Related Research Articles

Headache is the symptom of pain in the face, head, or neck. It can occur as a migraine, tension-type headache, or cluster headache. There is an increased risk of depression in those with severe headaches.

Macrocephaly is a condition in which circumference of the human head is abnormally large. It may be pathological or harmless, and can be a familial genetic characteristic. People diagnosed with macrocephaly will receive further medical tests to determine whether the syndrome is accompanied by particular disorders. Those with benign or familial macrocephaly are considered to have megalencephaly.

Torticollis, also known as wry neck, is a dystonic condition defined by an abnormal, asymmetrical head or neck position, which may be due to a variety of causes. The term torticollis is derived from the Latin words tortus, meaning "twisted" and collum, meaning "neck."

The vestibular system, in vertebrates, is a sensory system that creates the sense of balance and spatial orientation for the purpose of coordinating movement with balance. Together with the cochlea, a part of the auditory system, it constitutes the labyrinth of the inner ear in most mammals.

Dizziness is an imprecise term that can refer to a sense of disorientation in space, vertigo, or lightheadedness. It can also refer to disequilibrium or a non-specific feeling, such as giddiness or foolishness.
Hypotonia is a state of low muscle tone, often involving reduced muscle strength. Hypotonia is not a specific medical disorder, but a potential manifestation of many different diseases and disorders that affect motor nerve control by the brain or muscle strength. Hypotonia is a lack of resistance to passive movement, whereas muscle weakness results in impaired active movement. Central hypotonia originates from the central nervous system, while peripheral hypotonia is related to problems within the spinal cord, peripheral nerves and/or skeletal muscles. Severe hypotonia in infancy is commonly known as floppy baby syndrome. Recognizing hypotonia, even in early infancy, is usually relatively straightforward, but diagnosing the underlying cause can be difficult and often unsuccessful. The long-term effects of hypotonia on a child's development and later life depend primarily on the severity of the muscle weakness and the nature of the cause. Some disorders have a specific treatment but the principal treatment for most hypotonia of idiopathic or neurologic cause is physical therapy and/or occupational therapy for remediation.
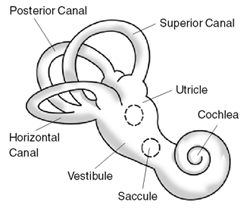
Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) is a disorder arising from a problem in the inner ear. Symptoms are repeated, brief periods of vertigo with movement, characterized by a spinning sensation upon changes in the position of the head. This can occur with turning in bed or changing position. Each episode of vertigo typically lasts less than one minute. Nausea is commonly associated. BPPV is one of the most common causes of vertigo.
Vertigo is a condition where a person has the sensation of movement or of surrounding objects moving when they are not. Often it feels like a spinning or swaying movement. This may be associated with nausea, vomiting, sweating, or difficulties walking. It is typically worse when the head is moved. Vertigo is the most common type of dizziness.

Spasmodic torticollis is an extremely painful chronic neurological movement disorder causing the neck to involuntarily turn to the left, right, upwards, and/or downwards. The condition is also referred to as "cervical dystonia". Both agonist and antagonist muscles contract simultaneously during dystonic movement. Causes of the disorder are predominantly idiopathic. A small number of patients develop the disorder as a result of another disorder or disease. Most patients first experience symptoms midlife. The most common treatment for spasmodic torticollis is the use of botulinum toxin type A.
Persistent aura without infarction (PAWOI) is a rare and seemingly benign condition, first described in case reports in 1982 as "prolonged/persistent migraine aura status", and in 2000 as "migraine aura status", that is not yet fully understood. PAWOI is said to possibly be a factor involved in a variety of neurological symptoms, including visual snow, loss of vision, increased afterimages, tinnitus, and others. The pathogenesis of PAWOI is unknown. It is not clear which medical examinations are useful in diagnosing PAWOI. At present, PAWOI is usually diagnosed solely based on the patient's current and past symptoms. It is possible that an "overactive brain" or a chemical imbalance underlies the disorder. Various medications have been tried as treatment, notably acetazolamide, valproate, lamotrigine, topiramate, and furosemide.
The Epley maneuver or repositioning maneuver is a maneuver used by medical professionals to treat one common cause of vertigo, benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV) of the posterior or anterior canals of the ear. The maneuver works by allowing free-floating particles, displaced otoconia, from the affected semicircular canal to be relocated by using gravity, back into the utricle, where they can no longer stimulate the cupula, therefore relieving the patient of bothersome vertigo. The maneuver was developed by the physician, John M. Epley, and was first described in 1980.

