
Bcl-2, encoded in humans by the BCL2 gene, is the founding member of the Bcl-2 family of regulator proteins that regulate cell death (apoptosis), by either inhibiting (anti-apoptotic) or inducing (pro-apoptotic) apoptosis. It was the first apoptosis regulator identified in any organism.

Apoptosis regulator BAX, also known as bcl-2-like protein 4, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BAX gene. BAX is a member of the Bcl-2 gene family. BCL2 family members form hetero- or homodimers and act as anti- or pro-apoptotic regulators that are involved in a wide variety of cellular activities. This protein forms a heterodimer with BCL2, and functions as an apoptotic activator. This protein is reported to interact with, and increase the opening of, the mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel (VDAC), which leads to the loss in membrane potential and the release of cytochrome c. The expression of this gene is regulated by the tumor suppressor P53 and has been shown to be involved in P53-mediated apoptosis.

The p53 upregulated modulator of apoptosis (PUMA) also known as Bcl-2-binding component 3 (BBC3), is a pro-apoptotic protein, member of the Bcl-2 protein family. In humans, the Bcl-2-binding component 3 protein is encoded by the BBC3 gene.The expression of PUMA is regulated by the tumor suppressor p53. PUMA is involved in p53-dependent and -independent apoptosis induced by a variety of signals, and is regulated by transcription factors, not by post-translational modifications. After activation, PUMA interacts with antiapoptotic Bcl-2 family members, thus freeing Bax and/or Bak which are then able to signal apoptosis to the mitochondria. Following mitochondrial dysfunction, the caspase cascade is activated ultimately leading to cell death.

Phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate-induced protein 1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the PMAIP1 gene, and is also known as Noxa.

Bcl-2 homologous antagonist/killer is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BAK1 gene on chromosome 6. The protein encoded by this gene belongs to the BCL2 protein family. BCL2 family members form oligomers or heterodimers and act as anti- or pro-apoptotic regulators that are involved in a wide variety of cellular activities. This protein localizes to mitochondria, and functions to induce apoptosis. It interacts with and accelerates the opening of the mitochondrial voltage-dependent anion channel, which leads to a loss in membrane potential and the release of cytochrome c. This protein also interacts with the tumor suppressor P53 after exposure to cell stress.

The BCL2 associated agonist of cell death (BAD) protein is a pro-apoptotic member of the Bcl-2 gene family which is involved in initiating apoptosis. BAD is a member of the BH3-only family, a subfamily of the Bcl-2 family. It does not contain a C-terminal transmembrane domain for outer mitochondrial membrane and nuclear envelope targeting, unlike most other members of the Bcl-2 family. After activation, it is able to form a heterodimer with anti-apoptotic proteins and prevent them from stopping apoptosis.

B-cell lymphoma-extra large (Bcl-xL), encoded by the BCL2-like 1 gene, is a transmembrane molecule in the mitochondria. It is a member of the Bcl-2 family of proteins, and acts as an anti-apoptotic protein by preventing the release of mitochondrial contents such as cytochrome c, which leads to caspase activation and ultimately, programmed cell death.
Bim is a 1975 film from Trinidad and Tobago.
Inhibitors of apoptosis are a group of proteins that mainly act on the intrinsic pathway that block programmed cell death, which can frequently lead to cancer or other effects for the cell if mutated or improperly regulated. Many of these inhibitors act to block caspases, a family of cysteine proteases that play an integral role in apoptosis. Some of these inhibitors include the Bcl-2 family, viral inhibitor crmA, and IAP's.
B-cell lymphoma 6 protein is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL6 gene. Like BCL2, BCL3, BCL5, BCL7A, BCL9 and BCL10, it has clinical significance in lymphoma.

Bcl-2-like 1 or BCL2L1 is a human gene. Through alternative splicing, it encodes both of the human proteins Bcl-xL and Bcl-xS.

Bcl-2-like protein 11, commonly called BIM, is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL2L11 gene.

B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 10 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL10 gene. Like BCL2, BCL3, BCL5, BCL6, BCL7A, and BCL9, it has clinical significance in lymphoma.

Bcl-2-like protein 2 is a 193-amino acid protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL2L2 gene on chromosome 14. It was originally discovered by Leonie Gibson, Suzanne Cory and colleagues at the Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research, who called it Bcl-w.

B-cell lymphoma/leukemia 11A is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BCL11A gene.

Bcl-2-modifying factor is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BMF gene.

BCL2/adenovirus E1B 19 kDa protein-interacting protein 2 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the BNIP2 gene.
Oblimersen is an antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotide being studied as a possible treatment for several types of cancer, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia, B-cell lymphoma, and breast cancer. It may kill cancer cells by blocking the production of Bcl-2—a protein that makes cancer cells live longer—and by making them more sensitive to chemotherapy.

The Bcl-2 family consists of a number of evolutionarily-conserved proteins that share Bcl-2 homology (BH) domains. The Bcl-2 family is most notable for their regulation of apoptosis, a form of programmed cell death, at the mitochondrion. The Bcl-2 family proteins consists of members that either promote or inhibit apoptosis, and control apoptosis by governing mitochondrial outer membrane permeabilization (MOMP), which is a key step in the intrinsic pathway of apoptosis. A total of 25 genes in the Bcl-2 family were identified by 2008.
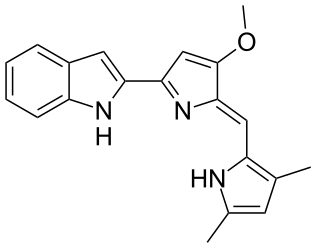
Obatoclax mesylate, also known as GX15-070, is an experimental drug for the treatment of various types of cancer. It was discovered by Gemin X, which was acquired by Cephalon, which has since been acquired by Teva Pharmaceuticals. Several Phase II clinical trials were completed that investigated use of Obatoclax in the treatment of leukemia, lymphoma, myelofibrosis, and mastocytosis.
















