Related Research Articles

Arroyo Seco is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) in Monterey County, California, southeast of Monterey Bay. The appellation encompasses 18,240 acres (29 sq mi) in the valley adjacent to the Arroyo Seco Creek with approximately 8,500 acres (3,440 ha) of cultivation. The region's proximity to the Pacific Ocean produces the maritime climate, and is best suited for those cool climate grape varieties.

Willamette Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) which lies in the Willamette Valley of Oregon. The AVA is the wine growing region which encompasses the drainage basin of the Willamette River. It stretches from the Columbia River in the north to just south of Eugene in the south, where the Willamette Valley ends; and from the Oregon Coast Range in the west to the Cascade Mountains in the east. At 5,360 square miles, it is the largest AVA in the state, and contains most of the state's wineries; approximately 908 as of 2021.

Columbia Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) which lies within the Columbia River Plateau, through much of central and southern Washington state, with a section crossing the state boundary into northern Oregon south of the Columbia River. The viticultural area includes the drainage basin of the Columbia River and its tributaries through much of Washington. It was established by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury on December 13, 1984 after evaluating the petition filed by Drs, Walter Clore and Wade Wolfe of Prosser, Washington on behalf of Washington’s oldest and largest winery, Chateau Ste. Michelle, and by William Blosser of the Sokol Blosser Winery, Dundee, Oregon. Allen Shoup, president of Chateau Ste. Michelle, understood the importance of obtaining appellation status to grow the reputation of the Northwest viticulture industry.
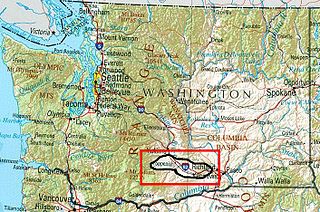
Yakima Valley is the first American Viticultural Area (AVA) established within Washington state, gaining the recognition on May 4, 1983. Within the vast Columbia Valley AVA, Yakima Valley appellation cultivates more than 53,000 acres (21,448 ha) giving the region the largest concentration of wineries and vineyards in the state. The most widely planted varietals in the area are Chardonnay, Riesling, Merlot, Cabernet Sauvignon, Pinot gris, and Syrah. Nearly 40% of Washington's annual wine production is made from Yakima Valley grapes. In addition to grapes, the Yakima Valley is also home to several fruit orchards growing apples, cherries, nectarines, peaches, pears and plums. Around the town of Zillah, there is the Zillah Fruit Loop driving tour through the area's orchards and vineyards. The area is also home to nearly 80% of the US hop production.

Santa Maria Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) which straddles the boundary of Santa Barbara and San Luis Obispo counties in California's multi-county Central Coast AVA. It was established on August 5, 1981, by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) as California's second oldest AVA. A portion of the AVA crosses the Cuyama River into the southernmost corner of San Luis Obispo County. The east–west orientation of the 152.3 square miles with a wide, open valley and rolling hills means cool winds and fog flow in freely from the Pacific Ocean, settling most noticeably in lower-lying areas. The result is a mild Mediterranean climate that lengthens the growing season and contributes to the eventual sugar/acid balance in the grapes from Santa Maria Valley's 7,500 acres (3,000 ha) cultivated vineyards. On January 28, 2011, the AVA was granted an 29.4 square miles expansion to its southern boundary.

Temecula Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) in the Temecula Valley, located in southwestern Riverside County, California against the eastern slopes of the Santa Ana Mountains. It was initially established by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury as "Temecula" on October 23, 1984 based on submitted petitions from by the Rancho Califomia/Temecula Winegrowers Association and Callaway Vineyard and Winery, Temecula, California in 1982. It was renamed "Temecula Valley" by the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) in 2004, approving the 2001 petition by Temecula Valley Winegrowers Association. The petition stated the name change would provide a more accurate description of the Temecula geography and greater clarity as to its location for wine consumers and the public. The petition did not request any change to the established AVA boundaries. This was the first American Viticultural Area to change its name after the initial approval. Temecula Valley encompasses 33,000 acres (52 sq mi) and 5,000 acres (8 sq mi) is located in a "protected" area referred to as the Citrus/Vineyard Zone. This area is generally located in and around the Rancho California Road area with Riverside County. County guidelines strictly enforce the number of acres needed to build a winery, lodging and other limited housing and commercial ventures.

Paso Robles is the third American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in San Luis Obispo (SLO) County, California. It was established by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury on November 3, 1983 based on a petition submitted by Martin Brothers Winery. The area encompasses 609,673 acres (953 sq mi) with approximately 18,500 acres (7,487 ha) cultivated with wine grapes known for their heritage varietal Zinfandel, Cabernet Sauvignon, and Rhône-style wines.

