
The Royal Abbey of Our Lady of Fontevraud or Fontevrault was a monastery in the village of Fontevraud-l'Abbaye, near Chinon, in the former French Duchy of Anjou. It was founded in 1101 by the itinerant preacher Robert of Arbrissel. The foundation flourished and became the centre of a new monastic Order, the Order of Fontevraud. This order was composed of double monasteries, in which the community consisted of both men and women — in separate quarters of the abbey — all of whom were subject to the authority of the Abbess of Fontevraud. The Abbey of Fontevraud itself consisted of four separate communities, all managed by the same abbess.

Maine is one of the traditional provinces of France. It corresponds to the former County of Maine, whose capital was also the city of Le Mans. The area, now divided into the departments of Sarthe and Mayenne, has about 857,000 inhabitants.

The monastic Congregation of Savigny started in the abbey of Savigny, situated in northern France, on the confines of Normandy and Brittany, in the Diocese of Coutances. It originated in 1105 when Vitalis of Mortain established a hermitage in the forest at Savigny in France.

The Valliscaulian Order was a religious order of the Catholic Church. It was named after Vallis Caulium or Val-des-Choux, its first monastery, located in Burgundy. The order was founded at the end of the twelfth century and lasted until its absorption by the Cistercians in the eighteenth century.

Pontigny Abbey, the church of which in recent decades has also been the cathedral of the Mission de France, otherwise the Territorial Prelature of Pontigny, was a Cistercian monastery located in Pontigny on the River Serein, in the present diocese of Sens and department of Yonne, Burgundy, France. Founded in 1114, it was the second of the four great daughter houses of Cîteaux Abbey. It was suppressed in 1791 in the French Revolution and destroyed except for the church. In 1843 it was re-founded as a community of the Fathers of St. Edmund. In 1909 it passed into private ownership. In 1941 it became the mother house of the Mission de France, a territorial prelature.

Savigny Abbey was a monastery near the village of Savigny-le-Vieux (Manche), in northern France. It was founded early in the 12th century. Initially it was the central house of the Congregation of Savigny, who were Benedictines; by 1150 it was Cistercian.

La Trappe Abbey, also known as La Grande Trappe, is a monastery in Soligny-la-Trappe, Orne, France. It is known for being the house of origin of the Trappists, to whom it gave its name.

Vaux-de-Cernay Abbey is a former Cistercian monastery in northern France (Île-de-France), situated in Cernay-la-Ville, in the Diocese of Versailles, Yvelines. The abbey was abandoned during the French Revolution and fell into partial ruin. Most of the buildings, except for the church, were restored in the late 19th century by Charlotte de Rothschild, and the property is now a hotel.

Molesme Abbey was a well-known Benedictine monastery in Molesme, in Laignes, Côte-d'Or, Duchy of Burgundy, on the border of the Dioceses of Langres and Troyes.

Melleray Abbey was a Cistercian monastery, founded about the year 1134. It was situated in La Meilleraye-de-Bretagne in the vicinity of Châteaubriant in Brittany, in the present Loire-Atlantique, France, and in the Diocese of Nantes. Between 1817 and 2016 it was a house of Trappist monks. Since 2016 it has been used by the Chemin Neuf Community.
Marguerite de Sablé, Dame de Sablé, was a French noblewoman and one of the wealthiest heiresses in the counties of Anjou and Maine. She was the eldest daughter of Robert IV de Sablé, and the wife of William des Roches, Seneschal of Anjou, who two years after his marriage to Marguerite became one of the greatest barons in Anjou and Maine, her considerable inheritance having passed to him upon her father's death in 1193.
Jeanne des Roches, Dame de Sablé was a French noble heiress, ruler of de baronies of La Suze, de Briollay, de Mayet, de Loupeland, de Chateauneuf-sur-Sarte, de Genneteil, de Precigné, de Agon, and de Craon; and the suo jure seneschal of Anjou, from 1222. The seneschalship passed to her husband, Amaury I, Sire de Craon, as well as the vast Sablè barony.

The County of Anjou was a French county that was the predecessor to the Duchy of Anjou. Its capital was Angers, and its area was roughly co-extensive with the diocese of Angers. Anjou was bordered by Brittany to the west, Maine to the north, Touraine to the east and Poitou to the south. Its 12th century Count Geoffrey created the nucleus of what became the Angevin Empire. The adjectival form is Angevin, and inhabitants of Anjou are known as Angevins. In 1360, the county was raised into the Duchy of Anjou within the Kingdom of France. This duchy was later absorbed into the French royal domain in 1482 and remained a province of the kingdom until 1790.

Redon Abbey, or Abbey of Saint-Sauveur, Redon, in Redon in the present Ille-et-Vilaine, Brittany, France, is a former Benedictine abbey founded in 832 by Saint Conwoïon, at the point where the Oust flows into the Vilaine, on the border between Neustria and Brittany.

Igny Abbey or Val d'Igny Abbey is a Cistercian abbey located in Arcis-le-Ponsart, Marne, France. It was founded in 1128 for Cistercian monks, dissolved in 1791 during the French Revolution, re-established in 1876 for Trappist monks, destroyed in 1918, reopened in 1929 for Trappist nuns and modernised in 2008–12 to accommodate three or four pre-existing communities.
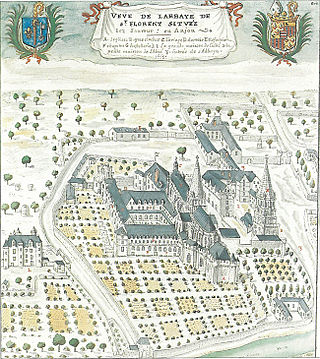
The Abbey of Saint-Florent, Saumur, also Saint-Florent-lès-Saumur or Saint-Florent-le-Jeune, was a Benedictine abbey in Anjou founded in the 11th century near Saumur, France. It was the successor of the Abbey of Saint-Florent-le-Vieil which was abandoned by its monks during raids of the Vikings.

Maurice II de Craon was Lord of Craon, Governor of Anjou and Maine under Henry II, a military figure and Anglo-Norman of the 12th century. Maurice II also possessed fiefs in England which he held courtesy of Henry II.

Port-du-Salut Abbey, also the Abbey of Notre-Dame du Port du Salut is a Trappist monastery located in Entrammes, Mayenne, France. The main monastery building dates from around the 13th century.

Perseigne Abbey is a former Cistercian abbey, formally established in 1145 on land given by William III, Count of Ponthieu, and suppressed in 1791 during the French Revolution. It is located in the north of the Sarthe département near to Neufchâtel-en-Saosnois, on the edge of the Perseigne forest, not far from Alençon.

Buzay Abbey, dedicated to Our Lady, was a Cistercian Abbey at Rouans in Pays de la Loire, France, formerly in Brittany, founded in 1135 and dissolved in 1790.

















