
Andrés de Santa Cruz y Calahumana was a Bolivian general and politician who served as interim president of Peru in 1827, the interim president of Peru from 1836 to 1838 and the sixth president of Bolivia from 1829 to 1839. He also served as Supreme Protector of the short-lived Peru-Bolivian Confederation from 1836 to 1839, a political entity created mainly by his personal endeavors.

The Peru–Bolivian Confederation was a short-lived state that existed in South America between 1836 and 1839. The country was a loose confederation made up of three states: North Peru and South Peru—states that arose from the division of the Peruvian Republic due to the civil wars of 1834 and 1835 to 1836—as well as the Bolivian State.

Agustín Gamarra Messia was a Peruvian soldier and politician, who served as the 4th and 6th President of Peru.

Manuel Bulnes Prieto was a Chilean military and political figure. He was twice President of Chile, from 1841 to 1846 and from 1846 to 1851.

The Battle of Ayacucho was a decisive military encounter during the Peruvian War of Independence. This battle secured the independence of Peru and ensured independence for the rest of belligerent South American states. In Peru it is considered the end of the Spanish American wars of independence in this country, although the campaign of Antonio José de Sucre continued through 1825 in Upper Peru and the siege of the fortresses Chiloé and Callao eventually ended in 1826.

The Battle of Yungay was the final battle of the War of the Confederation, fought on January 20, 1839, near Yungay, Peru. The United Restoration Army, led by Chilean General Manuel Bulnes, consisting mainly of Chileans and 600 North Peruvian dissidents, attacked the Peru-Bolivian Confederation forces led by Andrés de Santa Cruz in northern Peru, 200 kilometers (120 mi) north of Lima.

The Battle of Tarapacá occurred on 27 November 1879 during the Tarapacá Campaign of the War of the Pacific. Three Chilean columns of almost 3,900 soldiers attacked a numerically inferior Peruvian contingent of 3,046 troops at Tarapacá - 500 of which were at Quillahuasa, 1 hour away from the battlefield - commanded by Gen Juan Buendía, resulting in a harsh defeat. The Chilean 2nd Line Regiment was the most damaged unit, losing almost half of its force, along with its commander Col. Eleuterio Ramírez and his second in command, Lt. Col. Bartolomé Vivar. The unit lost its banner, which was recovered six months later after the Battle of Tacna. Despite the victory, the Allies could not contest for the domination of the Tarapacá department, abandoning it to Chilean control.

The War of the Confederation was a military confrontation waged by the United Restoration Army, the alliance of the land and naval forces of Chile and the Restoration Army of Peru, formed in 1836 by Peruvian soldiers opposed to the confederation, and the Argentine Confederation against the Peru–Bolivian Confederation between 1836 and 1839. As a result of the Salaverry-Santa Cruz War, the Peru-Bolivia Confederation was created by General Andrés de Santa Cruz, which caused a power struggle in southern South America, with Chile and the Argentine Confederation, as both distrusted this new and powerful political entity, seeing their geopolitical interests threatened. After some incidents, Chile and the Argentine Confederation declared war on the Peru-Bolivian Confederation, although both waged war separately.

Felipe Santiago Salaverry del Solar was a Peruvian soldier and politician who served as the Supreme Chief of Peru.

José Miguel de Velasco Franco was a Bolivian military officer and statesman who served as the fourth president of Bolivia on four occasions: 1828, 1829, 1839–1841, and 1848. Velasco also served as the second vice president from 1829 to 1835 under Andrés de Santa Cruz, though the first two of his terms were as vice president-designate, pending Santa Cruz's arrival to the country.

Sebastián Ágreda was a Bolivian military officer and statesman who served as the seventh president of Bolivia for 29 days in 1841. In addition to his short term as president, he also held a number of other governmental roles as well as being a prominent figure in the Bolivian military.

Mariano Enrique Calvo Cuéllar was a Bolivian lawyer, general and politician who served as the de facto eighth president of Bolivia briefly in 1841. He also served as the third vice president from 1835 to 1839 during which he also held the powers of acting president while President Andrés de Santa Cruz was in Peru. He would also be given the rank of general and commander of the Bolivian Army by Santa Cruz.

Chilean-Peruvian relations are the historical and current bilateral relations between the adjoining South American countries of the Republic of Chile and the Republic of Peru. Peru and Chile have shared diplomatic relations since at least the time of the Inca Empire in the 15th century. Under the Viceroyalty of Peru, Chile and Peru had connections using their modern names for the first time. Chile aided in the Peruvian War of Independence by providing troops and naval support.
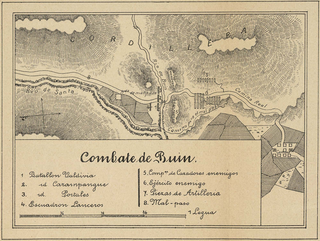
The Battle of Buin was fought on January 6, 1839, during the Chilean second expedition of the War of the Confederation. The Restoring Army rearguard led by General Manuel Bulnes successfully held the bridge over the Buin River in the North Peruvian territory from the attack of the Confederacy Army commanded by Marshal Andres de Santa Cruz, yet retreated to San Miguel leaving the field before Santa Cruz could engage him again.

Francisco Burdett O'Connor was an officer in the Irish Legion of Simón Bolívar's army in Venezuela. He later became Chief of Staff to Antonio José de Sucre and Minister of War of Bolivia. Aside from Bolívar and Sucre, he is one of the few military officers of the Spanish American wars of independence to be bestowed the title of Libertador (Liberator).

The Peruvian Civil War of 1834 was a revolt by supporters of former president Agustín Gamarra against the government. Gamarra had wanted Pedro Pablo Bermúdez as his successor to the presidency instead of Luis José de Orbegoso. On April 17, 1834, the two sides clashed in the Battle of Huaylacucho, in Huancavelica resulting in a victory for the revolutionaries. On April 24, 1834, there was another clash near Jauja. Although the revolutionaries surrendered, Orbegoso was overthrown the next year by his subordinate Felipe Santiago Salaverry, sparking the Salaverry-Santa Cruz War.

The Salaverry-Santa Cruz War, sometimes called the Peruvian Civil War of 1835–1836, was an internal conflict in Peru with the involvement of the Bolivian army of Andres de Santa Cruz. It ended with the defeat and execution of Felipe Santiago Salaverry and the creation of the Peru-Bolivian Confederation.

The Tarija War, also known as the War between Argentina and the Peru–Bolivian Confederation, was an armed conflict that occurred between 1837 and 1839. Because it happened while the Peru–Bolivian Confederation was engaged in a parallel war against the Republic of Chile during the so-called War of the Confederation, both conflicts are often confused. The Tarija War began on May 19, 1837, when Juan Manuel de Rosas, who was in charge of managing foreign relations for the Argentine Confederation and was governor of the Province of Buenos Aires, declared war directly on President Andres de Santa Cruz because of the Tarija Question and Confederation's support for the Unitarian Party.

The Peruvian Republic was a state that seceded from the Peru–Bolivian Confederation in 1838 under the leadership of General Luis Orbegoso.
Events in the year 1835 in Bolivia.


