Santa Clara Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located mostly in Santa Clara County, California. The area served an important role in the early history of California wine and was home to the pioneer winemakers Paul Masson and Charles Lefranc. It was established on April 27, 1989 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury after evaluating the petition proposing a viticultural area in Santa Clara, San Benito, San Mateo and Alameda Counties that extends from lower San Francisco Bay with the cities of San Jose, Santa Clara, Menlo Park, Mountain View and Fremont toward the southern boundary near Gilroy and Morgan Hill, outlining the viticultural area named "Santa Clara Valley." It includes the historic winegrowing areas of Santa Clara County not already within the [Santa Cruz Mountains viticultural area, plus the area near Mission San José in Alameda County and a small part of San Benito County. Santa Clara Valley encompasses the established viticultural areas, Pacheco Pass and San Ysidro District.

Central Coast is a vast American Viticultural Area (AVA) that spans along the Central California Pacific coastline from the San Francisco Bay Area south through Monterey, San Luis Obispo and Santa Barbara Counties. It was established on November 25, 1985 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury after reviewing the petition submitted by Taylor California Cellars, a winery in Gonzales, California, to establish the "Central Coast" viticultural area. The boundaries of the Central Coast, which have been expanded twice, includes portions of six counties where approximately 100,000 acres (40,469 ha) cultivated with Chardonnay being more than half of the varietal. Within the multi-county AVA are numerous established appellations that share the same maritime climate produced by the Pacific Ocean.
Arroyo Grande Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in San Luis Obispo County, California approximately 12 miles (19 km) southeast of the county seat San Luis Obispo. Arroyo Grande Valley was recognized on February 5, 1990 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF) as the state's 60th AVA based on the petition filed in 1987 by Don Talley of Talley Vineyards and William S. Greenough of Saucelito Canyon Vineyard for the establishment of the "Arroyo Grande Valley" viticultural area in San Luis Obispo County. The 16 miles (26 km) long, approximately 67 square miles valley appellation benefits from its east-northeast orientation allowing the breeze from the Pacific Ocean to moderate the climate of the area. The valley is divided by a fog line produced by the cool maritime layer where Zinfandel, Petite Sirah and Rhône varietals are grown on the higher elevations near Lopez Lake and the cooler mid-valley vineyards being home to Chardonnay and Pinot noir. On April 8, 2022, the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) approved the designation of the expansive San Luis Obispo (SLO) Coast AVA overlapping the boundaries of Edna Valley and Arroyo Grande Valley viticultural areas because they share common features. However, these two previously established areas still have unique characteristics to retain their viticultural area distinctions within SLO Coast. Edna Valley lies immediately to the northwest, the Los Padres National Forest straddles the north leg boundary, the Santa Maria Valley AVA lies to the southeast of Arroyo Grande Valley, and the Pacific Ocean communities of Oceano, Grover City and Arroyo Grande abut its southwestern border.

Santa Cruz Mountains AVA is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) centered on the Santa Cruz Mountains. Its territory spans three California counties, Santa Clara, Santa Cruz and San Mateo and was established January 4, 1982 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury. Santa Cruz Mountains AVA was among the first AVA to be defined by its mountainous topography. Based on elevation, it largely follows the fog line along the coast, extending down to 800 feet (240 m) on the eastern slope toward San Francisco Bay, 400 feet (120 m) on the western slope to the Pacific Ocean and extending along the ridge crest line at 3,000 feet (910 m) elevation plus.

Sierra Foothills is a vast American Viticultural Area (AVA) encompassing the foothill "belt" of the Sierra Nevada in north-central California, United States. It was established on December 18, 1987 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury after evaluating the petition filed by the Sierra Foothills Winery Association of Somerset, California for the establishment of a "Sierra Foothills" viticultural area in portions of Yuba, Nevada, Placer, El Dorado, Amador, Calaveras, Tuolumne and Mariposa Counties. Wine grapes were introduced to the area in the nineteenth century during the California Gold Rush. Over 280 vineyards/wineries are located within its boundaries.
The Chiles Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in Napa County, California and a sub-region within Napa Valley AVA. It was established as California's 81st AVA by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF) on April 19, 1999 after the ATF received the petition from Mr. Volker Eisele, owner of the Volker Eisele Vineyard and Winery proposing a new viticultural area in Napa County to be known as "Chiles Valley District".

