of Nizam-ul-Mulk. He was appointed as Naib Subahdar to his elder brother, Ghazi ud-Din Khan Feroze Jung II, the Prime Minister of Mughal Empire, with the title Salabat Jung. He was invested by Imperial firman, at Aurangabad, Maharashtra, 12 September 1749. He was granted the titles of Khan Bahadur and Salabat Jung during his father's lifetime.
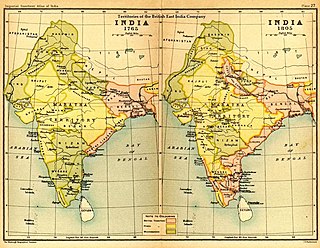
The Maratha Conquests were a series of conquests in the Indian subcontinent which led to the building of the Maratha Empire. These conquests were started by Shivaji in 1659, from the victory at the Battle of Pratapgad against Bijapur. The expansion of the empire was limited and interrupted by the Mughal conquests of south India by Mughal emperor Aurangzeb. Marathas were forced to defend their territories against the overwhelmingly strong Mughal army in the 27 years long Deccan wars. They were able to defend their territories and gain an upper hand over Mughals in the sustained conflict.

Madhavrao II was the 12th Peshwa of the Maratha Empire in India, from his infancy. He was known as Sawai Madhav Rao or Madhav Rao Narayan. He was the posthumous son of Narayanrao Peshwa, murdered in 1773 on the orders of Raghunathrao. Madhavrao II was considered the legal heir, and was installed as Peshwa by the Treaty of Salbai in 1782 after First Anglo-Maratha War.
The Battle of Rakshasbhuvan in India was fought on 10 August 1763. After the defeat of the Maratha Empire at the Battle of Panipat, their rivals started seizing the opportunity to recover their losses in the past at the hands of Marathas. Particularly, the Nizam of Hyderabad wanted to recover territory he had lost at the Battle of Udgir where all of his dukes and earls were killed. He decided to launch a war on the Marathas.
The Battle of Bhopal was fought on 24 December 1737 in Bhopal between the Maratha Empire and the combined army of the Nizam and several Mughal generals.
The Battle of Alegaon was fought between Nizam Ali Khan of Hyderabad and Raghunathrao of the Maratha Empire against Madhavrao I of the Maratha Empire. Raghunathrao had established an alliance with Nizam Ali Khan of Hyderabad. When conflict arose between Raghunathrao and Madhavrao I, a joint campaign by Nizam Ali Khan and Raghunathrao resulted in Madhavrao I being heavily defeated. Madhavrao I surrendered on 12 November 1762. Nizam Ali Khan got all of his territories lost at the Battle of Udgir. Madhavrao I submitted to his uncle, Raghunathrao.

Shams ul-Umara, Shams ul-Mulk, Shams ud-Daula, Nawab Muhammad' Abu’l Fath Khan Bahadur, Taigh Jang Bahadur ['Abu’l Khair Khan II] [Imam JungIII] was an Indian nobleman and founder of the House of Paigah.
The Battle of Palkhed was fought on 28 February 1728 at the village of Palkhed, near the city of Nashik, in what is now Maharashtra, India, between the Maratha Empire and the Nizam-ul-Mulk, Asaf Jah I of Hyderabad wherein the Marathas defeated the Nizam.