Nystagmus is a condition of involuntary eye movement. Infants can be born with it but more commonly acquire it in infancy or later in life. In many cases it may result in reduced or limited vision. Due to the involuntary movement of the eye, it has been called "dancing eyes".

Paroxysmal exercise-induced dystonia or PED is a rare neurological disorder characterized by sudden, transient, involuntary movements, often including repetitive twisting motions and painful posturing triggered by exercise or other physical exertion. PED is in the class of paroxysmal dyskinesia which are a group of rare movement disorders characterized by attacks of hyperkinesia with intact consciousness. The term paroxysmal indicates that the episodes are sudden and short lived and usually unpredicted, and return to normal is rapid. The number of reported cases of people with PED is very small leading to difficulty in studying and classifying this disease and most studies are limited to a very small number of test subjects.
Sandifer syndrome is an eponymous paediatric medical disorder, characterised by gastrointestinal symptoms and associated neurological features. There is a significant correlation between the syndrome and gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD); however, it is estimated to occur in less than 1% of children with reflux.
Vestibular migraine (VM) is vertigo with migraine, either as a symptom of migraine or as a related neurological disorder.
PHACE syndrome is a cutaneous condition characterized by multiple congenital abnormalities. The mnemonic PHACE stands for Posterior fossa brain malformations, Hemangioma, Arterial lesions, Cardiac abnormalities, and Eye abnormalities. PHACE syndrome may affect infants with a large plaque-type facial hemangiomas. Children who present this dermatologic manifestation should receive careful ophthalmologic, cardiac, and neurologic assessment. According to one study of infants with large hemangiomas, one-third have extracutaneous manifestations consistent with the diagnosis of PHACE syndrome. The most common are cerebrovascular and cardiovascular anomalies.
Benign paroxysmal vertigo of childhood is an uncommon neurological disorder which presents with recurrent episodes of dizziness. The presentation is usually between the ages of 2 years and 7 years of age and is characterised by short episodes of vertigo of sudden onset when the child appears distressed and unwell. The child may cling to something or someone for support. The episode lasts only minutes and resolves suddenly and completely. It is a self-limiting condition and usually resolves after about eighteen months, although many go on to experience migrainous vertigo when older.
People with epilepsy may be classified into different syndromes based on specific clinical features. These features include the age at which seizures begin, the seizure types, and EEG findings, among others. Identifying an epilepsy syndrome is useful as it helps determine the underlying causes as well as deciding what anti-seizure medication should be tried. Epilepsy syndromes are more commonly diagnosed in infants and children. Some examples of epilepsy syndromes include benign rolandic epilepsy, childhood absence epilepsy and juvenile myoclonic epilepsy. Severe syndromes with diffuse brain dysfunction caused, at least partly, by some aspect of epilepsy, are also referred to as epileptic encephalopathies. These are associated with frequent seizures that are resistant to treatment and severe cognitive dysfunction, for instance Lennox-Gastaut syndrome and West syndrome.

Occipital epilepsy is a neurological disorder that arises from excessive neural activity in the occipital lobe of the brain that may or may not be symptomatic. Occipital lobe epilepsy is fairly rare, and may sometimes be misdiagnosed as migraine when symptomatic. Epileptic seizures are the result of synchronized neural activity that is excessive, and may stem from a failure of inhibitory neurons to regulate properly.

Recurrent painful ophthalmoplegic neuropathy (RPON), previously known as ophthalmoplegic migraine (OM), is a rare neurological disorder that is characterized by repeated headache attacks and reversible ipsilateral paresis of one or more ocular cranial nerves (CN). Oculomotor nerve (CNIII) is by far the most common cranial nerve involves in RPON, while abducens nerve (CNVI) and trochlear nerve (CNIV) involvements are also reported. Globally, RPON was estimated to have an annual incidence rate of 0.7 per million as of 1990, no further epidemiological studies have been conducted. It occurs more often in children and females.
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 Deonna, T. & Martin, D. (1981) Benign paroxysmal torticollis in infancy. Archives of Disease in Childhood. 56:956-959.
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 Drigo, P. Carli, G. & Laverda, A.M. (2000) Benign paroxysmal torticollis of infancy. Brain and Development. 22:169-172.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Eviatar, L. (1994) Benign Paroxysmal Torticollis. Pediatric Neurology. 11:72.