Edna Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in San Luis Obispo (SLO) County, California encompassing the rural town of Edna which is 9 miles (14 km) southeast of the county seat San Luis Obispo and north of the small coastal town Arroyo Grande. It was established by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF) as the county's first AVA within California’s multi-county Central Coast AVA effective May 12, 1982. It became an sub-appellation of the county’s newest San Luis Obispo Coast viticultural area since April 2022. The valley is diagonally flanked by Lake Lopez to the south and Islay Hill to the north. The elongated valley extends along a northwest-southeast axis bordered to the west by the Santa Lucia Mountains and surrounded by volcanic mountains and characterized by black humus and clay-rich soils. With moderate sunshine, cool maritime fog, and rich oceanic and volcanic soils, the Edna Valley appellation has California's longest growing season. The valley is kept cool by breezes from the Pacific Ocean and morning fog. The extended growing season allows complex flavors to develop in the grapes.

El Dorado is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in El Dorado County, California, east of the state’s capital, Sacramento and centered around the county seat of Placerville. It was established on November 14, 1983 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF), Treasury after approving the submitted petition from the El Dorado Wine Grape Growers Association of Camino, California applying to establish a viticultural area named "El Dorado.” The area includes parts of El Dorado County on the north border by the Middle Fork American River and on the south by the South Fork of the Cosumnes River. El Dorado viticultural area lies within the vast 4,062 square miles Sierra Foothills viticultural area, one of the largest appellations in California, which extends about 170 miles (274 km) through portions of Yuba, Nevada, Placer, El Dorado, Amador, Calaveras, Tuolumne and Mariposa Counties. The El Dorado viticultural area encompasses 1,093,120 acres (1,708 sq mi) which entirely includes Fair Play and a small portion of northeastern California Shenandoah Valley AVAs.

California Shenandoah Valley is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located within portions of Amador County and El Dorado County, California. The area was established on January 27, 1983 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives (ATF), Treasury after approving the petition from the Amador County Wine Grape Growers Association proposing a viticultural area in Amador County, California, to be known as "Shenandoah Valley." It lies within the vast multi-county Sierra Foothills viticultural area boundaries and borders the northwest boundary of Fiddletown viticultural area which received recognition later the same year. In the petition, the area consists of approximately 10,000 acres (16 sq mi) with about1,200 acres (486 ha) under vine. The petition requested ATF for the Shenandoah Valley viticultural area to be situated to the north and west of Fiddletown, and to the north and east of Plymouth.

San Benito is an American Viticultural Area (AVA) located in San Benito County, California. It was established on November 4, 1987 by the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury after evaluating the petition submitted by Almaden Vineyards, a winery and grape grower in the area, proposing that a portion of San Benito County be established as a viticultural area to be known as "San Benito."

Santa Barbara County wine is an appellation that designates wine made from grapes grown mostly in Santa Barbara County, California which is located approximately 50 miles (80 km) north of Los Angeles County. County names in the United States automatically qualify as legal appellations of origin for wine produced from grapes grown in that county and do not require registration with the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) of the Treasury Department. TTB was created in January 2003, when the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms, or ATF, was extensively reorganized under the provisions of the Homeland Security Act of 2002.

San Luis Obispo (SLO) County wine is a appellation that designates wine made from grapes grown in San Luis Obispo (SLO) County, California which is sandwiched between Santa Barbara County to the south and Monterey County at the northern boundary on the Pacific coast. Its location sits halfway between the cities of San Francisco and Los Angeles on the north–south axis of U.S. Route 101 and Pacific Coast Highway (PCH). The county lies entirely within the Central Coast viticultural area. County names in the United States automatically qualify as legal appellations of origin for wine produced from grapes grown in that county and do not require registration with the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB) of the Treasury Department. TTB was created in January of 2003, when the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms, or ATF, was extensively reorganized under the provisions of the Homeland Security Act of 2002.

Monterey County wine is a appellation that designates wine made from grapes grown in Monterey County, California which lies entirely within the expansive multi-county Central Coast viticultural area. County names in the United States automatically qualify as legal appellations of origin for wine produced from grapes grown in that county and do not require registration with the Alcohol and Tobacco Tax and Trade Bureau (TTB). TTB was created in January 2003, when the Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms, or ATF, was extensively reorganized under the provisions of the Homeland Security Act of 2002.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 "Ben Lomond Mountain Viticultural Area" (27 CFR Part 9 [T.D. ATF-264; Re: Notice No. 629] Final Rule). Federal Register . 52 (236). Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco and Firearms (ATF), Treasury: 46589–46592. December 9, 1987.
 This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain.
This article incorporates text from this source, which is in the public domain. - 1 2 3 "Ben Lomond Mountain: Appellation Profile". Appellation America. 2007. Archived from the original on September 8, 2013. Retrieved May 24, 2021.