Related Research Articles

Year 634 (DCXXXIV) was a common year starting on Saturday of the Julian calendar. The denomination 634 for this year has been used since the early medieval period, when the Anno Domini calendar era became the prevalent method in Europe for naming years.
The Banu Makhzum was one of the wealthy clans of the Quraysh. They are regarded as being among the three most powerful and influential clans in Mecca before the advent of Islam, the other two being the Banu Hashim and the Banu Umayya.
Abū Dujānā Simāk bin Kharāshā was a companion of Muhammad and a skilled swordsman who is mentioned in Hadith narrations from the six major Hadith collections of Sunni Islam.
The Battle of Buzakha took place between Khalid ibn al-Walid and Tulayha, in September 632.
The Battle of Ghamra took place between Khalid ibn al-Walid and the remaining army of Buzakha, 20 miles from Buzakha.
The Battle of Naqra took place in October 633 between rebel armies and Khalid ibn al-Walid's army during the Ridda Wars.

The Battle of Yamama was fought in December 632 as part of the Ridda Wars against a rebellion within the Rashidun Caliphate in the region of al-Yamama between the forces of Abu Bakr and Musaylima, a self-proclaimed prophet.
The Battle of the River, also known as Battle of Al Madhar, took place in Mesopotamia between the forces of the Rashidun Caliphate and the Sasanian Empire. Muslims, under Khalid ibn al-Walid's command, defeated the numerically superior Sasanian army.

The Battle of Ayn al-Tamr took place in modern-day Iraq (Mesopotamia) between the early Muslim Arab forces and the Sassanians along with their Arab Christian auxiliary forces. Ayn al-Tamr is located west of Anbar and was a frontier post which had been established to aid the Sassanids.
The Battle of Daumat al-Jandal took place between Muslims and Rebel Arab tribes in August 633 CE. This was a part of the Riddah wars. Daumat al-Jandal was given to Iyad ibn Ghanm to crush the rebels, but he failed in doing so, and send for help to Khalid ibn Walid who was in Iraq in those days.

Battle of Muzayyah was between the Muslim Arab army and the Sasanian Empire. When Khalid ibn Walid left from Ayn al-Tamr to Dumat Al-Jandal for the help of Iyad ibn Ghanm, the Persian court believed that Khalid had returned to Arabia with a large part of his army. The Persians decided to throw the Muslims back into the desert and regain the territories and the prestige which the Persian Empire had lost. The Persians had resolved not to fight Khalid again, but they were quite prepared to fight the Muslims without Khalid ibn al-Walid.

Battle of Saniyy was between the Muslim Arab army and the Sasanian Empire. When Khalid ibn Walid gone from Ayn al-Tamr to Dumat Al-Jandal for the help of Iyad ibn Ghanm, The Persian court believed that Khalid had returned to Arabia with a large part of his army, Persians decided to throw the Muslims back into the desert and regain the territories and the prestige which the Empire had lost. The Persians had resolved not to fight Khalid again, but they were quite prepared to fight the Muslims without Khalid ibn al-Walid. Khalid ibn al-Walid first defeated them at the battle of Muzayyah and then advanced towards Saniyy.

The battle of Zumail was fought in 633 CE in Mesopotamia. It was a major Muslim victory in their conquest of that area. Under cover of night the Arab Muslims attacked the Christian-Arab forces, loyal to the Sasanian Empire, from three different sides. The Christian-Arab forces were unable to withstand the Muslim's surprise attack and soon dispersed but failed to escape from the battlefield and became the victims of a three sided attack by Khalid ibn al-Walid's army. At Zumail nearly the whole Christian Arab army was slaughtered by Khalid's Corps.

The Battle of Ullais was fought between the forces of the Rashidun Caliphate and the Sasanian Persian Empire in the middle of June 633 AD in Iraq, and is sometimes referred to as the Battle of Blood River since, as a result of the battle, there were enormous amounts of Persian Sasanian and Arab Christian casualties.

The Battle of Al-Anbar was between the Muslim Arab army under the command of Khalid ibn al-Walid and the Sasanian Empire. The battle took place at Anbar which is located approximately 80 miles from the ancient city of Babylon. Khalid besieged the Sassanian Persians in the city fortress, which had strong walls. Scores of Muslim archers were used in the siege. The Persian governor, Shirzad, eventually surrendered and was allowed to retire. The Battle of Al-Anbar is often remembered as the "Action of the Eye" since Muslim archers used in the battle were told to aim at the "eyes" of the Persian garrison.
Battle of al-Qaryatayn was a minor battle between the Ghassanid Arab allies of the Byzantine empire, and the Rashidun Caliphate army. It was fought after Khalid ibn Walid had conquered Tadmur in Syria. His army marched to al-Qaryatayn, the inhabitants of which resisted the Muslims. They were fought, defeated and plundered.

The Battle of the Iron Bridge was fought between the Muslim Rashidun army and the Byzantine army in 637 AD. The battle took its name from a nearby nine-arch stone bridge spanning the Orontes River which had gates trimmed with iron. It was one of the last battles fought between the Byzantines and Rashidun Caliphate in the province of Syria. The aftermath of the battle marked the nearly complete annexation of the province into the Rashidun Caliphate with the fall of its capital, Antioch.
The siege of Germanicia or Marash was led by Muslim forces of the Rashidun Caliphate during their campaigns in Anatolia in 638. The city surrendered without much bloodshed. This expedition is important because it marks the end of the military career of the legendary Arab Muslim general Khalid ibn Walid, who was dismissed from the army a few months after his return from the expedition.
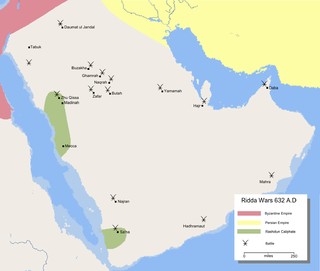
The Battle of Dhu al-Qassah took place in the area of Dhu al-Qassah, located approximately 36 kilometres (22 mi) east of Medina, in the Medina Province, in the central-western part of Saudi Arabia, from July 25 to July 30, 632. It pitted the forces of the Rashidun Caliphate led by Caliph Abu Bakr As-Siddiq against the rebel apostates led by General Hibal ibn Khuwailid,.

The Battle of Abraq took place in the Abraq area, located about 8 kilometres (5.0 mi) north of Al Hinakiyah, in the Nejd region, in the central-western part of Saudi Arabia, in mid-August 632. It pitted the forces of the Rashidun Caliphate, led by Caliph Abu Bakr As-Siddiq, against rebellious Arab tribes led, according to Agha Ali Ibrahim Akram, by General Hibal ibn Khuwailid.
References
This article includes a list of references, related reading, or external links, but its sources remain unclear because it lacks inline citations .(December 2014) |
- A.I. Akram, The Sword of Allah: Khalid bin al-Waleed, His Life and Campaigns Lahore, 1969
- A.I. Akram, The Sword of Allah: Khalid bin al-Waleed, His Life and Campaigns, Nat. Publishing. House, Rawalpindi (1970) ISBN 0-7101-0104-X.
14°12′41″N44°24′12″E / 14.21139°N 44.40333°E